Abstract
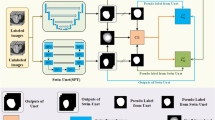
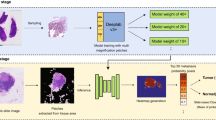
Due to the difficulty to accurately define the morphologies of Helicobacter Pylori (H. pylori) and the complexity of dealing with the whole slide images (WSIs), no computer-aided solution has currently been presented for detecting H. pylori infection in WSIs. We present the first image semantic segmentation solution for the computer-aided detection of H. pylori in WSIs. The solution only requires polygon annotations as weak supervision, which roughly, instead of pixel-level accurately, label the H. pylori infected areas in WSIs. We propose a new weakly supervised multi-task learning framework (WSMLF) that aims to improve the segmentation performance by more effectively exploiting the weak supervision. To make more effective usage of the weak supervision, we extract multiple inaccurate targets representing different modes of the true target from the available weak annotations. For improvement of the segmentation performance, we design a weakly supervised multi-task learning algorithm that can automatically learn from the weighted summarization of the extracted multiple inaccurate targets. These two advances constitute the resulting technique WSMLF. Introducing the proposed WSMLF to several common deep image semantic segmentation approaches for the detection of H. pylori in WSIs, we observe that WSMLF can enable these approaches to achieve more reasonable segmentation results, which eventually improve the detection performance of H. pylori by at most 6%. WSMLF provides new thoughts for more effectively employing weak supervision to achieve more effective results for image semantic segmentation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Kwak S (2018) Learning pixel-level semantic affinity with image-level supervision for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, In
Andermatt S, Pezold S, Cattin P (2016) Multi-dimensional gated recurrent units for the segmentation of biomedical 3D-data. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Pp 142–151
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:2481–2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Baxter J (1997) A Bayesian/information theoretic model of learning to learn via multiple task sampling. Mach Learn 28:7–39. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007327622663
Bell S, Upchurch P, Snavely N, Bala K (2015) Material recognition in the wild with the Materials in Context Database. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3479–3487
Bian X, Lim SN, Zhou N (2016) Multiscale fully convolutional network with application to industrial inspection. In: 2016 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 1–8
Bottou L (2010) Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In: proceedings of COMPSTAT’2010
Caruana RA (1993) Multitask learning: a knowledge-based source of inductive bias. In: machine learning proceedings 1993. Elsevier, pp 41–48
Caruana R (1997) Multitask Learning. Mach Learn 1:41–75. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007379606734
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, Atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40:834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Chen L-C, Zhu Y, Papandreou G et al (2018) Encoder-decoder with Atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science, In, pp 833–851
Cicek O, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS et al (2016) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention – MICCAI 2016. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Cutler AF, Havstad S, Ma CK, Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Schubert TT (1995) Accuracy of invasive and noninvasive tests to diagnose helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology 109:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(95)90278-3
Dolz J, Gopinath K, Yuan J, Lombaert H, Desrosiers C, Ben Ayed I (2019) HyperDense-net: a hyper-densely connected CNN for multi-modal image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38:1116–1126. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2878669
Drozdzal M, Vorontsov E, Chartrand G, et al (2016) The importance of skip connections in biomedical image segmentation. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Pp 179–187
Duchi J, Hazan E, Singer Y (2010) Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. In: COLT 2010 - the 23rd conference on learning theory
Duong L, Cohn T, Bird S, Cook P (2015) Low resource dependency parsing: cross-lingual parameter sharing in a neural network parser. In: Proceedings of the 53rd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th international joint conference on natural language processing (volume 2: short papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, pp 845–850
Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Sun G, Cheng M-M, Jianbing Shen LS (2020) Camouflaged object detection. CVPR, In
Ford AC, Forman D, Hunt R et al (2015) Helicobacter pylori eradication for the prevention of gastric neoplasia. In: Moayyedi P (ed) Cochrane database of systematic reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK
Foulds J, Frank E (2010) A review of multi-instance learning assumptions. In: A review of multi-instance learning assumptions. Knowl. Eng, Rev
Frénay B, Verleysen M (2014) Classification in the presence of label noise: a survey. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst 25:845–869. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2292894
Gao W, Wang L, Li YF, Zhou ZH (2016) Risk minimization in the presence of label noise. In: 30th AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI 2016
Garcia-Garcia A, Orts-Escolano S, Oprea S, Villena-Martinez V, Martinez-Gonzalez P, Garcia-Rodriguez J (2018) A survey on deep learning techniques for image and video semantic segmentation. Appl Soft Comput 70:41–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.05.018
Ghosh S, Das N, Das I, Maulik U (2019) Understanding deep learning techniques for image segmentation. ACM Comput Surv 52:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1145/3329784
Greenspan H, van Ginneken B, Summers RM (2016) Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2553401
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 770–778
Ishizawa T, Mitsuhashi Y, Sugiki H, Hashimoto H, Kondo S (1998) Basal cell carcinoma within vulvar Paget’s disease. Dermatology 197:388–390. https://doi.org/10.1159/000018039
Kingma DP, Ba JL (2015) Adam: a method for stochastic gradient descent. ICLR Int Conf Learn Represent
Korez R, Likar B, Pernuš F, Vrtovec T (2016) Model-based segmentation of vertebral bodies from MR images with 3D CNNs. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Pp 433–441
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, In, pp 1097–1105
Le TN, Nguyen TV, Nie Z et al (2019) Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput Vis Image Underst 184:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2019.04.006
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, van der Laak JAWM, van Ginneken B, Sánchez CI (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005
Liu Y, Cheng M-M, Fan D-P, et al (2018) Semantic edge detection with diverse deep supervision. arXiv.org
Mehta S, Rastegari M, Shapiro L, Hajishirzi H (2019) ESPNetv2: a light-weight, power efficient, and general purpose convolutional neural network. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, In
Mentis A, Lehours P, Mégraud F (2015) Epidemiology and diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 20:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12250
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S-A (2016) V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV). IEEE, pp 565–571
O’Connor A, O’Morain CA, Ford AC (2017) Population screening and treatment of helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.195
Pinheiro PO, Lin T-Y, Collobert R, Dollár P (2016) Learning to refine object segments. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Pp 75–91
Rajchl M, Lee MCH, Oktay O, Kamnitsas K, Passerat-Palmbach J, Bai W, Damodaram M, Rutherford MA, Hajnal JV, Kainz B, Rueckert D (2017) DeepCut: object segmentation from bounding box annotations using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36:674–683. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2621185
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Pp 234–241
Ruder S (2017) An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks. arXiv.org
Saha M, Chakraborty C (2018) Her2Net: a deep framework for semantic segmentation and classification of cell membranes and nuclei in breast Cancer evaluation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27:2189–2200. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2795742
Settles B (2010) Active learning literature survey. Mach Learn 10.1.1.167.4245
Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T (2017) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:640–651. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683
Shi M, Ferrari V (2016) Weakly supervised object localization using size estimates. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics)
Shichijo S, Hirata Y, Sakitani K, Yamamoto S, Serizawa T, Niikura R, Watabe H, Yoshida S, Yamada A, Yamaji Y, Ushiku T, Fukayama M, Koike K (2015) Distribution of intestinal metaplasia as a predictor of gastric cancer development. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 30:1260–1264. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12946
Shichijo S, Nomura S, Aoyama K, Nishikawa Y, Miura M, Shinagawa T, Takiyama H, Tanimoto T, Ishihara S, Matsuo K, Tada T (2017) Application of convolutional neural networks in the diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection based on endoscopic images. EBioMedicine 25:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.10.014
Shuai B, Zuo Z, Wang B, Wang G (2016) DAG-Recurrent Neural Networks for Scene Labeling. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3620–3629
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv.org
Singh SK, Dhawale CA, Misra S (2013) Survey of object detection methods in camouflaged image. IERI Procedia 4:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ieri.2013.11.050
Stenström B, Mendis A, Marshall B (2008) Helicobacter pylori: the latest in diagnosis and treatment. Aust Fam Physician 37:608–612
Szegedy C, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, et al (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1–9
Wang L, Hua G, Sukthankar R, Xue J, Niu Z, Zheng N (2017) Video object discovery and co-segmentation with extremely weak supervision. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:2074–2088. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2612187
Warthin AS, Starry AC (1922) The staining of spirochetes in cover-glass smears by the silver-agar method. J Infect Dis 30:592–600. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/30.6.592
Yang Y, Hospedales TM (2016) Trace norm regularised deep multi-task learning. arXiv.org
Yang Y, Chen N, Jiang S (2018) Collaborative strategy for visual object tracking. Multimed Tools Appl 77:7283–7303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4633-x
Yang M, Yu K, Zhang C et al (2018) DenseASPP for semantic segmentation in street scenes. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, In
Yang Y, Wu Y, Chen N (2019) Explorations on visual localization from active to passive. Multimed Tools Appl 78:2269–2309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6347-0
Yang Y, Lv H, Chen N et al (2020) FTBME: feature transferring based multi-model ensemble. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08746-4
Yu F, Koltun V (2015) Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv.org
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2014) Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. Proceedings of European conference on computer vision–ECCV 2014:818–833
Zhao B, Feng J, Wu X, Yan S (2017) A survey on deep learning-based fine-grained object classification and semantic segmentation. Int J Autom Comput 14:119–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-017-1053-3
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al (2017) Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 6230–6239
Zhao J, Liu JJ, Fan DP et al (2019) EGNet: edge guidance network for salient object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, In
Zhou Z-H (2018) A brief introduction to weakly supervised learning. Natl Sci Rev 5:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwx106
Zhou ZH (2018) A brief introduction to weakly supervised learning. In: A brief introduction to weakly supervised learning. Natl. Sci, Rev
Zhou S, Wu J-N, Wu Y, Zhou X (2015) Exploiting local structures with the Kronecker layer in convolutional networks. arXiv.org
Zhou X, Ito T, Takayama R, et al (2016) Three-dimensional CT image segmentation by combining 2D fully convolutional network with 3D majority voting. In: lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Pp 111–120
Zhu X (2006) Semi-supervised learning literature survey. Technical Report 1530, Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2020YFS0088); the 1·3·5 project for disciplines of excellence Clinical Research Incubation Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (2019HXFH036); the National Key Research and Development Program (2017YFC0113908), China; the Technological Innovation Project of Chengdu New Industrial Technology Research Institute (2017-CY02-00026-GX); and the West China Hospital, Sichuan University (139170022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yang, Y., Yuan, Y. et al. Detecting helicobacter pylori in whole slide images via weakly supervised multi-task learning. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 26787–26815 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09185-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09185-x