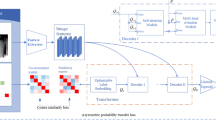
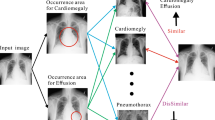
Abstract
The widely used ChestX-ray14 dataset addresses an important medical image classification problem and has the following caveats: 1) many lung pathologies are visually similar, 2) a variant of multiple diseases including lung cancer, tuberculosis, and pneumonia are present in a single scan at the same time, i.e. multiple labels. Existing literature uses state-of-the-art deep learning models being transfer learned where output neurons of the networks are trained for individual diseases to cater for multiple disease labels in each image. However, most of them don’t consider the label relationship explicitly between present and absent classes. In this work we have proposed a pair of novel error functions that can be employed for any deep learning model, Multi-label Softmax Loss (MSML) and Correlation Loss (CorLoss), to specifically address the properties of multiple labels and visually similar data. Moreover, we provide a fine-grained perspective into this problem and use bilinear pooling as an encoding scheme to increase discrimination of the model. The experiments are conducted on the ChestX-ray14 dataset. We first report improvements using our proposed loss with various backbone networks. After that, we extend our experiments to prove the rich disparity being learned by the model with our proposed losses, which can be fused with other models to improve the overall performances.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We will omit i in the rest of the article for simplification.
Overall performance of number-of-labels dependent results are lower than baseline because health images are removed. 5-Label, 6-Label and 7-Label subset is not reported due to small number of samples.
We inherit the α = 0.1 and β = 0.3 from Section 3.4 and then equally weighted gradients are used for bilinear model training
To facilitate the verification process, we use a small model ResNet18 for this experiment.
References
Arandjelovic R, Gronat P, Torii A, Pajdla T, Sivic J (2016) Netvlad: Cnn architecture for weakly supervised place recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5297–5307
Armato SG, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP, Zhao B, Aberle DR, Henschke CI, Hoffman EA et al (2011) The lung image database consortium (lidc) and image database resource initiative (idri): a completed reference database of lung nodules on ct scans. Medical physics 38(2):915–931
Farrell R, Oza O, Zhang N, Morariu VI, Darrell T, Davis LS (2011) Birdlets: Subordinate categorization using volumetric primitives and pose-normalized appearance. In: in ICCV, IEEE, pp 161–168
Ge ZY, McCool C, Sanderson C, Corke P (2015) Subset feature learning for fine-grained category classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp 46–52
Ge ZY, McCool C, Sanderson C, Wang P, Liu L, Reid I, Corke P (2016) Exploiting temporal information for dcnn-based fine-grained object classification. arXiv:1608.00486
Gong Y, Jia Y, Leung T, Toshev A, Ioffe S (2013) Deep convolutional ranking for multilabel image annotation. arXiv:1312.4894
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: CVPR
Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Zisserman A et al (2015) Spatial transformer networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2017–2025
Kingma Diederik P, Ba Jimmy (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Krause J, Jin H, Yang J, Li F-F (2015) Fine-grained recognition without part annotations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5546–5555
Lin T-Y, RoyChowdhury A, Maji S (2015) Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition. In: ICCV
Lu H, Li Y, Chen M, Kim H, Serikawa S (2018) Brain intelligence: go beyond artificial intelligence. Mobile Networks and Applications 23(2):368–375
Luke MJ, Mehrizi A, Folger GM, Rowe RD (1966) Chronic nasopharyngeal obstruction as a cause of cardiomegaly, cor pulmonale, and pulmonary edema. Pediatrics 37(5):762–768
Mahapatra D, Ge Z, Sedai S, Chakravorty R (2018) Joint registration and segmentation of xray images using generative adversarial networks. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Springer, pp 73–80
Martins A, Astudillo R (2016) From softmax to sparsemax: A sparse model of attention and multi-label classification. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp 1614–1623
Payer C, Štern D, Bischof H, Urschler M (2016) Regressing heatmaps for multiple landmark localization using cnns. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, pp 230–238
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, Duan T, Ding D, Bagul A, langlotz C, Shpanskaya K et al (2017) Chexnet: Radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning. arXiv:1711.05225
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1985) Learning internal representations by error propagation, Tech. Rep., California Univ San Diego La Jolla Inst for Cognitive Science
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2014) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Sa I, Ge Z, Dayoub F, Upcroft B, Perez T, McCool C (2016) Deepfruits: a fruit detection system using deep neural networks. Sensors 16(8):1222
Sedai S, Mahapatra D, Ge Z, Chakravorty R, Garnavi R (2018) Deep multiscale convolutional feature learning for weakly supervised localization of chest pathologies in x-ray images. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Springer, pp 267–275
Verbeek J Discriminative metric learning in nearest neighbor models for image annotation
Wang X, Peng Y, Lu L, Lu Z, Bagheri M, Summers RM (2017) Chestx-ray8: Hospital-scale chest x-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3462–3471
Wei X-S, Luo J-H, Wu J, Zhou Z-H (2017) Selective convolutional descriptor aggregation for fine-grained image retrieval. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(6):2868–2881
Xu Z, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG (2015) A discriminative cnn video representation for event detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1798–1807
Xue X, Zhang W, Zhang J, Wu B, Fan J, Lu Y (2011) Correlative multi-label multi-instance image annotation. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, pp 651–658
Yao L, Poblenz E, Dagunts D, Covington B, Bernard D, Lyman K (2017) Learning to diagnose from scratch by exploiting dependencies among labels. arXiv:1710.10501
Zhang H, Xu T, Elhoseiny M, Huang X, Zhang S, Elgammal A, Metaxas D (2016) Spda-cnn: Unifying semantic part detection and abstraction for fine-grained recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1143–1152
Zhang N, Donahue J, Girshick R, Darrell T (2014) Part-based r-cnns for fine-grained category detection. In: ECCV
Zhou Q, Yang W, Gao G, Ou W, Lu H, Chen J, Latecki LJ (2018) Multi-scale deep context convolutional neural networks for semantic segmentation. World Wide Web, pp 1–16
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Airdoc for research funding support. The authors acknowledge Zitong Huang for driving useful discussions and support for the project. We also thank Nvidia AI Technology Centre for providing technical and hardware support for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Z., Mahapatra, D., Chang, X. et al. Improving multi-label chest X-ray disease diagnosis by exploiting disease and health labels dependencies. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 14889–14902 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08260-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08260-2