Abstract
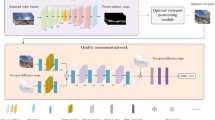
360-degree videos contain an omnidirectional view with ultra-high resolution, which will lead to the bandwidth-hungry issue in virtual reality (VR) applications. However, only a part of a 360-degree video is displayed on the head-mounted displays (HMDs). Thus, we propose a viewport-adaptive 360-degree video coding approach based on a novel viewport prediction strategy. Specifically, we firstly introduce a novel viewport prediction model based on deep 3-dimensional convolutional neural networks. In this model, a video saliency encoder and a trajectory encoder are trained to extract the features of video content and the history view path. With the outputs of the two encoders, a video prior analysis network is trained to adaptively determine the best fusion weight to generate the final feature. Moreover, benefiting from the viewport prediction model, a viewport-adaptive rate-distortion optimization (RDO) method is presented to decrease the bitrate and ensure an immersive experience. In addition, we also consider the scaling factor of the area from rectangular plane to spherical surface. Therefore, the Lagrange multiplier and quantization parameter are adaptively adjusted based on the weight of each coding tree unit. The experiments have demonstrated that the proposed RDO method gains considerably better RD performance than the traditional RDO method.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
“The TensorFlow website,” [Online]. Available: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow.
“The dataset website,” [Online]. Available: https://github.com/xuyanyu-shh/VR-EyeTracking.
“JCT-VC Subversion Repository for the HEVC test Model Version HM16.15,” [Online]. Available: https://hevc.hhi.fraunhofer.de/svn/svn_HEVCSoftware/tags/HM-16.15.
References
Adeel A (2016) Gopro test sequences for virtual reality video coding. Document JVET-C0021. Geneva, CH
Bottou L (2012) Stochastic gradient descent tricks. Springer, Berlin, pp 421–436
Boyce J, Alshina E, Abbas A, Ye Y (2016) JVET common test conditions and evaluation procedures for 360 video. In: JVET, JVET-D1030. Chengdu, China
Carreira J, Agrawal P, Fragkiadaki K, Malik J (2016) Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4733–4742
Chaabouni S, Benois-Pineau J, Hadar O, Amar CB (2016) Deep learning for saliency prediction in natural video. arXiv:1604.08010
Cheng M M, Mitra N J, Huang X, Torr P H S, Hu S M (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):569–582
Choi KP, Vladyslav Z, Choi M, Alshina E (2016) Test sequence formats for virtual reality video coding; Document: JVET- C0050 JVET of ITU-T SG 16 WP 3 and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 3rd Meeting: Geneva, CH, 26 May 2016
Corbillon X, Simon G, Devlic A, Chakareski J (2017) Viewport-adaptive navigable 360-degree video delivery. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. communications, pp 1–7
Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, Hausser P, Hazirbas C, Golkov V, van der Smagt P, Cremers D, Brox T (2015) Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision, pp 2758–2766
Fan C L, Lee J, Lo W C, Huang C Y, Chen K T, Hsu C H (2017) Fixation prediction for 360 deg video streaming in head-mounted virtual reality. In: Proceedings of the 27th workshop on network and operating systems support for digital audio and video, NOSSDAV’17. ACM, New York, pp 67–72
Gitman Y, Erofeev M, Vatolin D, Andrey B, Alexey F (2014) Semiautomatic visual-attention modeling and its application to video compression. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICIP, pp 1105–1109
Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2012) Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(10):1915–1926
Guo C, Zhang L (2010) A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(1):185–198
Guo C, Ma Q, Zhang L (2008) Spatio-temporal saliency detection using phase spectrum of quaternion fourier transform. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8
Hacisalihzade S S, Stark L W, Allen J S (1992) Visual perception and sequences of eye movement fixations: a stochastic modeling approach. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, and Cybern 22(3):474–481
Hadizadeh H, Bajić IV (2014) Saliency-aware video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(1):19–33
Huang X, Shen C, Boix X, Zhao Q (2015) Salicon: Reducing the semantic gap in saliency prediction by adapting deep neural networks. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision, pp 262–270
Hu Q, Zhou J, Zhang X, Gao Z, Sun M (2018) In-loop perceptual model-based rate-distortion optimization for HEVC real-time encoder. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing
Hu H, Lin Y, Liu M, Cheng H, Chang Y, Sun M (2017) Deep 360 pilot: Learning a deep agent for piloting through 360deg sports video. arXiv:1705.01759
Itti L, Baldi P (2005) A principled approach to detecting surprising events in video. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn 1:631–637
ITU-R: Methodology for the subjective assessment of quality of television pictures. ITU-R Rec. BT.500-11 (2002)
Jayant N, Johnston J, Safranek R (1993) Signal compression based on models of human perception. Proc IEEE 81(10):1385–1422
Judd T, Ehinger K, Durand F, Torralba A (2009) Learning to predict where humans look. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision, pp 2106–2113
Kruthiventi S S S, Ayush K, Babu R V (2017) Deepfix: A fully convolutional neural network for predicting human eye fixations. IEEE Trans Image Process 26 (9):4446–4456
Li F, Li N (2016) Region-of-interest based rate control algorithm for h.264/avc video coding. Multimed Tools Appl 75(8):4163–4186
Li G, Yu Y (2016) Visual saliency detection based on multiscale deep cnn features. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(11):5012–5024
Li Y, Xu J, Chen Z. (2017) Spherical domain rate-distortion optimization for 360-degree video coding. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp 709–714
Li Y, Xu J, Chen Z (2018) Spherical domain rate-distortion optimization for omnidirectional video coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29:1–1
Li B, Li H, Li L, Zhang J (2014) λ domain rate control algorithm for high efficiency video coding. IEEE Trans Image Process 23 (9):3841–3854
Liu R, Cao J, Lin Z, Shan S (2014) Adaptive partial differential equation learning for visual saliency detection. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3866–3873
Liu N, Han J, Zhang D, Wen S, Liu T (2015) Predicting eye fixations using convolutional neural networks. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 362–370
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum H Y (2011) Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33 (2):353–367
Majid M, Owais M, Anwar S M (2018) Visual saliency based redundancy allocation in hevc compatible multiple description video coding. Multimed Tools Appl 77(16):20,955–20,977
Meuel H, Munderloh M, Ostermann J (2011) Low bit rate roi based video coding for hdtv aerial surveillance video sequences. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition WORKSHOPS, pp 13–20
Ogasawara K, Miyazaki T, Sugaya Y, Omachi S (2017) Object-based video coding by visual saliency and temporal correlation. IEEE Trans Emerging Topics in Comput PP(99):1–1
Pan J, Sayrol E, Giro-I-Nieto X, McGuinness K, O’Connor N E (2016) Shallow and deep convolutional networks for saliency prediction. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 598–606
Quan F, Han B, Ji L, Gopalakrishnan V (2016) Optimizing 360 video delivery over cellular networks. In: ACM SIGCOMM AllThingsCellular, pp 583–586
Rai Y, Gutiérrez J, Le Callet P (2017) A dataset of head and eye movements for 360 degree images. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACM on multimedia systems conference, MMSys’17. ACM, New York, pp 205–210
Requirements for high quality for vr. In: Tech. Rep. MPEG 116/M39532, JTC1/SC29/WG, ISO/IEC, Chengdu, CN Oct 2016. Chengdu, CN, 2016
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. ArXiv e-prints
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Ghahramani Z, Welling M, Cortes C, Lawrence ND, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 27. Curran Associates, Inc, New York, pp 568–576
Sitzmann V, Serrano A, Pavel A, Agrawala M, Gutierrez D, Wetzstein G (2016) Saliency in VR: how do people explore virtual environments? arXiv:1612.04335
Shen L, Liu Z, Zhang Z (2013) A novel h.264 rate control algorithm with consideration of visual attention. Multimed Tools Appl 63(3):709–727
Sreedhar K K, Aminlou A, Hannuksela M M, Gabbouj M (2016) Viewport-adaptive encoding and streaming of 360-degree video for virtual reality applications. In: IEEE international symposium on multimedia (ISM), pp 583–586
Sullivan G J, Wiegand T (1998) Rate-distortion optimization for video compression. IEEE Signal Process Mag 15(6):74–90
Sullivan G, Ohm J, Han W J, Wiegand T (2013) High efficiency video coding (HEVC) text specification draft 10. JCTVC-L1003. Geneva, CH
Sun W, Guo R (2016) Test sequences for virtual reality video coding from letinvr. In: JVET, JVET-D0179. Chengdu, China
Sun C, Wang H J, Li H (2008) Macroblock-level rate-distortion optimization with perceptual adjustment for video coding. In: Proc. IEEE data compress. conf., pp 546–546
Sun Y, Lu A, Yu L (2016) AHG8: WS-PSNR for 360 video objective quality evaluation. In: JVET, JVET-D0040. Chengdu, China
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Tang C W (2007) Spatiotemporal visual considerations for video coding. IEEE Trans Multimed 9(2):231–238
Tang C W, Chen C H, Yu Y H, Tsai C J (2006) Visual sensitivity guided bit allocation for video coding. IEEE Trans Multimed 8(1):11–18
Tang L, Wu Q, Li W, Liu Y (2018) Deep saliency quality assessment network with joint metric. IEEE Access 6:913–924
Tran D, Bourdev L, Fergus R, Torresani L, Paluri M (2015) Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision, pp 4489–4497
Wandell B (1995) Foundations of vision. Sinauer, Sunderland MA
Wang Z, Lu L, Bovik A C (2003) Foveation scalable video coding with automatic fixation selection. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(2):243–254
Wang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang M H (2015) Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3183–3192
Wang S, Rehman A, Wang Z, Ma S, Gao W (2013) Perceptual video coding based on SSIM-inspired divisive normalization. IEEE Trans Image Process 22 (4):1418–1429
Wang L, Xiong Y, Wang Z, Qiao Y, Lin D, Tang X, Van Gool L (2016) Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) European conference on computer vision. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 20–36
Wiegand T, Sullivan G, Bjontegaard G, Luthra A (2003) Overview of the H.264/AVC video coding standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13 (7):560–576
Wei H, Zhou X, Zhou W, Yan C, Duan Z, Shan N (2016) Visual saliency based perceptual video coding in HEVC. In: Proc. Int. symp. circuits syst., pp 2547–2550
Xu Y, Dong Y, Wu J, Sun Z, Shi Z, Yu J, Gao S (2018) Gaze prediction in dynamic 360∘ immersive videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5333–5342
Zare A, Aminlou A, Hannuksela MM, Gabbouj M (2016) HEVC-compliant tile-based streaming of panoramic video for virtual reality applications. In: Proc. of ACM multimedia, pp 583–586
Zeng H, Yang A, Ngan K N, Wang M (2016) Perceptual sensitivity-based rate control method for high efficiency video coding. Multimed Tools Appl 75 (17):10,383–10,396
Zhang F, Bull D R (2016) HEVC enhancement using content-based local QP selection. In: Proc. IEEE ICIP, pp 4215–4219
Zhang J, Shan S, Kan M, Chen X (2014) Coarse-to-fine auto-encoder networks (cfan) for real-time face alignment. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 1–16
Zhang M, Ma K T, Lim J H, Zhao Q, Feng J (2017) Deep future gaze: Gaze anticipation on egocentric videos using adversarial networks. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3539–3548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Zhou, J., Zhang, X. et al. Viewport-adaptive 360-degree video coding. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 12205–12226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08390-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08390-7