Abstract
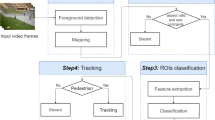
In this paper, we propose a hybrid system for pedestrian detection, in which both thermal and visible images of the same scene are used. The proposed method is achieved in two basic steps: (1) Hypotheses generation (HG) where the locations of possible pedestrians in an image are determined and (2) hypotheses verification (HV), where tests are done to check the presence of pedestrians in the generated hypotheses. HG step segments the thermal image using a modified version of OTSU thresholding technique. The segmentation results are mapped into the corresponding visible image to obtain the regions of interests (possible pedestrians). A post-processing is done on the resulting regions of interests to keep only significant ones. HV is performed using random forest as classifier and a color-based histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) together with the histograms of oriented optical flow (HOOF) as features. The proposed approach has been tested on OSU Color-Thermal, INO Video Analytics and LITIV data sets and the results justify its effectiveness.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhloufi MA, Porcher C, Bendada A (2013) Fusion of thermal infrared and visible spectrum images for robust pedestrian tracking. In: Proceedings of SPIE, volume, 9076
Ansari M El, Lahmyed R, Tremeau A (2018) A hybrid pedestrian detection system based on visible images and lidar data. In: Proceedings of the 13th international joint conference on computer vision, imaging and computer graphics theory and applications - volume 5: VISAPP, pages 325–334. INSTICC, SciTePress
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Gool LV (2008) Speeded-up robust features (surf). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Castillo JC, Serrano-Cuerda J, Sokolova MV, Costa A, Novais P (2012) Multispectrum video for proactive response in intelligent environments. In: 2012 8th international conference on intelligent environments (IE). IEEE, pp 178–185
Charfi S, Ansari M El (2018) Computer-aided diagnosis system for colon abnormalities detection in wireless capsule endoscopy images. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(3):4047–4064
Choi S, Kim E, Lee K, Oh S (2017) Real-time nonparametric reactive navigation of mobile robots in dynamic environments. Robot Auton Syst 91:11–24
Christianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom
Cuntoor N, Kale A, Chellappa R (2003) Combining multiple evidences for gait recognition. In: 2003 international conference on multimedia and Expo, 2003. ICME’03. Proceedings, vol 3. IEEE, pp III–113
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2005. CVPR 2005, volume 1. IEEE, pp 886–893
Davis JW, Sharma V (2007) Background-subtraction using contour-based fusion of thermal and visible imagery. Comput Vis Image Underst 106(2):162–182
Dollár P, Appel R, Belongie S, Perona P (2014) Fast feature pyramids for object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(8):1532–1545
Elguebaly T, Bouguila N (2011) A nonparametric bayesian approach for enhanced pedestrian detection and foreground segmentation. In: 2011 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, pp 21–26
Elguebaly T, Bouguila N (2013) Finite asymmetric generalized gaussian mixture models learning for infrared object detection. Comput Vis Image Underst 117(12):1659–1671
Ellahyani A, Ansari M El, Jaafari I El (2016) Traffic sign detection and recognition based on random forests. Appl Soft Comput 46:805–815
Fendri E, Boukhriss RR, Hammami M (2017) Fusion of thermal infrared and visible spectra for robust moving object detection. Pattern Anal Applic 20(4):907–926
Foster JP, Nixon MS, Prügel-Bennett A (2003) Automatic gait recognition using area-based metrics. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(14):2489–2497
Gascuena JM, Serrano-Cuerda J, Castillo JC, Fernández-Caballero A, López MT (2014) A multi-agent system for infrared and color video fusion. In: Trends in practical applications of heterogeneous multi-agent systems. The PAAMS collection. Springer, pp 131–138
Gavrila DM, Munder S (2007) Multi-cue pedestrian detection and tracking from a moving vehicle. Int J Comput Vis 73(1):41–59
Ge J, Luo Y, Tei G (2009) Real-time pedestrian detection and tracking at nighttime for driver-assistance systems. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 10(2):283–298
Guo L, Ge P-S, Zhang M-H, Li L-H, Zhao Y-B (2012) Pedestrian detection for intelligent transportation systems combining adaboost algorithm and support vector machine. Expert Systems with Applications 39(4):4274–4286
Herrmann C, Müller T, Willersinn D, Beyerer J (2016) Real-time person detection in low-resolution thermal infrared imagery with mser and cnns. In: SPIE security+ defence, pp 99870I–99870I. International society for optics and photonics
Huang D-Y, Wang C-H (2009) Optimal multi-level thresholding using a two-stage otsu optimization approach. Pattern Recogn Lett 30(3):275–284
Hwang S, Park J, Kim N, Choi Y, Kweon IS (2015) Multispectral pedestrian detection benchmark dataset and baseline. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1037–1045
Ino, “ino video analytics dataset.” https://www.ino.ca/en/video-analytics-dataset/. Accessed 6 Sept 2017
John V, Mita S, Liu Z, Qi B (2015) Pedestrian detection in thermal images using adaptive fuzzy c-means clustering and convolutional neural networks. In: 2015 14th IAPR international conference on machine vision applications (MVA). IEEE, pp 246–249
Jungling K, Arens M (2009) Feature based person detection beyond the visible spectrum. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, 2009. CVPR Workshops 2009. IEEE, pp 30–37
Källhammer J-E, Smith K, Matsangas P (2016) Modeling ratings of in-vehicle alerts to pedestrian by leveraging field operational tests data in a controlled laboratory study. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour
Kassani PH, Teoh ABJ (2016) A new sparse model for traffic sign classification using soft histogram of oriented gradients. Appl Soft Comput
Kim K, Chalidabhongse TH, Harwood D, Davis L (2005) Real-time foreground–background segmentation using codebook model. Real-Time Image 11(3):172–185
Lahmyed R, Ansari M El (2016) Multisensors-based pedestrian detection system. In: 2016 IEEE/ACS 13th International Conference of Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA). IEEE, pp 1–4
Lee L, Dalley G, Tieu K (2003) Learning pedestrian models for silhouette refinement. In: ICCV, vol 1, pp 663–670
Level Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histogram. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 9(1):62–66
Li H, Zhu J, Tao D (2018) Asymmetric projection and dictionary learning with listwise and identity consistency constraints for person re-identification. IEEE Access 6:37977–37990
Li Jianfu, Gong Weiguo, Li W, Liu X (2010) Robust pedestrian detection in thermal infrared imagery using the wavelet transform. Infrared Phys Technol 53(4):267–273
Li Z, Bo Wu, Nevatia S (2007) Pedestrian detection in infrared images based on local shape features. In: 2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition CVPR’07. IEEE, pp 1–8
Liang C-W, Juang C-F (2015) Moving object classification using local shape and hog features in wavelet-transformed space with hierarchical svm classifiers. Appl Soft Comput 28:483–497
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Lucas BD, Kanade T, et al (1981) An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision
Morales Y, Miyashita T, Hagita N (2017) Social robotic wheelchair centered on passenger and pedestrian comfort. Robot Auton Syst 87:355–362
Nanda H, Davis L (2002) Probabilistic template based pedestrian detection in infrared videos. In: Intelligent vehicle symposium 2002. IEEE, volume 1, pp 15–20
Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Harwood D (1996) A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recogn 29(1):51–59
Ouloul IM, Moutakki Z, Afdel K, Amghar A (2018) Improvement of age estimation using an efficient wrinkles descriptor. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 1–35
Perš J, Kristan M, Perše M, Kovačič S (2007) Motion based human identification using histograms of optical flow. na
Perš J, Sulić V, Kristan M, Perše M, Polanec K, Kovačič S (2010) Histograms of optical flow for efficient representation of body motion. Pattern Recog Lett 31(11):1369–1376
Premebida C, Ludwig O, Nunes U (2009) Lidar and vision-based pedestrian detection system. J Field Rob 26(9):696–711
Qingbo J, Enze Z, Xinqi Y, Yu X, Yun L (2016) Face recognition method based on hog and dmma from single training sample. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 75(21):13163–13177
Radman A, Suandi SA (2018) Robust face pseudo-sketch synthesis and recognition using morphological-arithmetic operations and hog-pca. Multimedia Tools and Applications. pp 1–22
San-Biagio M, Crocco M, Cristani M (2012) Recursive segmentation based on higher order statistics in thermal imaging pedestrian detection. In: 2012 5th international symposium on communications control and signal processing (ISCCSP). IEEE, pp 1–4
Serrano-Cuerda J (2014) Robust human detection through fusion of color and infrared video. ELCVIA: Electronic Letters On Computer Vision And Image Analysis 13(2):0017–18
Souaidi M, Abdelouahad AA, Ansari M El (2017) A fully automated ulcer detection system for wireless capsule endoscopy images. In: 2017 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP). IEEE, pP 1–6
Souaidi M, Abdelouahed AA, Ansari M El (2018) Multi-scale completed local binary patterns for ulcer detection in wireless capsule endoscopy images. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 1–18
Souaidi M, Charfi S, Abdelouahad AA, Ansari M El (2018) New features for wireless capsule endoscopy polyp detection. In: 2018 international conference on intelligent systems and computer vision (ISCV). IEEE, pp 1–6
Sun Hao, Wang Cheng, Wang B, El-Sheimy N (2011) Pyramid binary pattern features for real-time pedestrian detection from infrared videos. Neurocomputing 74 (5):797–804
Tao D, Guo Y, Li Y, Gao X (2018) Tensor rank preserving discriminant analysis for facial recognition. IEEE Trans on Image Process 27(1):325–334
Torabi A, Massé G, Bilodeau G-A (2012) An iterative integrated framework for thermal–visible image registration, sensor fusion, and people tracking for video surveillance applications. Comput Vis Image Underst 116(2):210–221
Usher JM, McCool R, Strawderman L, Carruth DW, Bethel CL, May DC (2017) Simulation modeling of pedestrian behavior in the presence of unmanned mobile robots. Simul Model Pract Theory 75:96–112
Vapnik VN, Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory, volume 1. Wiley, New York
Wagner J, Fischer V, Herman M, networks SB (2016) Multispectral pedestrian detection using deep fusion convolutional neural. In: 24th European symposium on artificial neural networks computational intelligence and machine learning (ESANN), pp 509–514
Wang Y, Wang Z, Tao D, Zhuo S, Xu X, Pu S, Song M (2017) Allfocus: patch-based video out-of-focus blur reconstruction. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27(9):1895–1908
Yang T, Fu D, Pan S (2017) Pedestrian tracking for infrared image sequence based on trajectory manifold of spatio-temporal slice. Multimedia Tools and Applications 76(8):11021–11035
Zhang J, Li F-W, Nie W-Z, Li W-H, Su Y-T (2016) Visual attribute detction for pedestrian detection. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 1–18
Zin TT, Takahashi H, Hama H, Toriu T (2011) Fusion of infrared and visible images for robust person detection. INTECH Open Access Publisher
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahmyed, R., El Ansari, M. & Ellahyani, A. A new thermal infrared and visible spectrum images-based pedestrian detection system. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 15861–15885 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6974-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6974-5