Abstract
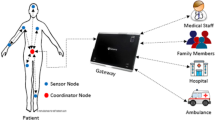
Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) is evolving as the successful way of monitoring patient health and offers enhanced healthcare solutions to provide the better quality of life for the urban community. As it involves wireless communications, securing the privacy-related data is a key constraint in WBAN. To ensure privacy, it is essential to include authentication to prevent unauthorized access by intruders. This paper proposes the privacy preserving LightwEight two factors Authentication Protocol (LEAP) for WBAN based on genus-2 Hyper Elliptic Curve (HEC). Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) collects signals from sensors from the BAN. PDA transmits the healthcare data to the Healthcare Service Provider (HSP) connected in the public network. Hence, the two-factor mutual authentication protocol is established between PDA and HSP. Since PDA is considered as a resource constraint device, the lightweight mutual authentication is required. Genus 2 Hyper elliptic curve (HEC) is carefully designed to prevent all possible cryptographic attacks, which is more suitable for lightweight authentication since it provides the high degree of security with the lesser key size even as compared to the elliptic curve. Using the rigorous formal security analysis using BAN logic, it is proved that the proposed scheme is secure against possible attacks. Also, the privacy preserving lightweight authentication scheme is implemented using the most-widely accepted Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and Applications (AVISPA) tool, and the simulation results reveal that proposed scheme is secure and robust.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin R, Islam SH, Biswas GP, Khan MK, Kumar N (2018) A robust and anonymous patient monitoring system using wireless medical sensor networks. Future Gen Comput Syst Elsevier. 80:483–495
Chen Z, Ren W, Ren Y, Choo KK (2018) LiReK: a lightweight and real-time key establishment scheme for wearable embedded devices by gestures or motions. Future Gen Comput Syst Elsevier 84:126–138
Das AK, Zeadally S, Wazid M (2017) Lightweight authentication protocols for wearable devices. Comput Electric Eng, Elsevier. 63:196–208
Ever YK (2018) Secure-anonymous user Authentication scheme for e-healthcare application using wireless medical sensor networks. IEEE Syst J
Fan K, Jiang W, Li H, Yang Y (2018) Lightweight RFID protocol for medical privacy protection in IoT. IEEE Trans Industr Inform 14(4):1656–1665
Hayajneh T, Almashaqbeh G, Ullah S, Vasilakos AV (2014) A survey of wireless technologies coexistence in WBAN: analysis and open research issues. Wirel Netw 20(8):2165–2199
He D, Zeadally S (2015 Jan) Authentication protocol for an ambient assisted living system. IEEE Commun Mag 53(1):71–77
He D, Zeadally S, Wu L, Wang H (2017) Analysis of handover authentication protocols for mobile wireless networks using identity-based public key cryptography. Comput Netw, Elsevier. 128:154–163
He D, Zeadally S, Kumar N, Lee JH (2017) Anonymous authentication for wireless body area networks with provable security. IEEE Syst J 11(4):2590–2601
Jung M, Han K, Cho J (2015) Advanced verification on WBAN and cloud computing for the u-health environment. Multimed Tools Appl, Springer. 74(16):6151–6168
Li X, Peng J, Kumari S, Wu F, Karuppiah M, Choo KK (2017) An enhanced 1-round authentication protocol for wireless body area networks with user anonymity. Comput Electric Eng, Elsevier 61:238–249
Li X, Ibrahim MH, Kumari S, Sangaiah AK, Gupta V, Choo KK (2017) Anonymous mutual authentication and key agreement scheme for wearable sensors in wireless body area networks. Comput Netw, Elsevier 129:429–443
Li S, Cui J, Zhong H, Zhang Y, He Q. (2017) LEPA: a lightweight and efficient public auditing scheme for cloud-assisted wireless body sensor networks. Sec Commun Netw, Wiley Publ 2017
Li CT, Shih DH, Wang CC (2018) Cloud-assisted mutual authentication and privacy preservation protocol for telecare medical information systems. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, Elsevier 157:191–203
Li X, Niu J, Kumari S, Wu F, Sangaiah AK, Choo KK (2018) A three-factor anonymous authentication scheme for wireless sensor networks in the internet of things environments. J Netw Comput Appl, Elsevier 103:194–204
Li F, Han Y, Jin C (2018) Cost-effective and anonymous access control for wireless body area networks. IEEE Syst J 12(1):747–758
Ma L, Ge Y, Zhu Y (2014) TinyZKP: a lightweight authentication scheme based on zero-knowledge proof for wireless body area networks. Wireless Person Commun, Springer 77(2):1077–1090
Movassaghi S, Abolhasan M, Lipman J, Smith D, Jamalipour A (2014) Wireless body area networks: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 16(3):1658–1686
Omala AA, Kibiwott KP, Li F (2017) An efficient remote authentication scheme for wireless body area network. J Med Syst, Springer 41(2):25
Salayma M, Al-Dubai A, Romdhani I, Nasser Y (2017) Wireless body area network (WBAN): a survey on reliability, fault tolerance, and technologies coexistence. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 50(1):3
Sharma G, Kalra S (2018) A lightweight multi-factor secure smart card based remote user authentication scheme for cloud-IoT applications. J Inform Sec Appl, Elsevier 42:95–106
Shen J, Chang S, Shen J, Liu Q, Sun X (2018) A lightweight multi-layer authentication protocol for wireless body area networks. Future Gen Comput Syst, Elsevier. 78:956–963
Shen J, Gui Z, Ji S, Shen J, Tan H, Tang Y (2018) Cloud-aided lightweight certificate-less authentication protocol with anonymity for wireless body area networks. J Netw Comput Appl, Elsevier. 106:117–123
Shen J, Chang S, Liu Q, Shen J, Ren Y (2018) Implicit authentication protocol and self-healing key management for WBANs. Multimed Tools Appl, Springer 77(9):11381–11401
Ullah S, Li XY, Zhang L (2017) A review of Signcryption schemes based on hyper elliptic curve. In big data computing and communications (BIGCOM), 2017 3rd international conference: 51–58). IEEE
Wang M, Yan Z (2018) Privacy-preserving authentication and key agreement protocols for D2D group communications. IEEE Trans Indust Inform. 14(8):3637–3647
Wang W, Shi X, Qin T (2018) Encryption-free Authentication and Integrity Protection in Body Area Networks through Physical Unclonable Functions. Smart Health, Elsevier
Wazid M, Das AK, Vasilakos AV (2018) Authenticated key management protocol for cloud-assisted body area sensor networks. J Netw Comput Appl, Elsevier
Wu F, Li X, Xu L, Kumari S, Karuppiah M, Shen J (2017) A lightweight and privacy-preserving mutual authentication scheme for wearable devices assisted by cloud server. Comput Electric Eng, Elsevier. 63:168–181
Wu F, Li X, Sangaiah AK, Xu L, Kumari S, Wu L, Shen J (2018) A lightweight and robust two-factor authentication scheme for personalized healthcare systems using wireless medical sensor networks. Future Gen Comput Syst Elsevier. 82:727–737
Xu J, Wei L, Wu W, Wang A, Zhang Y, Zhou F (2018) Privacy-preserving data integrity verification by using lightweight streaming authenticated data structures for healthcare cyber-physical system. Future Gen Comput Syst, Elsevier
Zhao Z (20141) An efficient anonymous authentication scheme for wireless body area networks using elliptic curve cryptosystem. J Med Syst Springer 38(2):13
Acknowledgements
This part of the work is funded by the Science and Engineering Board (SERB), Government of India under the ECR grant (ECR/2017/000679/ES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasikaladevi, N., Malathi, D. Privacy preserving light weight authentication protocol (LEAP) for WBAN by exploring Genus-2 HEC. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 18037–18054 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7149-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7149-8