Abstract
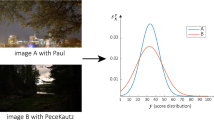
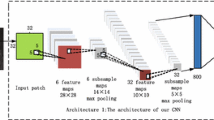
Image quality assessment is a challenge problem in image processing area. Previous works usually predict the mean opinion score (MOS) to evaluate image quality. However, it is found that the distribution of opinion scores provides richer and more precise semantics information. Therefore, in this work, we focus on the distribution of opinion scores (DOS) and aims to comprehensively evaluate image quality via automatically predicting DOS. Specifically, we first extract image features via convolutional neural network and then adopt the label distribution support vector regressor (LDSVR) algorithm to predict score distribution. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to introduce label distribution learning approach for image quality assessment. Extensive experiments have been carried out and validate that the proposed algorithm can well predict the DOS and provide a comprehensive assessment to image quality.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We linear map score range from TID to HDR for fair comparison.
References
Cabral RS, Torre F, Costeira JP, Bernardino A (2011) Matrix completion for multi-label image classification. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 190–198
Ciocca G, Corchs S, Gasparini F, Schettini R (2014) How to assess image quality within a workflow chain: an overview. Int J Digit Libr 15(1):1–25
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Tzeng E, Darrell T (2014) Decaf: a deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 647–655
Drucker H, Burges CJ, Kaufman L, Smola AJ, Vapnik V (1997) Support vector regression machines. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 155–161
Fattal R, Lischinski D, Werman M (2002) Gradient domain high dynamic range compression. ACM Trans Graph 21(3):249–256
Gatys L, Ecker AS, Bethge M (2015) Texture synthesis using convolutional neural networks, pp 262–270
Gatys LA, Ecker AS, Bethge M (2015) A neural algorithm of artistic style. Computing research repository. arXiv:1508.06576
Geng X (2013) Label distribution learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28 (7):1734–1748
Geng X, Peng H (2015) Pre-release prediction of crowd opinion on movies by label distribution learning. In: IEEE international conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3511–3517
Geng X, Yin C, Zhou ZH (2013) Facial age estimation by learning from label distributions. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(10):2401–12
Guo Y, Liu Y, Bakker EM, Guo Y, Lew MS (2018) CNN-RNN: a large-scale hierarchical image classification framework. Multimed Tools Appl 77(8):10, 251–10, 271
HDRsoft (Accessed on May, 2016) Photomatix. http://www.hdrsoft.com/
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Jing P, Su Y, Nie L, Gu H, Liu J, Wang M (2018) A framework of joint low-rank and sparse regression for image memorability prediction. Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, pp 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2832095
Johnson J, Alahi A, Fei-Fei L (2016) Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 694–711
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: International conference on neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Kundu D, Ghadiyaram D, Bovik AC, Evans BL (2017) No-reference quality assessment of tone-mapped HDR pictures. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(6):2957–2971
Larson GW, Rushmeier H, Piatko C (1997) A visibility matching tone reproduction operator for high dynamic range scenes. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 3(4):291–306
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, Zhu L, Tao Shen H (2018) Transfer independently together: a generalized framework for domain adaptation. Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2820174
Mittal A, Moorthy AK, Bovik AC (2012) No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(12):4695–4708
Moorthy AK, Bovik AC (2011) Blind image quality assessment: from natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(12):3350–3364
Nie L, Wang M, Zha ZJ, Chua TS (2012) Oracle in image search: a content-based approach to performance prediction. ACM Trans Inf Syst 30(2):13, 1–13, 23
Nocedal J, Wright SJ (2006) Numerical optimization. Springer, Berlin
Pece F, Kautz J (2013) Bitmap movement detection: HDR for dynamic scenes. Journal of Virtual Reality and Broadcasting 10(2):1–8
Pérez-Cruz F, Alarcón-Diana PL, Navia-Vázquez A, Artés-Rodríguez A (2001) Fast training of support vector classifiers. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 734–740
Pietra SD, Pietra VD, Lafferty J (1995) Inducing features of random fields. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(4):380–393
Ponomarenko N, Ieremeiev O, Lukin V, Egiazarian K, Jin L, Astola J, Vozel B, Chehdi K, Carli M, Battisti F (2013) Color image database TID2013: peculiarities and preliminary results. In: European workshop on visual information processing, pp 106–111
Qi S, Jing P, Wang X, Nie L (2016) Quality biased multimedia data retrieval in microblogs. J Vis Commun Image Represent 40:838–846
Raman S, Chaudhuri S (2009) Bilateral filter based compositing for variable exposure photography. In: Eurographics (short papers), pp 1–4
Razavian AS, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, Carlsson S (2014) CNN Features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 512–519
Rubin TN, Chambers A, Smyth P, Steyvers M (2012) Statistical topic models for multi-label document classification. Mach Learn 88(1–2):157–208
Saad MA, Bovik AC, Charrier C (2012) Blind image quality assessment: a natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21 (8):3339–3352
Sánchez-Fernández M, de Prado-Cumplido M, Arenas-García J, Pérez-Cruz F (2004) SVM multiregression for nonlinear channel estimation in multiple-input multiple-output systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process 52(8):2298–2307
Schölkopf B, Smola A (2001) Learning with kernels: support vector machines, regularization, optimization, and beyond. MIT Press, Cambridge
Sheikh HR, Bovik AC, De VG (2005) An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans Image Process 14 (12):2117–2128
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:14091556
Song S, Huang H, Ruan T (2018) Abstractive text summarization using LSTM-CNN based deep learning. Accepted by Multimedia Tools and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5749-3
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Vedaldi A, Lenc K (2015) MatConvNet – convolutional neural network for MATLAB. In: ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 689–692
Wang J, Zhao Y, Wu X, Hua XS (2011) A transductive multi-label learning approach for video concept detection. Pattern Recogn 44(10-11):2274–2286
Wang D, Wang B, Zhao S, Yao H, Liu H (2017) Off-the-shelf CNN features for 3D object retrieval. Multimedia Tools and Applications (1):1–17
Wei X, Huang H, Nie L, Feng F, Hong R, Chua TS (2018) Quality matters: assessing cQA pair quality via transductive multi-view learning. In: International joint conferences on artificial intelligence
Xie L, Shen J, Han J, Zhu L, Shao L (2017) Dynamic multi-view hashing for online image retrieval. In: International joint conferences on artificial intelligence
Xu C, Yang J, Gao J (2017) Coupled-learning convolutional neural networks for object recognition. Accepted by Multimedia Tools and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5262-0
Zhu L, Huang Z, Chang X, Song J, Shen HT (2017) Exploring consistent preferences: discrete hashing with pair-exemplar for scalable landmark search. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on multimedia conference, pp 726–734
Zhu L, Shen J, Xie L, Cheng Z (2017) Unsupervised visual hashing with semantic assistant for content-based image retrieval. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29 (2):472–486
Zhu L, Huang Z, Li Z, Xie L, Shen HT (2018) Exploring auxiliary context: discrete semantic transfer hashing for scalable image retrieval. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(11):5264–5276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, A., Wang, J., Liu, J. et al. Comprehensive image quality assessment via predicting the distribution of opinion score. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 24205–24222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6985-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6985-2