Abstract
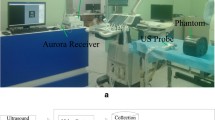
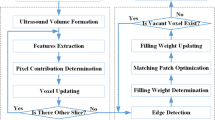
Although the ultrasonic C-scan technique has been extensively applied in nondestructive testing (NDT) in recent years, 3D reconstruction from ultrasonic C-scan images has not been well addressed. This paper develops a novel and efficient 3D reconstruction technique based on an improved K-nearest neighbor filtering for ultrasonic C-scan data of the tissue-mimicking phantoms. An edge-points-predicting approach based on K-nearest neighbor filtering is first proposed to predict the undetected edge points and to reduce the noise points for 2D ultrasonic images. Then, the 3D model is reconstructed from the clean edges by utilizing the surface rendering algorithm. The proposed approach is validated using the ultrasonic C-scan data of a liver model embedded in a tissue-mimicking phantom. The comparisons with other methods are presented in the experiments. The results demonstrate the effectiveness and the significantly improved reconstruction results of the proposed approach.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelopoulou A, Psarrou A, Garcia-Rodriguez J, Orts-Escolano S, Azorin-Lopez J (2015) 3D reconstruction of medical images from slices automatically landmarked with growing neural models. Neurocomputing 150(PA):16–25
Barry CD, Gee AH, Berman L (1997) Three-dimensional freehand ultrasound: image reconstruction and volume analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 23(8):1209–1224
Baselice F (2017) Ultrasound image despeckling based on statistical similarity. Ultrasound Med Biol 43(9):2065–2078
Cai S, Huang J, Chen J, Huang Y, Ding X, Zeng D (2018) Prominent edge detection with deep metric expression and multi-scale features. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6581-5
Chen Y, Navarro L, Wang Y, Courbebaisse G (2014) Segmentation of the thrombus of giant intracranial aneurysms from CT angiography scans with lattice Boltzmann method. Med Image Anal 18(1):1–8
Chikmurge D, Harnale S (2018) Feature extraction of DICOM images using canny edge detection algorithm. Adv Intell Syst Comput 632:185–196
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 13(1):21–27
Ferrante E, Paragios N (2017) Slice-to-volume medical image registration: a survey. Med Image Anal 39:101–123
Ghose S, Dowling JA, Rai R, Liney GP (2017) Substitute CT generation from a single ultra short time echo MRI sequence: preliminary study. Phys Med Biol 62(8):2950–2960
Huang Q, Zeng Z (2017) A review on real-time 3D ultrasound imaging technology. Biomed Res Int 2017:6027029. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6027029
Huang QH, Zheng YP (2009) A new adaptive interpolation algorithm for 3D ultrasound imaging with speckle reduction and edge preservation. Comput Med Imaging Graph 33(2):100–110
Jaffar MA, Zia S, Latif G, Mirza AM, Mehmood I et al (2012) Anisotropic diffusion based brain MRI segmentation and 3D reconstruction. Int J Comput Int Sys 5(3):494–504
Kainz B, Steinberger M, Wein W, Kuklisova-Murgasova M et al (2015) Fast volume reconstruction from motion corrupted stacks of 2D slices. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(9):1901–1913
karaman M, Wygant IO, Oralkan O, Khuri-Yakub B (2009) Minimally redundant 2-D array designs for 3-D medical ultrasound imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(7):1051–1061
Katunin A (2015) Stone impact damage identification in composite plates using modal data and quincunx wavelet analysis. Arch Civ Mech Eng 15:251–261
Katunin A, Dragan K, Dziendzikowski M (2015) Damage identification in aircraft composite structures: a case study using various non-destructive testing techniques. Compos Struct 127:1–9
Kerr W, Rowe P, Pierce SG (2017) Accurate 3D reconstruction of bony surfaces using ultrasonic synthetic aperture techniques for robotic knee arthroplasty. Comput Med Imaging Graph 58:23–32
Khvostikov A, Krylov A, Kamalov J, Megroyan A (2015) Influence of ultrasound despeckling on the liver fibrosis classification. In: 5th International Conference on Image Processing, Theory, Tools and Applications 2015, pp 440–445
Kim K, Habas PA, Rousseau F, Glenn OA et al (2010) Intersection based motion correction of multislice MRI for 3-D in utero fetal brain image formation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(1):146–158
Kim D, Ramani S, Fessler JA (2015) Combining ordered subsets and momentum for accelerated X-ray CT image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(1):167–178
Kuklisova-Murgasova M, Quaghebeur G, Rutherford MA, Hajnal JV, Schnabel JA (2012) Reconstruction of fetal brain MRI with intensity matching and complete outlier removal. Med Image Anal 16(8):1550–1564
Kumar A, Rajkumar KV, Palanichamy P, Jayakumar T, Chellapandian R, Kasiviswanathan KV, Lande BK (2007) Development and applications of C-scan ultrasonic facility. BARC Newsletter 31(42):14989–14997
Kuo J, Mamou J, Aristizábal O, Zhao X, Ketterling JA, Wang Y (2016) Nested graph cut for automatic segmentation of high-frequency ultrasound images of the mouse embryo. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(2):427–441
Mederos, Amenta N, Velho L, Figueiredo LH (2005) Surface reconstruction from noisy point clouds. Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing 255:53–62
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S (2016) V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. 4th International Conference on 3D Vision, pp 565–571
Moon H, Ju G, Park S, Shin H (2016) 3D freehand ultrasound reconstruction using a piecewise smooth Markov random field. Comput Vis Image Underst 151:101–113
Poudel P, Illanes A, Arens C, Hansen C, Friebe M (2017) Active contours extension and similarity indicators for improved 3D segmentation of thyroid ultrasound images[C]// Medical Imaging 2017: Imaging Informatics for Healthcare, Research, and Applications. International Society for Optics and Photonicss. SPIE Medical Imaging, Orlando
Quan EM, Lalush DS (2010) Three-dimensional imaging properties of rotation-free square and hexagonal micro-CT systems. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(3):916–923
Rim Y, McPherson D, Kim H (2013) Volumetric three dimensional intravascular ultrasound visualization using shape-based nonlinear interpolation. Biomed Eng Online 12(1):39
Rodtook A, Kirimasthong K, Lohitvisate W, Makhanov SS (2018) Automatic initialization of active contours and level set method in ultrasound images of breast abnormalities. Pattern Recogn 79:172–182
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, vol 9351, pp 234–241
Solberg OV, Lindseth F, Torp H, Blake RE et al (2007) Freehand 3d ultrasound reconstruction algorithms-a review. Ultrasound Med Biol 33(7):991–1009
Toonkum P, Suwanwela NC, Chinrungrueng C (2011) Reconstruction of 3D ultrasound images based on cyclic regularized Savitzky–Golay filters. Ultrasonics 51(2):136–147
Verma J, Nath M, Tripathi P, Saini KK (2017) Analysis and identification of kidney stone using K-th nearest neighbour (KNN) and support vector machine (SVM) classification techniques. Pattern Recognit Image Anal 27(3):574–580
Wang J, Ye M, Liu Z, Wang C (2009) Precision of cortical bone reconstruction based on 3D CT scans. Comput Med Imaging Graph 33(3):235–241
Wen T, Yang F, Gu J, Wang L (2015) A novel Bayesian-based nonlocal reconstruction method for freehand 3D ultrasound imaging. Neurocomputing 168:104–118
Wronkowicz A, Katunin A, Dragan K (2015) Ultrasonic C-scan image processing using multilevel thresholding for damage evaluation in aircraft vertical stabilizer. I J Image, Graphics and Signal Processing11:1–8
Xu Q, Yu H, Mou X, Zhang L, Hsieh J et al (2012) Low-dose X-ray CT reconstruction via dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(9):1682–1697
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant No.61672084 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under grant No.XK1802-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, H., Yang, T., Yang, P. et al. 3D reconstruction for ultrasonic C-scan images of tissue-mimicking phantom based on an improved K-nearest neighbor filtering. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 23597–23616 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7686-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7686-1