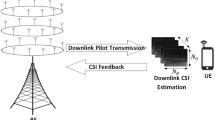
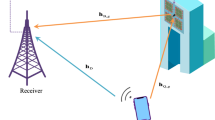
Abstract
Imperfect channel state information (CSI) may seriously worsen the system performance for classical MIMO communications. In order to overcome the impacts of imperfect CSI for Internet of things, we propose a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) based MIMO detection algorithm, where the DCNN is trained offline and works online to refine the imperfect CSI and improve the bit error rate of the wireless systems. Two types of learning based detectors, i.e., with or without accurate CSI, are proposed in this paper to reduce the detrimental effects of imperfect CSI. The impacts of the important system parameters, such as normalized Doppler frequency and the correlation factor are evaluated in different setup scenarios. Simulation results suggest that, compared with the classical maximum likelihood detector, the proposed learning based detectors shows considerable gains.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, Brevdo E, Chen Z, Citro C, Corrado GS, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M, Ghemawat S, Goodfellow I, Harp A, Irving G, Isard M, Jia Y, Jozefowicz R, Kaiser L, Kudlur M, Levenberg J, Mané D., Monga R, Moore S, Murray D, Olah C, Schuster M, Shlens J, Steiner B, Sutskever I, Talwar K, Tucker P, Vanhoucke V, Vasudevan V, Viégas F., Vinyals O, Warden P, Wattenberg M, Wicke M, Yu Y, Zheng X (2015) TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems. http://tensorflow.org/. Software available from tensorflow.org
Aquilina P, Ratnarajah T (2015) Performance analysis of ia techniques in the mimo ibc with imperfect csi. IEEE Trans Commun 63(4):1259–1270. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2408336
Chen C, Zhong W, Yang H, Du P (2018) On the performance of mimo-noma-based visible light communication systems. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 30(4):307–310. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2017.2785964
Chen J, Si J, Li Z, Huang H (2012) On the performance of spectrum sharing cognitive relay networks with imperfect csi. IEEE Commun Lett 16(7):1002–1005. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2012.042512.120100
Chen Z, Sohrabi F, Yu W (2019) Multi-cell sparse activity detection for massive random access: Massive mimo versus cooperative mimo. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 18(8):4060–4074. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2019.2920823
Deng D, Fan L, Lei X, Tan W, Xie D (2017) Joint user and relay selection for cooperative noma networks. IEEE Access 5:20220–20227
Deng D, Fan L, Zhao R, Hu RQ (2016) Secure communications in multiple amplify-and-forward relay networks with outdated channel state information. Trans Emerg Telecommun Technol 27(4):494–503
Deng D, Li X, Zhao M, Rabie KM, Kharel R (2020) Deep learning-based secure MIMO communications with imperfect CSI for heterogeneous networks. Sensors 20(6):1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061730
Fan L, Lei X, Fan P, Hu R (2012) Outage probability analysis and power allocation for two-way relay networks with user selection and outdated channel state information. Communications Letters, IEEE 16(5):638–641
Farrag S, Alexan W (2020) Secure 3d data hiding technique based on a mesh traversal algorithm. Multimedia Tools and Applications pp(99):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09437-w
Feng C, Jing Y, Jin S (2016) Interference and outage probability analysis for massive mimo downlink with mf precoding. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23 (3):366–370. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2015.2511630
Gao H, Su Y, Zhang S, Diao M (2019) Antenna selection and power allocation design for 5g massive mimo uplink networks. China Communications 16 (4):1–15
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A (2016) Deep learning. MIT Press, Cambridge. http://www.deeplearningbook.org
Gradshteyn I, Ryzhik I (2007) Table of integrals, series, and products, 7 edn. Academic Press, Elsevier Inc, San Diego, California 92101-4495, USA
He Q, Wang Z, Hu J, Blum RS (2019) Performance gains from cooperative mimo radar and mimo communication systems. IEEE Signal Process Lett 26(1):194–198. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2018.2880836
Lee H, Lee SH, Quek TQS (2019) Deep learning for distributed optimization: Applications to wireless resource management. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 37(10):2251–2266. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933890
Li L, et al. (2020) A unified framework for hs-uav noma networks: Performance analysis and location optimization. IEEE Wireless Commun Lett 99(1). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2964730
Li L, Li J, Li L (2020) Performance analysis of impaired swipt noma relaying networks over imperfect weibull channels. IEEE Syst J 99(1):680–695. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2019.2919654
Li L, Li J, Liu Y, Ding Z, Nallanathan A (2020) Residual transceiver hardware impairments on cooperative noma networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 19(1):680–695
Li L, Liu M, Deng C (2020) Full-duplex cooperative noma relaying systems with i/q imbalance and imperfect sic. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 9(1):17–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2019.2919654
Li Y, Hu X, Zhuang Y, Gao Z, Zhang P, El-Sheimy N (2019) Deep reinforcement learning (drl): Another perspective for unsupervised wireless localization. IEEE Internet of Things J, 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2957778
Liu S, Liu Z, Sun D, Yang H, Yi K, Wang K (2018) On the performance of wireless-powered cooperative df relaying networks with imperfect csi. China Communications 15(11):79–92. https://doi.org/10.1109/CC.2018.8543051
jian Luo T (2020) High-resolution sar images segmentation using nsct denoising and qiga based parameters selection of pcnn model. Multimed Tools Appl pp(99):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09536-8
Mao Q, Hu F, Hao Q (2018) Deep learning for intelligent wireless networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials 20 (4):2595–2621. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2846401
Michalopoulos DS, Suraweera HA, Karagiannidis GK, Schober R (2012) Amplify-and-forward relay selection with outdated channel estimates. IEEE Trans Commun 60(5):1278–1290
Ming Z, Zhou S, Zhou W, Zhu J (2017) An improved uplink sparse coded multiple access. IEEE Commun Lett 21(1):176–179
O’Shea TJ, Corgan J, Clancy TC Jayne C, Iliadis L (eds) (2016) Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Otoum S, Kantarci B, Mouftah HT (2019) On the feasibility of deep learning in sensor network intrusion detection. IEEE Netw Lett 1(2):68–71. https://doi.org/10.1109/LNET.2019.2901792
Pan C, Ren H, Wang K, Xu W, Elkashlan M, Nallanathan A, Hanzo L (2020) Multicell mimo communications relying on intelligent reflecting surfaces. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun pp(pp):1–12
Qiu S, Chen D, Qu D, Luo K, Jiang T (2018) Downlink precoding with mixed statistical and imperfect instantaneous csi for massive mimo systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(4):3028–3041. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2017.2774836
Simon MK, Alouini MS (2005) Digital communication over fading channels, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Su Y, Lu X, Zhao Y, Huang L, Du X (2019) Cooperative communications with relay selection based on deep reinforcement learning in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors J 19(20):9561–9569. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2925719
Van Luong T, Ko Y (2017) A tight bound on ber of mcik-ofdm with greedy detection and imperfect csi. IEEE Commun Lett 21(12):2594–2597. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2747549
Wang Y, Zhao M, Deng D, Zhou S, Zhou W (2018) Fractional sparse code multiple access and its optimization. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 7 (6):990–993
Ye H, Li GY, Juang B (2018) Power of deep learning for channel estimation and signal detection in ofdm systems. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 7(1):114–117. https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2017.2757490
Zhu J, Gong C, Zhang S, Zhao M, Zhou W (2018) Foundation study on wireless big data: Concept, mining, learning and practices. China Ccommunications 15(12):1–15
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province with grant number 2018A030313736, Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Guangdong with grant number 2019GZDXM002, Application Technology Collaborative Innovation Center of GZPYP with grant number 2020ZX01, Yangcheng scholar, scientific research project of Guangzhou Education Bureau with grant number 202032761, Project of Technology Development Foundation of Guangdong with grant number 706049150203, the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant 62001320, Key Scientific Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province Grant 20A510007, the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province under Grant 2020JQ-844, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province under Grant NSFRF180309, the Key Research and Development Program of Shanxi under Grant 201903D121117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, D., Li, X. & Menon, V.G. Learning based MIMO communications with imperfect channel state information for Internet of Things. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 31265–31276 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10387-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10387-6