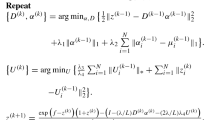Abstract
Reconstructing an original image from its corrupted observation is an important and fundamental problem in many image processing applications. Generally, the L1-norm or L2-norm combined with a regularization term (the total variation (TV), total generalized variation (TGV) or nuclear norm) is used to fit the impulse noise and Gaussian noise, respectively. However, these methods can only be used to remove a single type of noise from images, and traditional regularization terms often have difficulties in capturing some important prior knowledge of images, such as nonlocal self-similarity, low rank and sparsity. To overcome the above issues, we propose a mixed noise removal model with L1-L2 fidelity terms and a popular nonlocal low-rank regularization term, which has been shown to have more effective image denoising performance than traditional regularization methods. To solve this model, the split Bregman iteration method (SBIM) is adopted to decompose the difficult minimization optimization problem into four simple subproblems. Extensive experiments on natural images demonstrate that the effectiveness of the proposed method is better than that of other state-of-the-art methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiko R, Ikehara M (2019) Blind denoising of mixed gaussian-impulse noise by single cnn. In: ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp 1717–1721
Ahn B, Cho NI (2017) Block-matching convolutional neural network for image denoising, arXiv:1704.00524
Alkinani MH, El-Sakka MR (2017) Patch-based models and algorithms for image denoising: a comparative review between patch-based images denoising methods for additive noise reduction. EURASIP J Image Video Process 2017(1):1–27
Bovik AC (2010) Handbook of image and video processing. Academic press
Buades A, Coll B, Morel JM (2005) A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Bredies K, Kunisch K, Pock T (2010) Total generalized variation. SIAM J Imaging Sci 3(3):492–526
Burger HC, Schuler CJ, Harmeling S (2012) Image denoising with multi-layer perceptrons, part 1: comparison with existing algorithms and with bounds, arXiv:1211.1544
Cai J-F, Chan R, Nikolova M (2008) Two-phase approach for deblurring images corrupted by impulse plus gaussian noise. Inverse Probl Imaging 2 (2):187–204
Cai J-F, Candès EJ, Shen Z (2010) A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J Optim 20(4):1956–1982
Cai X, Chan R, Zeng T (2013) A two-stage image segmentation method using a convex variant of the mumford–shah model and thresholding. SIAM J Imaging Sci 6(1):368–390
Chambolle A (2004) An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications. J Math Imaging Vis 20(1-2):89–97
Chambolle A, Pock T (2011) A first-order primal-dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging. J Math Imaging Vis 40(1):120–145
Chatterjee P, Milanfar P (2009) Clustering-based denoising with locally learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(7):1438–1451
Deng L-J, Feng M, Tai X-C (2019) The fusion of panchromatic and multispectral remote sensing images via tensor-based sparse modeling and hyper-laplacian prior. Inf Fusion 52:76–89
Dong W, Xin L, Lei Z, Shi G (2011) Sparsity-based image denoising via dictionary learning and structural clustering. In: Computer vision & pattern recognition
Dong W, Zhang L, Shi G, Li X (2013) Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 22 (4):1620–1630
Dong W, Shi G, Li X, Ma Y, Huang F (2014) Compressive sensing via nonlocal low-rank regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(8):3618–3632
Duval V, Aujol J-F, Gousseau (2010) On the parameter choice for the non-local means
Eckart C, Young G (1936) The approximation of one matrix by another of lower rank. Psychometrika 1(3):211–218
Ferstl D, Reinbacher C, Ranftl R, Rüther M, Bischof H (2013) Image guided depth upsampling using anisotropic total generalized variation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 993–1000
Froment J (2014) Parameter-free fast pixelwise non-local means denoising. Image Process Line 4:300–326
Goldstein T, Osher S (2009) The split bregman method for l1-regularized problems. SIAM J Imaging Sci 2(2):323–343
He B, Yang H, Wang S (2000) Alternating direction method with self-adaptive penalty parameters for monotone variational inequalities. J Optim Theory Appl 106(2):337–356
He B, Tao M, Yuan X (2012) Alternating direction method with gaussian back substitution for separable convex programming. SIAM J Optim 22 (2):313–340
Hebert T, Leahy R (1989) A generalized em algorithm for 3-d bayesian reconstruction from poisson data using gibbs priors. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 8(2):194–202
Huang T, Dong W, Xie X, Shi G, Bai X (2017) Mixed noise removal via laplacian scale mixture modeling and nonlocal low-rank approximation. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3171–3186
Ji H, Huang S, Shen Z, Xu Y (2011) Robust video restoration by joint sparse and low rank matrix approximation. SIAM J Imaging Sci 4(4):1122–1142
Jia T, Shi Y, Zhu Y, Wang L (2016) An image restoration model combining mixed l1/l2 fidelity terms. J Vis Commun Image Represent 38:461–473
Jiang J, Zhang L, Yang J (2014) Mixed noise removal by weighted encoding with sparse nonlocal regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(6):2651–2662
Jiang J, Yang J, Cui Y, Luo L (2015) Mixed noise removal by weighted low rank model. Neurocomputing 151:817–826
Jung M (2015) Kang Simultaneous cartoon and texture image restoration with higher-order regularization. SIAM J Imaging Sci 8(1):721–756
Jung M (2017) Piecewise-smooth image segmentation models with [formula] data-fidelity terms. J Sci Comput 70(3):1229–1261
Jung M, Kang M (2015) Efficient nonsmooth nonconvex optimization for image restoration and segmentation. J Sci Comput 62(2):336–370
Knoll F, Bredies K, Pock T, Stollberger R (2011) Second order total generalized variation (tgv) for mri. Magn Reson Med 65(2):480–491
Kostadin D, Alessandro F, Vladimir K, Karen E (2007) Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(8):2080–2095
Lan X, Roth S, Huttenlocher D, Black MJ (2006) Efficient belief propagation with learned higher-order markov random fields. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 269–282
Liao X, Li K, Yin J (2017) Separable data hiding in encrypted image based on compressive sensing and discrete fourier transform. Multimed Tools Appl 76(20):20739–20753
Liao X, Yu Y, Li B, Li Z, Qin Z (2019) A new payload partition strategy in color image steganography. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
Mahmoudi M, Sapiro G (2005) Fast image and video denoising via nonlocal means of similar neighborhoods. IEEE Signal Process Lett 12(12):839–842
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G, Zisserman A (2010) Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision
Michael E, Michal A (2006) Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Tip 15(12):3736–3745
Milovic C, Bilgic B, Zhao B, Acosta-Cabronero J, Tejos C (2018) Fast nonlinear susceptibility inversion with variational regularization. Magn Reson Med 80(2):814–821
Mohan J, Krishnaveni V, Guo Y (2014) A survey on the magnetic resonance image denoising methods. Biomed Signal Processing Control 9:56–69
Osher S, Wang B, Yin P, Luo X, Barekat F, Pham M, Lin A (2018) Laplacian smoothing gradient descent, arXiv:1806.06317
Qin Z, Goldfarb D, Ma S (2015) An alternating direction method for total variation denoising. Optim Methods Softw 30(3):594–615
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E (1992) Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena 60(1-4):259–268
Srebro N, Jaakkola T (2003) Weighted low-rank approximations. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03), pp 720–727
Tihonov AN (1963) Solution of incorrectly formulated problems and the regularization method. Sov Math 4:1035–1038
Wang Y, Yang J, Yin W, Zhang Y (2008) A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction. SIAM J Imaging Sci 1 (3):248–272
Wang F, Huang H, Liu J (2019) Variational based mixed noise removal with cnn deep learning regularization. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
Weisheng D, Guangming S, Xin L (2013) Nonlocal image restoration with bilateral variance estimation: a low-rank approach. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(2):700–711
Xiao Y, Zeng T, Yu J, Ng MK (2011) Restoration of images corrupted by mixed gaussian-impulse noise via l1–l0 minimization. Pattern Recogn 44 (8):1708–1720
Xie Y, Gu S, Liu Y, Zuo W, Zhang W, Zhang L (2016) Weighted schatten p-norm minimization for image denoising and background subtraction. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(10):4842–4857
Xiong B, Yin Z (2011) A universal denoising framework with a new impulse detector and nonlocal means. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(4):1663–1675
Yan M (2013) Restoration of images corrupted by impulse noise and mixed gaussian impulse noise using blind inpainting. SIAM J Imaging Sci 6(3):1227–1245
Yang Y, Sun J, Li H, Xu Z (2017) Admm-net: A deep learning approach for compressive sensing mri. corr, arXiv:1705.06869
Yang J, Zhang Y, Yin W (2009) An efficient tvl1 algorithm for deblurring multichannel images corrupted by impulsive noise. SIAM J Sci Comput 31(4):2842–2865
Zhang Y (2010) An alternating direction algorithm for nonnegative matrix factorization, Technical Report
Zhang D, Hu Y, Ye J, Li X, He X (2012) Matrix completion by truncated nuclear norm regularization. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 2192–2199
Zhang K, Zuo W, Chen Y, Meng D, Zhang L (2017) Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3142–3155
Zhang K, Zuo W, Gu S, Zhang L (2017) Learning deep cnn denoiser prior for image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3929–3938
Zhou T, Bhaskar H, Liu F, Yang J, Cai P (2017) Online learning and joint optimization of combined spatial-temporal models for robust visual tracking. Neurocomputing 226:221–237
Zhou W, Zhang Y, Liu Y (2017) Matrix-value linear regression for image denoising. DEStech Transactions on Computer Science and Engineering, no. mmsta
Zhou T, Liu F, Bhaskar H, Yang J (2018) Robust visual tracking via online discriminative and low-rank dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 48 (9):2643–2655
Zhou T, Thung K-H, Liu M, Shen D (2019) Brain-wide genome-wide association study for alzheimer’s disease via joint projection learning and sparse regression model. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 66(1):165–175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: Demo parameters selection process for GN0.01 noise removal
Appendix: Demo parameters selection process for GN0.01 noise removal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Li, C. A mixed model with multi-fidelity terms and nonlocal low rank regularization for natural image noise removal. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 33043–33069 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09565-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09565-3