Abstract
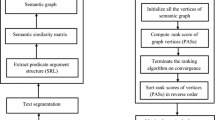
Text summarization presents several challenges such as considering semantic relationships among words, dealing with redundancy and information diversity issues. Seeking to overcome these problems, we propose in this paper a new graph-based Arabic summarization system that combines statistical and semantic analysis. The proposed approach utilizes ontology hierarchical structure and relations to provide a more accurate similarity measurement between terms in order to improve the quality of the summary. The proposed method is based on a two-dimensional graph model that makes uses statistical and semantic similarities. The statistical similarity is based on the content overlap between two sentences, while the semantic similarity is computed using the semantic information extracted from a lexical database whose use enables our system to apply reasoning by measuring semantic distance between real human concepts. The weighted ranking algorithm PageRank is performed on the graph to produce significant score for all document sentences. The score of each sentence is performed by adding other statistical features. In addition, we address redundancy and information diversity issues by using an adapted version of Maximal Marginal Relevance method. Experimental results on EASC and our own datasets showed the effectiveness of our proposed approach over existing summarization systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsharizadeh M, Ebrahimpour-Komleh H, Bagheri A (2018) Query-oriented text summarization using sentence extraction technique. 2018 4th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR). https://doi.org/10.1109/icwr.2018.8387248
Alami N, Meknassi M, Alaoui Ouatik S, Ennahnahi N (2015) Arabic text summarization based on graph theory. In: 2015 IEEE/ACS 12th International Conference of Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Marrakech, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/aiccsa.2015.7507254
Alami N, En-nahnahi N, Ouatik SA, Meknassi M (2018) Using unsupervised deep learning for automatic summarization of Arabic documents. Arab J Sci Eng 43(12):7803–7815
Alami N, Meknassi M, En-nahnahi N (2019) Enhancing unsupervised neural networks based text summarization with word embedding and ensemble learning. Expert Syst Appl 123:195–211
Alguliyev RM, Aliguliyev RM, Isazade NR (2015) An unsupervised approach to generating generic summaries of documents. Appl Soft Comput 34:236–250
Al-Radaideh QA, Bataineh DQ (2018) A hybrid approach for Arabic text summarization using domain knowledge and genetic algorithms. Cogn Comput 10(4):651–669
Baralis E, Cagliero L, Mahoto N, Fiori A (2013) GRAPHSUM : discovering correlations among multiple terms for graph-based summarization. Inf Sci 249:96–109
Baruah N, Sarma SK, Borkotokey S (2019) A novel approach of text summarization using Assamese WordNet. 2019 4th international conference on information systems and computer networks (ISCON). https://doi.org/10.1109/iscon47742.2019.9036285
Boudchiche M, Mazroui A, Ould Abdallahi Ould Bebah M, Lakhouaja A, Boudlal A (2017) AlKhalil Morpho sys 2: a robust Arabic morpho-syntactic analyzer. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences 29(2):141–146
Brin S, Page L (1998) The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual web search engine. Computer Networks and ISDN Systems 30(1):107–117
Carbonell J, Goldstein J (1998) The use of MMR, diversity-based re-ranking for reordering documents and producing summaries. In: Proceedings of SIGIR 1998. Melbourne, Australia, pp 335–336
Chennoufi A, Mazroui A (2017) Morphological, syntactic and diacritics rules for automatic diacritization of Arabic sentences. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences 29(2):156–163
Dhungana UR, Shakya S, Baral K, Sharma B (2015) Word sense disambiguation using WSD specific WordNet of polysemy words. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 9th international conference on semantic computing (IEEE ICSC 2015). Anaheim, CA, pp 148–152. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOSC.2015.7050794
Douzidia FS, Lapalme G (2004) Lakhas, an Arabic summarization system. In: Proc. of 2004 Doc. Understanding Conf. (DUC2004), Boston, MA
Edmundson HP (1969) New methods in automatic extracting. J ACM 16(2):264–285
Elbarougy R, Behery G, El Khatib A (2020) Extractive Arabic text summarization using modified PageRank algorithm. Egyptian Informatics Journal 21(2):73–81
Elberrichi Z, Abidi K (2012) Arabic text categorization: a comparative study of different representation modes. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology 9:465–470
El-Fishawy N, Hamouda A, Attiya GM, Atef M (2014) Arabic summarization in twitter social network. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 5(2):411–420
El-Haj M, Kruschwitz U, Fox C (2010) Using mechanical turk to create a corpus of arabic summaries. In: proceedings of the 7th international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC), Valletta, Malta, pp 36–39, in the language resources (LRs) and human language technologies (HLT) for Semitic languages workshop.
El-Haj M, Kruschwitz U, Fox C (2011) Experimenting with automatic text summarisation for Arabic. In: Vetulani Z (ed) Human language technology. Challenges for Computer Science and Linguistics, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 490–499
El-Kassas WS, Salama CR, Rafea AA, Mohamed HK (2020) EdgeSumm: graph-based framework for automatic text summarization. Inf Process Manag 57(6):102264
El-Kassas WS, Salama CR, Rafea AA, Mohamed HK (2021) Automatic text summarization: a comprehensive survey. Expert Syst Appl 165:113679
Erkan G, Radev DR (2004) LexRank: graph-based lexical centrality as salience in text summarization. J Artif Intell Res 22:457–479
Estiri A, Kahani M, Ghaemi H, Abasi M (2014) Improvement of an abstractive summarization evaluation tool using lexical-semantic relations and weighted syntax tags in Farsi language. In: 2014 Iranian Conference on Intelligent Systems (ICIS). Bam 2014:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/iraniancis.2014.6802594
Fang H, Lu W, Wu F, Zhang Y, Shang X, Shao J, Zhuang Y (2015) Topic aspect-oriented summarization via group selection. Neurocomputing 149:1613–1619
Fattah MA (2014) A hybrid machine learning model for multi-document summarization. Appl Intell 40(4):592–600
Fattah MA, Ren F (2009) GA, MR, FFNN, PNN and GMM based models for automatic text summarization. Comput Speech Lang 23(1):126–144
Ferreira R, de Souza CL, Freitas F, Lins RD, de Frana SG, Simske SJ, Favaro L (2014) A multi-document summarization system based on statistics and linguistic treatment. Expert Syst Appl 41(13):5780–5787
Gao JB, Zhang BW, Chen XH (2015) A WordNet-based semantic similarity measurement combining edge-counting and information content theory. Eng Appl Artif Intell 39:80–88
Gao Z, Xu C, Zhang H, Li S, de Albuquerque VHC (2020) Trustful internet of surveillance things based on deeply represented visual co-saliency detection. IEEE Internet Things J 7(5):4092–4100
Gao Z, Zhang H, Dong S, Sun S, Wang X, Yang G, Wu W, Li S, de Albuquerque VHC (2020) Salient object detection in the distributed cloud-edge intelligent network. IEEE Netw 34(2):216–224
Habash NY (2010) Introduction to Arabic natural language processing. Synthesis Lectures on Human Language Technologies 3:1–187
Heu JU, Qasim I, Lee DH (2015) FoDoSu: multi-document summarization exploiting semantic analysis based on social folksonomy. Inf Process Manag 51(1):212–225
Hovy EH (2005) Automated text summarization. In: Mitkov R (ed) The Oxford handbook of computational linguistics. Oxford Univ, Press, pp 583–598
Ibrahim A, Elghazaly T (2013) Rhetorical representation and vector representation in summarizing arabic text. Natural language processing and information systems, lecture notes in computer science, vol 7934 pp 421–424. Springer, Berlin
Kang B, Nguyen TQ (2019) Random Forest with learned representations for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(7):3542–3555
Khoja S (1999) Stemming Arabic Text. http://zeus.cs.pacificu.edu/shereen/research.htm
Khoja S (2001) APT: Arabic part-of-speech tagger. In: Proceedings of the student workshop at the second meeting of the north American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL2001). Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, pp 20–25
Lin CY (2004) ROUGE: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. Proceedings of workshop on text summarization branches out, post-conference workshop of ACL, In, pp 74–81
Luhn HP (1958) The automatic creation of literature abstracts. IBM J Res Dev 2(2):159–165
Malik R, Subramaniam V, Kaushik S (2007) Automatically selecting answer templates to respond to customer emails. In: Proceedings of the 20th international joint conference on Artifical intelligence. Hyderabad, India, pp 1659–1664
Mani I, Maybury MT (1999) Advances in automatic summarization. MIT Press, Cambridege, MA
Mihalcea R, Tarau P (2004) TextRank: bringing order into texts. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing 2004. Barcelona, Spain, pp 404–411
Miller GA (1995) WordNet: a lexical database for English. Commun ACM 38(11):39–41
Mohamed M, Oussalah M (2019) SRL-ESA-TextSum: a text summarization approach based on semantic role labeling and explicit semantic analysis. Inf Process Manag 56(4):1356–1372
Nguyen-Hoang TA, Nguyen K, Tran QV (2012) TSGVi: a graph-based summarization system for Vietnamese documents. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 3:305–313
Oufaida H, Nouali O, Blache P (2014) Minimum redundancy and maximum relevance for single and multidocument arabic text summarization. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences 26(4):450–461
Pal AR, Saha D (2014) An approach to automatic text summarization using WordNet. In: 2014 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), Gurgaon, pp 1169-1173. https://doi.org/10.1109/iadcc.2014.6779492
Patel D, Shah S, Chhinkaniwala H (2019) Fuzzy logic based multi document summarization with improved sentence scoring and redundancy removal technique. Expert Syst Appl 134:167–177
Patil AP, Dalmia S, Abu Ayub Ansari S, Aul T, Bhatnagar V (2014) Automatic text summarizer. In: In: 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), New Delhi, pp 1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2014.6968629
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238
Rani R, Lobiyal DK (2020) An extractive text summarization approach using tagged-LDA based topic modeling. Multimed Tools Appl 80:3275–3305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09549-3
Rinaldi AM, Russo C (2020) Using a multimedia semantic graph for web document visualization and summarization. Multimed Tools Appl 80:3885–3925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09761-1
Shaheen M, Ezzeldin AM (2014) Arabic question answering: systems, resources, tools, and future trends. Arab J Sci Eng 39(6):4541–4564
Song S, Huang H, Ruan T (2018) Abstractive text summarization using LSTM-CNN based deep learning. Multimed Tools Appl 78(1):857–875
Wei TT, Lu YH, Chang HY, Zhou Q, Bao XY (2015) A semantic approach for text clustering using WordNet and lexical chains. Expert Syst Appl 42(4):2264–2275
Wu Z, Palmer M (1994) Verbs semantics and lexical selection. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.3115/981732.981751
Wu Z, Lei L, Li G, Huang H, Zheng C, Chen E, Xu G (2017) A topic modeling based approach to novel document automatic summarization. Expert Syst Appl 84:12–23
Yang K, He H, Al-Sabahi K, Zhang Z (2019) EcForest: extractive document summarization through enhanced sentence embedding and cascade forest. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 31:e5206. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5206
Yousefi-Azar M, Hamey L (2017) Text summarization using unsupervised deep learning. Expert Syst Appl 68:93–105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alami, N., Mallahi, M.E., Amakdouf, H. et al. Hybrid method for text summarization based on statistical and semantic treatment. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 19567–19600 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10613-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10613-9