Abstract
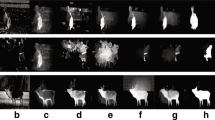
Current studies on salient detection have combined salient cues, such as contrast, prior information, and object edges, which work by segmenting the foreground from the background. However, existing models mostly lose tiny salient regions in scenes and fail to detect all salient regions. In this paper, we propose an optimization algorithm on salient detection based on line sketch. First, we generate the line sketches of images, which include all edges of the salient objects. Second, the detected line sketches are blended into the original images in soft light mode. Then, the sketch works as a mask to highlight the outlines. Finally, the processed images are used in the existing salient detection models. Our contribution is that the salient detection with the sketches extracting image outline can effectively improve the accuracy. Results prove that the proposed algorithm is efficient and improves the performance of models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Achanta, S. Hemami, F. Estrada, et al., “Frequency-tuned salient region detection,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on, 1597–1604 (2009).
S. Avidan and A. Shamir, “Seam carving for content-aware image resizing,” in ACM Transactions on graphics (TOG), 26(3), 10, ACM (2007).
A. Borji and L. Itti, “Scene classification with a sparse set of salient regions,” in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 1902–1908 (2011).
Borji A, Ahmadabadi MN, Araabi BN (2011) Cost-sensitive learning of top-down modulation for attentional control. Mach Vis Appl 22(1):61–76
A. Borji, S. Frintrop, D. N. Sihite, et al., “Adaptive object tracking by learning background context,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, 23–30, IEEE (2012).
Borji A, Sihite DN, Itti L (2012) Salient object detection: a benchmark. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
A. Borji, M. M. Cheng, Q. Hou, et al., “Salient object detection: A survey,” Eprint Arxiv 16(7), 3118 (2014).
A. Bousseau, M. Kaplan, J. Thollot, et al., “Interactive watercolor rendering with temporal coherence and abstraction,” in Proceedings of the 4th international symposium on Nonphotorealistic animation and rendering, 141–149, ACM (2006).
Chansri N, Koomsap P (2012) Automatic single-line drawing creation from a paper-based overtraced freehand sketch. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59(1–4):221–242
T. Chen, M. M. Cheng, P. Tan, et al., “Sketch2photo: internet image montage,” 1–10 (2009).
M.-M. Cheng, J. Warrell, W.-Y. Lin, et al., “Efficient salient region detection with soft image abstraction,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer vision, 1529–1536 (2013).
Christopoulos C, Skodras A, Ebrahimi T (2000) The jpeg2000 still image coding system: an overview. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 46(4):1103–1127
Cui C, Liu H, Lian T et al (2018) Distribution-oriented aesthetics assessment with semantic-aware hybrid network. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Fan D-P, Cheng M-M, Liu Y et al (2017) Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision
D.-P. Fan, M.-M. Cheng, J.-J. Liu, et al., “Salient objects in clutter: Bringing salient object detection to the foreground,” in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Springer (2018).
D. P. Fan, S. C. Zhang, Y. H. Wu, et al., “Face sketch synthesis style similarity: a new structure co-occurrence texture measure,” (2018).
D.-P. Fan, C. Gong, Y. Cao, et al., “Enhanced-alignment Measure for Binary Foreground Map Evaluation,” in International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 698–704. 2018 rl{http://dpfan.net/e-measure/}.
S. Frintrop, G. M. Garcia, and A. B. Cremers, “A cognitive approach for object discovery,” in International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2329–2334 (2014).
G. M. Garc’ıa, D. A. Klein, J. Stuckler, et al., “Adaptive multi-cue 3d tracking of arbitrary objects,” in Joint DAGM (German Association for Pattern Recognition) and OAGM Symposium, 357–366, Springer (2012).
J. Harel, C. Koch, and P. Perona, “Graph-based visual salient,” in Advances in neural information processing systems, 545–552 (2007).
A. Hertzmann, “Painterly rendering with curved brush strokes of multiple sizes,” in Proceedings of the 25th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, 453–460, ACM (1998).
C. Kanan and G. Cottrell, “Robust classification of objects, faces, and flowers using natural image statistics,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2472–2479 (2010).
D. A. Klein, D. Schulz, S. Frintrop, et al., “Adaptive real-time video-tracking for arbitrary objects,” in Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on, 772–777, Citeseer (2010).
Ko BC, Nam J-Y (2006) Object-of-interest image segmentation based on human attention and semantic region clustering. JOSA A 23(10):2462–2470
Lei J, Wang B, Fang Y et al (2016) A universal framework for salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 18(9):1783–1795
Li J, Levine MD, An X, Xu X, He H (2013) Visual salient based on scale-space analysis in the frequency domain. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(4):996–1010
C. Lu, L. Xu, and J. Jia, “Combining sketch and tone for pencil drawing production,” in Proceedings of the Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering, 65–73, Eurographics Association (2012).
Y.-F. Ma and H.-J. Zhang, “A model of motion attention for video skimming,” in Image Processing. 2002. Proceedings. 2002 International conference on, 1, I–I, IEEE (2002).
Y.-F. Ma, L. Lu, H.-J. Zhang, et al., “A user attention model for video summarization,” in Proceedings of the tenth ACM international conference on Multimedia, 533–542, ACM (2002).
Moosmann F, Larlus D, Jurie F (2006) Learning salient maps for object categorization. In: International workshop on the representation and use of prior knowledge in vision (in ECCV’06)
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y et al (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection[C]//2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE:733–740
Ren Z, Gao S, Chia LT et al (2014) Region-based saliency detection and its application in object recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 24(5):769–779
U. Rutishauser, D. Walther, C. Koch, et al., “Is bottom-up attention useful for object recognition? ,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2004. CVPR 2004. Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, II–37–II–44 Vol.2 (2004).
Shen H, Li S, Zhu C et al (2013) Moving object detection in aerial video based on spatiotemporal salient. Chin J Aeronaut 26(5):1211–1217
S. Stalder, H. Grabner, and L. Van Gool, “Dynamic objectness for adaptive tracking,” in Asian conference on computer vision, 43–56, Springer (2012).
Tang X, Wang X et al (2004) Face sketch recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 14(1):50–57
Treisman AM, Gelade G (1980) A feature-integration theory of attention. Cogn Psychol 12(1):97–136
R. G. Uhl and N. da Vitoria Lobo, “A framework for recognizing a facial image from a police sketch,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1996. Proceedings CVPR’96, 1996 IEEE computer society conference on, 586–593, IEEE (1996).
J. Wang and J.-D. Zucker, “Solving multiple-instance problem: a lazy learning approach,” (2000).
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Y. Wei, “Unsupervised object class discovery via salient-guided multiple class learning,” in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3218–3225 (2012).
Zeng K, Zhao M, Xiong C et al (2009) From image parsing to painterly rendering. ACM Trans Graph 29(1):2–1
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the NEPU Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. 2017PY ZL − 05, JY CX_CX06_2018 and JY CX_JG06_2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Bi, H., Guan, H. et al. Optimization algorithm on salient detection. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 6437–6445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08381-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08381-8