Abstract
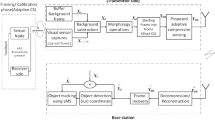
Wireless visual sensor network (WVSN) consists of a large number of nodes that are capable of acquiring, compressing and transmitting images. Surveillance becomes a vital application area of WVSN as they can be deployed in various environments to monitor and collect information. The lifetime of the nodes in the network depends on the energy consumption. Hence in this paper, block compressed sensing (BCS) based image transmission technique that utilizes Energy based Reweighted sampling (ERWS) in Modified Fast Haar Wavelet Transform (MFHWT) domain is proposed to reduce energy consumption considerably. Sparse binary random matrix is used to acquire CS measurements in MFHWT domain. In addition, the proposed technique also maintains the image quality. The developed algorithm is applied and tested for a car parking lot monitoring system. It is evident from the simulation results that the proposed method achieves better PSNR values even for fewer measurements. Experimental analysis is performed using Atmega 128 processor of Mica mote in WinAVR by Atmel. The proposed method has approximately 85.5% lesser energy consumption than other Compressed Sensing (CS) methods. Lossless Entropy Coding is applied to the ERWS measurements and considerable reduction in number of transmitted bits is also achieved. The algorithm has also been tested in WINGZ mote in real time.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato G, Carrara F, Falchi F, Gennaro C, Meghini C, Vairo C (2017) Deep learning for decentralized parking lot occupancy detection. Elsevier, Expert Syst Appl 72:327–334
Amir O (2017) Kotb, Yao-chun Shen, and Yi Huang, “smart parking guidance, monitoring and reservations: a review”. IEEE Intell Transp Syst Mag 9(2):6–16
Banerjee S, P Choudekar, MK Muju (2011) "Real time car parking system using image processing." Electronics Computer Technology (ICECT), 2011 3rd International Conference on. Vol. 2. IEEE
Bhardwaj A, Ali R (2009) Image compression using modified fast haar wavelet transform. World Appl Sci J 7(5):647–653
Candes EJ, Wakin MB (2008) An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process Mag 25(2):21–30
Corporative Traffic Logistics, http://www.corporatetraffic.com/
Deshpande S (2016) "M-parking: Vehicle parking guidance system using hierarchical Wireless Sensor Networks." 2016 13th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC). IEEE
Do MN, Vetterli M (2003) The finite ridgelet transform for image representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(1):16–28
Donoho DL (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(4):1289–1306
Faheem SA, Mahmud GM, Khan M, Rahman, Zafar H (2013) A Survey of Intelligent Car Parking System. J App Res Technol 11(5):714–726
Francesco M, Massimo V (2009) An efficient lossless compression algorithm for tiny nodes of monitoring wireless sensor networks. Comput J 52(8):969–987
L Gan (2007) Block compressed sensing of natural images. Proc IEEE 15th Int Conf Digit Sign Proc 403–406
Gao Z, Xiong C, Ding L, Zhou C (2013) Image representation using block compressive sensing for compression applications. J Vis Commun Image Represent 24(7):885–894
R Grodi, DB Rawat, F Rios-Gutierrez (2016) “Smart parking: parking occupancy monitoring and visualization system for smart cities”, in The proceedings of the SoutheastCon
R Hemalatha, S Radha, J Jalbin (2014) Efficient image transmission over WVSNs using two-measurement matrix based CS with enhanced OMP. Int J Distribut Sensor Netw
Hemalatha R, Radha S, Sudharsan S (2015) Energy-efficient image transmission in wireless multimedia sensor networks using block-based compressive sensing. Comput Electr Eng 44:67–79
Lee D-U (2009) Hyungjin Kim and Mohammad Rahimi estrin “energy-efficient image compression for resource-constrained platforms”. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(9):2100–2113
Lu L, Zhang J, Khan MK, Chen X, Alghathbar K (2010) Dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis: a novel approach for face and palmprint recognition in DCT domain. Int J Phys Sci 5(17):2543–2554
Lu L, J Zhang, J Xu, MK Khan, K Alghathbar (2010) dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis in DCT domain for face and palmprint recognition in the proceedings of 2010 international conference on information and communication technology convergence (ICTC), 17–19
Elena Marmol, Xavier Sevillano, “QuickSpot: a Video Analytics Solution for On-Street Vacant Parking Spot Detection”, Multimed Tools Appl, Vol. 75, No. (24), July 2016, pp. 17711–17743
MIT, http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/topic/microsystems-technology-laboratories.html
MIT Media Lab: http://www.media.mit.edu/
R Monika, R Hemalatha, S Radha (2015) Energy efficient weighted sampling matrix based CS technique for WSN. sensors. IEEE 1835–1838
Parkale YV, Nalbalwar SL (2016) Application of 1-D discrete wavelet transform based compressed sensing matrices for speech compression. Springer Plus 5(1):1–60
P Sermwuthisarn, S Auethavekiat, V Patanavijit (2009) A fast image recovery using compressive sensing technique with block based orthogonal matching pursuit in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS ‘09), 212–215
VWS Tang, Y Zheng, J Cao (2006) “An Intelligent Car Park Management System Based On Wireless Sensor Networks”, 2006 1st International Symposium On Pervasive Computing And Applications, pp. 65–70
Tropp JA, Gilbert AC (2007) Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 53(12):4655–4666
Tsaig Y, Donoho DL (2006) Extensions of compressed sensing. Signal Process 86(3):549–571
XueBi, Xiang-dongChen, Yu Zhang and Bin Liu “Image compressed sensing based on wavelet transform in contourlet domain” Signal Process, Volume 91, Issue 5, May 2011, pp. 1085–1092
Y Yang, OC Au, L Fang, X Wen, W Tang (2009) Reweighted Compressive Sampling for image compression. Proc IEEE Pic Coding Symp 1–4
Yusnita R, Norbaya F, Basharuddin N (2012) Intelligent Parking Space Detection System Based on Image Processing. Int J Innov Manag Technol 3.3:232
Zheng Y, J Cao (2006) "An intelligent car park management system based on wireless sensor networks." 2006 First International Symposium on Pervasive Computing and Applications. IEEE
C Zhou, C Xiong, R Mao, J Gong (2011) “Compressed sensing of images using nonuniform sampling,” in Proceedings of the 4th International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA ‘11), 2: 483–486
Zonoobi D, Kassim AA (2014) On ECG reconstruction using weighted-compressive sensing. IET Healthc Technol Lett 1(2):68–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monika, R., Hemalatha, R. & Radha, S. Energy efficient surveillance system using WVSN with reweighted sampling in modified fast Haar wavelet transform domain. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 30187–30203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6138-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6138-7