Abstract
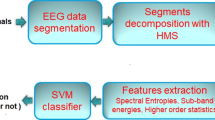
The detection of epileptic seizures by classifying electroencephalography (EEG) signals into ictal and interictal classes is a demanding challenge, because it identifies the seizure and seizure-free states of an epileptic patient. In previous works, several machine learning-based strategies were introduced to investigate and interpret EEG signals for the purpose of their accurate classification. However, non-linear and non-stationary characteristics of EEG signals make it complicated to get complete information about these dynamic biomedical signals. In order to address this issue, this paper focuses on extracting the most discriminating and distinguishing features of seizure EEG recordings to develop an approach that employs both fuzzy-based and traditional machine learning algorithms for epileptic seizure detection. The proposed framework classifies unknown EEG signal segments into ictal and interictal classes. The model is validated using empirical evaluation on two benchmark datasets, namely the Bonn and Children’s Hospital of Boston-Massachusetts Institute of Technology (CHB-MIT) datasets. The obtained results show that in both cases, K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) and Fuzzy Rough Nearest Neighbor (FRNN) give the highest classification accuracy scores, with improved sensitivity and specificity percentages.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrzejak RG, Lehnertz K, Mormann F, Rieke C, David P, Elger CE (2001) Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys Rev E 64:061907
Anugraha A, Vinotha E, Anusha R, Giridhar S, Narasimhan K (2017) A machine learning application for epileptic seizure detection. ICCIDS 2017: IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Data Science, Chennai, pp 1–4
Arunkumar N, Ramkumar K, Venkatraman V, Abdulhay E, Fernandes SL, Kadry S et al (2017) Classification of focal and non focal EEG using entropies. Pattern Recogn Lett 94:112–117
Atal DK, Singh M (2019) A hybrid feature extraction and machine learning approaches for epileptic seizure detection. Multidim Syst Sign Process:1–23
Bhattacharyya A, Pachori RB (2017) A multivariate approach for patient-specific EEG seizure detection using empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64:2003–2015
Bongiorni L, Balbinot A (2020) Evaluation of recurrent neural networks as epileptic seizure predictor. Array, 100038.
Boughorbel S, Jarray F, El-Anbari M (2017) Optimal classifier for imbalanced data using Matthews correlation coefficient metric. PLoS One 12:e0177678
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Derrac J, Garcia S, Herrera F (2014) Fuzzy nearest neighbor algorithms: taxonomy, experimental analysis and prospects. Inform Sciences 260:98–119
Feng Y, You H, Zhang Z, Ji R, Gao Y (2019) Hypergraph neural networks. Proc AAAI Conf Artificial Intell 33:3558–3565
Goldberger, A. L.; Amaral, L. A.; Glass, L; Hausdorff, J. M.; Ivanov, P. C.; Mark, R. G.; et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215-e220.
Gu Y, Cleeren E, Dan J, Claes K, Van Paesschen W, Van Huffel S et al (2018) Comparison between scalp EEG and behind-the-ear EEG for development of a wearable seizure detection system for patients with focal epilepsy. Sensors 18:29–46
Gupta V, Pachori RB (2019) Epileptic seizure identification using entropy of FBSE based EEG rhythms. Biomed Signal Process Control 53:101569
Han J; Pei J; Kamber M (2012) Data mining: concepts and techniques, 3rd ed.; Elsevier
Hühn J, Hüllermeier E (2009) FURIA: an algorithm for unordered fuzzy rule induction. Data Min Knowl Discov 19:293–319
Jana GC, Sharma R, Agrawal A (2020) A 1D-CNN-spectrogram based approach for seizure detection from EEG signal. Procedia Comput Sci 167:403–412
Jensen R, Cornelis C (2011) Fuzzy-rough nearest neighbour classification and prediction. Theor Comput Sci 412:5871–5884
Kaburlasos VG, Athanasiadis IN, Mitkas PA (2007) Fuzzy lattice reasoning (FLR) classifier and its application for ambient ozone estimation. Int J Approx Reason 45:152–188
Khan MA, Rubab S, Kashif A, Sharif MI, Muhammad N, Shah JH, Zhang YD, Satapathy SC (2020) Lungs cancer classification from CT images: an integrated design of contrast based classical features fusion and selection. Pattern Recogn Lett 129:77–85
Li M, Chen W, Zhang T (2017) Classification of epilepsy EEG signals using DWT-based envelope analysis and neural network ensemble. Biomed Signal Process Control 31:357–365
Li M, Chen W, Zhang T (2017) Automatic epileptic EEG detection using DT-CWT-based non-linear features. Biomed Signal Process Control 34:114–125
Mahjoub C, Jeannès RLB, Lajnef T, Kachouri A (2020) Epileptic seizure detection on EEG signals using machine learning techniques and advanced preprocessing methods. Biomed Eng/Biomedizinische Technik 65:33–50
Mursalin M, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Chawla NV (2017) Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier. Neurocomputing 241:204–214
Naz I, Muhammad N, Yasmin M, Sharif M, Shah JH, Fernandes SL (2019) Robust discrimination of leukocytes protuberant types for early diagnosis of leukemia. J Mech Med Biol 19:1950055
Olokodana I, Mohanty S; Kougianos E (2020) Distributed Kriging-Bootstrapped DNN Model for Fast, Accurate Seizure Detection from EEG Signals. In ISVLSI 2020: IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, pp. 264–269
Orhan U, Hekim M, Ozer M (2011) Signals classification using the K-means clustering and a multilayer perceptron neural network model. Expert Syst Appl 38:13475–13481
Orosco L, Correa AG, Diez P, Laciar E (2016) Patient non-specific algorithm for seizures detection in scalp EEG. Comput Biol Med 71:128–134
Park C, Choi G, Kim J, Kim S, Kim TJ, Min K, Jung KY, Chong J (2018) Epileptic seizure detection for multi-channel EEG with deep convolutional neural network. In ICEIC 2018: IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication, pp. 1–5
Patidar S, Panigrahi T (2017) Detection of epileptic seizure using Kraskov entropy applied on tunable-Q wavelet transform of EEG signals. Biomed Signal Process Control 34:74–80
Riaz F, Hassan A, Rehman S, Niazi IK, Dremstrup K (2016) EMD-based temporal and spectral features for the classification of EEG signals using supervised learning. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 24:28–35
Sarkar M (2007) Fuzzy-rough nearest neighbor algorithms in classification. Fuzzy Sets Syst 158:2134–2152
Sharif M, Amin J, Nisar MW, Anjum MA, Muhammad N, Shad SA (2020) A unified patch based method for brain tumor detection using features fusion. Cogn Syst Res 59:273–286
Shukla KK, Tiwari AK (2013) Efficient algorithms for discrete wavelet transform: with applications to denoising and fuzzy inference systems, Springer Science & Business Media
Subasi A, Kevric J, Canbaz MA (2019) Epileptic seizure detection using hybrid machine learning methods. Neural Comput Appl 31:317–325
Subramanian R, Wache J, Abadi MK, Vieriu RL, Winkler S, Sebe N (2018) ASCERTAIN: emotion and personality recognition using commercial sensors. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 9:147–160
Tiwari AK, Pachori RB, Kanhangad V, Panigrahi BK (2017) Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using key-point-based local binary pattern of EEG signals. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21:888–896
Ullah I, Hussain M, Aboalsamh H (2018) An automated system for epilepsy detection using EEG brain signals based on deep learning approach. Expert Syst Appl 107:61–71
Vapnik V (2013) The nature of statistical learning theory, Springer science & business media
Vidyaratne LS, Iftekharuddin KM (2017) Real-time epileptic seizure detection using EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 25:2146–2156
Wang Y, Li Z, Feng L, Zheng C, Zhang W (2017) Automatic detection of epilepsy and seizure using multiclass sparse extreme learning machine classification. Comput Math Methods Med 2017:6849360
Wang X, Gong G, Li N (2019) Automated recognition of epileptic EEG states using a combination of symlet wavelet processing, gradient boosting machine, and grid search optimizer. Sensors 19:219
Yadati N, Nimishakavi M, Yadav P,Nitin V, Louis A, Talukdar P (2019) Hypergcn: A new method for training graph convolutional networks on hypergraphs. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1511–1522
Yuan Q, Zhou W, Zhang L, Zhang F, Xu F, Leng Y (2017) Epileptic seizure detection based on imbalanced classification and wavelet packet transform. Seizure 50:99–108
Zhang T, Chen W (2017) LMD based features for the automatic seizure detection of EEG signals using SVM. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 25:1100–1108
Zhang Y, Yang S, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Han B, Zhou F (2018) Integration of 24 feature types to accurately detect and predict seizures using scalp EEG signals. Sensors 18:1372
Zhao S, Gholaminejad A, Ding G, Gao Y, Han J, Keutzer K (2019) Personalized emotion recognition by personality-aware high-order learning of physiological signals. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl (TOMM) 15:1–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aaeysha: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, review & editing. M. Bilal Qureshi: Supervsion, Review & editing. M. Afzaal: Data curation, validation, Software. M. Shuaib Qureshi: Formal analysis. M. Fayaz: Writing – review & editing, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest among authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aayesha, Qureshi, M.B., Afzaal, M. et al. Machine learning-based EEG signals classification model for epileptic seizure detection. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 17849–17877 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10597-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10597-6