Abstract
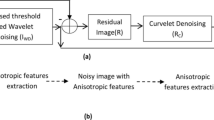
The diagnosis of dementia, particularly in the early stages is very much helpful with Positron emission tomography (PET) image processing. The most important challenges in PET image processing are noise removal and region of interests (ROIs) segmentation. Although denoising and segmentation are performed independently, but the performance of the denoising process significantly affects the performance of the segmentation process. Due to the low signals to noise ratio and low contrast, PET image denoising is a challenging task. Individual wavelet, curvelet and non-local means (NLM) based methods are not well suited to handle both isotropic (smooth details) and anisotropic (edges and curves) features due to its restricted abilities. To address these issues, the present work proposes an efficient denoising framework for reducing the noise level of brain PET images based on the combination of multi-scale transform (wavelet and curvelet) and tree clustering non-local means (TNLM). The main objective of the proposed method is to extract the isotropic features from a noisy smooth PET image using tree clustering based non-local means (TNLM). Then curvelet-based denoising is applied to the residual image to extract the anisotropic features such as edges and curves. Finally, the extracted anisotropic features are inserted back into the isotropic features to obtain an estimated denoised image. Simulated phantom and clinical PET datasets have been used in this proposed work for testing and measuring the performance in the medical applications, such as gray matter segmentation and precise tumor region identification without any interaction with other structural images like MRI or CT. The results in the experimental section show that the proposed denoising method has obtained better performance than existing wavelet, curvelet, wavelet-curvelet, non-local means (NLM) and deep learning methods based on the preservation of the edges. Qualitatively, a notable gain is achieved in the proposed denoised PET images in terms of contrast enhancement than other existing denoising methods.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessio AM, Kinahan PE (2006) Improved quantitation for pet/ct image reconstruction with system modeling and anatomical priors. Med Phys 33 (11):4095–4103
AlZubi S, Islam N, Abbod M (2011) Multiresolution analysis using wavelet, ridgelet, and curvelet transforms for medical image segmentation. J Biomed Imaging 2011:4
Bal A, Banerjee M, Chakrabarti A, Sharma P (2018) MRI brain tumor segmentation and analysis using rough-fuzzy C-Means and shape based properties. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences
Bal A, Banerjee M, Sharma P, Maitra M (2018) Brain tumor segmentation on MR image using k-means and fuzzy-possibilistic clustering. In: 2018 2nd international conference on electronics, materials engineering & Nano-Technology (IEMENTech), pp 1–8
Bal A, Banerjee M, Sharma P, Maitra M (2019) An efficient wavelet and curvelet-based pet image denoising technique. Med Biol Eng Comput 57 (12):2567–2598
Bal A, Banerjee M, Sharma P, Maitra M (2020) Gray matter segmentation and delineation from positron emission tomography (pet) image. In: Emerging technology in modelling and graphics. Springer, pp 359–372
Beghdadi A, Le Negrate A (1989) Contrast enhancement technique based on local detection of edges. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 46(2):162–174
Brox T, Kleinschmidt O, Cremers D (2008) Efficient nonlocal means for denoising of textural patterns. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(7):1083–1092
Buades A, Coll B, Morel J-M (2005) A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: 2005. CVPR 2005. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 2, IEEE, pp 60–65
Buades A, Coll B, Morel J-M (2005) A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one. Multiscale Model Simul 4(2):490–530
Cai TT, Silverman BW (2001) Incorporating information on neighbouring coefficients into wavelet estimation, sankhyā: The Indian Journal of Statistics Series B, pp 127–148
Candès EJ, Donoho DL (2004) New tight frames of curvelets and optimal representations of objects with piecewise c2 singularities. Commun Pure Appl Math 57(2):219–266
Candes E, Demanet L, Donoho D, Ying L (2006) Fast discrete curvelet transforms. Multiscale Model Simul 5(3):861–899
Chang SG, Yu B, Vetterli M (1998) Spatially adaptive wavelet thresholding with context modeling for image denoising. In: 1998. ICIP 98. Proceedings. 1998 International Conference on Image Processing, vol 1, IEEE, pp 535–539
Chang SG, Yu B, Vetterli M (2000) Adaptive wavelet thresholding for image denoising and compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(9):1532–1546
Chen G, Bui TD, Krzyzak A (2005) Image denoising using neighbouring wavelet coefficients. Integr Comput-Aided Eng 12(1):99–107
Christian BT, Vandehey NT, Floberg JM, Mistretta CA (2010) Dynamic pet denoising with hypr processing, Journal of nuclear medicine: official publication. Soc Nuclear Med 51(7):1147
Cui J, Gong K, Guo N, Wu C, Meng X, Kim K, Zheng K, Wu Z, Fu L, Xu B et al (2019) Pet image denoising using unsupervised deep learning. Eur J Nuclear Med Mol Imaging 46(13):2780–2789
Donoho DL, Johnstone IM (1994) Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage, biometrika, pp 425–455
Donoho DL (1995) De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 41(3):613–627
Dutta J, Leahy RM, Li Q (2013) Non-local means denoising of dynamic pet images. PloS one 8(12):e81390
Ellis S, Mallia A, McGinnity CJ, Cook GJ, Reader AJ (2018) Multitracer guided pet image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Rad Plasma Med Sci 2 (5):499–509
Gong K, Guan J, Liu C-C, Qi J (2018) Pet image denoising using a deep neural network through fine tuning. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci 3(2):153–161
Green GC (2005) Wavelet-based denoising of cardiac PET data. Carleton University
Huerga C, Castro P, Corredoira E, Coronado M, Delgado V, Guibelalde E (2017) Denoising of pet images by context modelling using local neighbourhood correlation. Phys Med Biol 62(2):633
Hyder SA, Sukanesh R (2011) An efficient algorithm for denoising mr and ct images using digital curvelet transform. In: Software Tools and Algorithms for Biological Systems. Springer, pp 471–480
Kekre H, Gharge S (2010) Texture based segmentation using statistical properties for mammographic images. Entropy 1:2
Kervrann C, Boulanger J, Coupé P (2007) Bayesian non-local means filter, image redundancy and adaptive dictionaries for noise removal. In: International conference on scale space and variational methods in computer vision. Springer, pp 520–532
Le Pogam A, Hanzouli H, Hatt M, Le Rest CC, Visvikis D (2013) Denoising of pet images by combining wavelets and curvelets for improved preservation of resolution and quantitation. Med Image Anal 17(8):877–891
Luisier F, Blu T, Unser M (2007) A new sure approach to image denoising: Interscale orthonormal wavelet thresholding. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(3):593–606
Mahmoudi M, Sapiro G (2005) Fast image and video denoising via nonlocal means of similar neighborhoods. IEEE Signal Process Lett 12(12):839–842
Maji P, Pal SK (2011) Rough-fuzzy pattern recognition: applications in bioinformatics and medical imaging, vol. 3. Wiley, New York
Mejia JM, Domínguez HdJO, Villegas OOV, Máynez LO, Mederos B (2014) Noise reduction in small-animal pet images using a multiresolution transform. IEEE Trans med Imaging 33(10):2010–2019
Mohideen SK, Perumal SA, Sathik MM (2008) Image de-noising using discrete wavelet transform. Int J Comput Sci Netw Secur 8(1):213–216
Mohl B, Wahlberg M, Madsen P (2003) Ideal spatial adaptation via wavelet shrinkage. J Acoust Soc Amer 114:1143–1154
Nguyen V-G, Lee S-J (2010) Nonlocal-means approaches to anatomy-based pet image reconstruction. In: 2010 IEEE Nuclear science symposium conference record (NSS/MIC). IEEE, pp 3273–3277
Om H, Biswas M (2012) An improved image denoising method based on wavelet thresholding. J Signal Inf Proces 3(01):109
Peter DJ, Govindan V, Mathew AT (2010) Nonlocal-means image denoising technique using robust m-estimator. J Comput Sci Technol 25(3):623–631
Qi J, Leahy RM (1999) A theoretical study of the contrast recovery and variance of map reconstructions from pet data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(4):293–305
Qi J, Leahy RM (2000) Resolution and noise properties of map reconstruction for fully 3-d pet. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19(5):493–506
RIDGELETS E (1998) Ridgelets: theory and applications, Ph.D. thesis, Ph. D. thesis, Stanford University, USA
Said AB, Hadjidj R, Melkemi KE, Foufou S (2016) Multispectral image denoising with optimized vector non-local mean filter. Digital Signal Process 58:115–126
Shalchian B, Rajabi H, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2009) Assessment of the wavelet transform in reduction of noise from simulated pet images. J Nuclear Med Technol 37(4):223–228
Shidahara M, Ikoma Y, Kershaw J, Kimura Y, Naganawa M, Watabe H (2007) Pet kinetic analysis: wavelet denoising of dynamic pet data with application to parametric imaging. Ann Nuclear Med 21(7):379–386
Shih Y-Y, Chen J-C, Liu R-S (2005) Development of wavelet de-noising technique for pet images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 29(4):297–304
Starck J-L, Candès EJ, Donoho DL (2002) The curvelet transform for image denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 11(6):670–684
Starck J-L, Murtagh F, Fadili JM (2010) Sparse image and signal processing: wavelets, curvelets, morphological diversity. Cambridge University Press
Taswell C (2000) The what, how, and why of wavelet shrinkage denoising. Comput Sci Eng 2(3):12–19
Turkheimer FE, Banati RB, Visvikis D, Aston JA, Gunn RN, Cunningham VJ (2000) Modeling dynamic pet-spect studies in the wavelet domain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 20(5):879–893
Wang G, Qi J (2014) Pet image reconstruction using kernel method. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(1):61–71
Wink AM, Roerdink JB (2004) Denoising functional mr images: a comparison of wavelet denoising and gaussian smoothing. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23 (3):374–387
Xu Z, Bagci U, Seidel J, Thomasson D, Solomon J, Mollura DJ (2014) Segmentation based denoising of pet images: An iterative approach via regional means and affinity propagation, in: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, pp 698–705
Yang H-Y, Wang X-Y, Wang Q-Y, Zhang X-J (2012) Ls-svm based image segmentation using color and texture information. J Vis Commun Image Represent 23(7):1095–1112
Acknowledgment
This research work was supported by the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences (BRNS), DAE, Government of India, under the Reference No. 34/14/13/2016-BRNS/34044. Sincere gratitude to Dr. Punit Sharma, MD at Apollo Gleneagles Hospital, Kolkata, India for providing the clinical PET brain datasets and valuable comments throughout this work. The authors would like to thank Dr. Haseeb Hassan, MD, DM at Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Kolkata, India, and Dr. Arindam Chatterjee, MD, at Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre (VECC), Kolkata, India for their helpful comments. The authors would like to thank the referees for providing their very valuable comments on the original version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, A., Banerjee, M., Chaki, R. et al. An efficient method for PET image denoising by combining multi-scale transform and non-local means. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 29087–29120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08936-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08936-0