Abstract
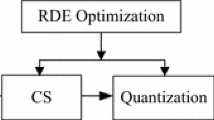
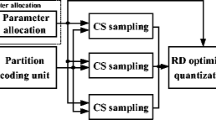
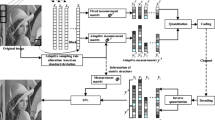
Compressive Imaging (CI) is a potential sensing technology for energy-efficient visual sensors, and its rate-distortion performance can be improved by adaptive Compressive Sensing (CS) of image. However, due to the unavailability of original image, it is a challenge for CI-based adaptive CS to extract an effective feature from measurements to evaluate the sparsity of image. In view of that, this paper presents an entropy-assisted adaptive CS system, whose merit is its definition of the sensed entropy without the original image. Based on sensed entropy, each image block is allocated sufficient measuring resources, guaranteeing a cost-effective reconstruction of image. Experimental results show that the proposed entropy-assisted adaptive CS system provides better objective and subjective recovery qualities with a low measuring and recovering complexity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baraniuk R (2007) Compressive sensing [Lecture Notes]. IEEE Signal Process Mag 24:118–121. https://doi.org/10.1109/CISS.2008.4558479
Baraniuk R, Davenport M, Devore R, Wakin M (2008) A simple proof of the restricted isometry property for random matrices. Constr Approx 45:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00365-007-9003-x
Baraniuk R, Goldstein T, Sankaranarayanan AC, Christoph S, Veeraraghavan A, Wakin MB (2017) Compressive video sensing: algorithms, architectures, and applications. IEEE Signal Process Mag 34:52–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2016.2602099
Becker S, Bobin J, Candès EJ (2011) NESTA: a fast and accurate first-order method for sparse recovery. SIAM J Imag Sci 4:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1137/090756855
Bioucas-Dias JM, Figueiredo MAT (2007) A new TwIST: two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 16:2992–3004. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2007.909319
Candès E, Romberg J (2007) Sparsity and incoherence in compressive sampling. Inverse Prob 23:969–985. https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/23/3/008
Chen C, Tramel EW, Fowler JE (2011) Compressed-sensing recovery of images and video using multihypothesis predictions. In: 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), 6–9 November 2011. IEEE, Pacific Grove, pp 1193–1198. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2011.6190204
Chen Z, Hon XS, Shao L, Gong C, Qian XM, Huang Y, Wang SD (2019) Compressive sensing multi-layer residual coefficients for image coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30:1109–1120. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2898908
Do TT, Gan L, Nguyen NH, Tran TD (2012) Fast and efficient compressive sensing using structurally random matrices. IEEE Trans Signal Process 60:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2011.2170977
Duarte M, Wakin M, Baraniuk R (2005) Fast reconstruction of piecewise smooth signals from incoherent projections. Workshop on Signal Processing with Adaptive Sparse Structured Representations 1–4
Elhoseny M, Hosny A, Hassanien AE, Muhammad K, Sangaiah AK (2017) Secure automated forensic investigation for sustainable critical infrastructures compliant with green computing requirements. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSUSC.2017.2782737
Figueiredo MT, Nowak RD, Wright SJ (2007) Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J Sel Top Sign Proces 1:586–597. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2007.910281
Fowler JE, Mun S, Tramel EW (2010) Block-based compressed sensing of images and video. Foundations and Trends? in Signal Processing 4:297–416. https://doi.org/10.1561/2000000033
Gan L (2007) Block compressed sensing of natural images. Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Cardiff, UK, pp 403–406, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDSP.2007.4288604
Gharbia R, Hassanien AE, Hassan EB, Mohamed E, Gunasekaran M (2018) Multi-spectral and panchromatic image fusion approach using stationary wavelet transform and swarm flower pollination optimization for remote sensing applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst 88:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.06.022
Ivan R, Damir S, Davor P (2019) Off-the-shelf measurement setup for compressive imaging. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 68:502–511. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2018.2847018
Kareth LL, Laura G, Henry A (2019) Temporal colored coded aperture design in compressive spectral video sensing. IEEE Trans Image Process 28:253–264. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2867171
Li R, Duan XM, Guo XL, He W, Lv YF (2017) Adaptive compressive sensing of images using spatial entropy. Comput Intell Neurosci 2017:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9059204
Memos VA, Psannis KE, Ishibashi Y, Kim BG, Gupta BB (2018) An efficient algorithm for media-based surveillance system (EAMSuS) in IoT smart city framework. Futur Gener Comput Syst 83:619–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.04.039
Muhammad K, Lloret J, Baik SW (2019) Intelligent and energy-efficient data prioritization in green smart cities: current challenges and future. IEEE Commun Mag 57:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2018.1800371
Mun S, Fowler JE (2010) Block compressed sensing of images using directional transforms. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Snowbird, UT, USA, pp. 3021–3024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/DCC.2010.90
Plageras AP, Psannis KE, Stergiou C, Wang H, Gupta BB (2018) Efficient IoT-based sensor BIG data collection–processing and analysis in smart buildings. Futur Gener Comput Syst 82:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.09.082
Psannis KE, Ishibashi Y (2006) Impact of video coding on delay and jitter in 3G wireless video multicast services. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 024616:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/WCN/2006/24616
Psannis KE, Stergiou C, Gupta BB (2018) Advanced media-based smart big data on intelligent cloud systems. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing 4(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSUSC.2018.2817043
Shen Y, Li S (2015) Sparse signals recovery from noisy measurements by orthogonal matching pursuit. Inverse Problems & Imaging 9:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2007.909319
Stergiou C, Psannis K, Kim E, Gupta BG, B (2018) Secure integration of IoT and cloud computing. Futur Gener Comput Syst 78:964–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2016.11.031
Vargas E, Espitia Ó, Arguello H, Tourneret JY (2019) Spectral image fusion from compressive measurements. IEEE Trans Image Process 28:2271–2282. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2884081
Wang AH, Liu L, Zeng B, Bai HH (2011) Progressive image coding based on an adaptive block compressed sensing. IEICE Electronics Express 8(8):575–581. https://doi.org/10.1587/elex.8.575
Wang LZ, Zhang T, Fu Y, Huang H (2019) HyperReconNet: joint coded aperture optimization and image reconstruction for compressive hyperspectral imaging. IEEE Trans Image Process 28:2257–2270. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2884076
Wei ZR, Zhang JL, Xu ZY, Liu Y, Huang YM, Fan XS (2019) Improving the signal-to-noise ratio of superresolution imaging based on single-pixel camera. IEEE Photonics J 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2019.2891061
Wu M, Zhu X, Gan Z, Li X (2012) Adaptive dictionary learning for distributed compressive video sensing. International Journal of Digital Content Technology & its Applications 6:141–149. https://doi.org/10.4156/jdcta.vol6.issue4.17
Xue JZ, Zhao YQ, Liao WZ, Chan JC-W (2019) Nonlocal tensor sparse representation and low-rank regularization for hyperspectral image compressive sensing reconstruction. Remote Sens 11:193. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020193
Yu Y, Wang B, Zhang L (2010) Saliency-based compressive sampling for image signals. IEEE Signal Process Lett 17:973–976. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2010.2080673
Zhang JG, Xiang QM, Yin YG, Chen C, Luo X (2017) Adaptive compressed sensing for wireless image sensor networks. Multimed Tools Appl 76:4227–4242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042.016.3496.x
Zheng S, Zhang X, Chen J, Kuo Y (2019) A high-efficiency compressed sensing based terminal-to-cloud video transmission system. IEEE Trans Multimedia 21:1905–1920. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2891415
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 61601396, 31872704, in part by Innovation Team Support Plan of University Science and Technology of Henan Province (no. 19IRTSTHN014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Duan, X., He, W. et al. Entropy-assisted adaptive compressive sensing for energy-efficient visual sensors. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 20821–20843 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08900-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08900-y