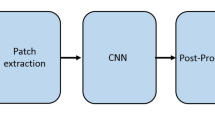
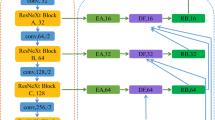
Abstract
The variations among shapes, sizes, and locations of tumors are obstacles for accurate automatic segmentation. U-Net is a simplified approach for automatic segmentation. Generally, the convolutional or the dilated convolutional layers are used for brain tumor segmentation. However, existing segmentation methods of the significant dilation rates degrade the final accuracy. Moreover, tuning parameters and imbalance ratio between the different tumor classes are the issues for segmentation. The proposed model, known as Residual-Dilated Dense Atrous-Spatial Pyramid Pooling (RD2A) 3D U-Net, is found adequate to solve these issues. The RD2A is the combination of the residual connections, dilation, and dense ASPP to preserve more contextual information of small sizes of tumors at each level encoder path. The multi-scale contextual information minimizes the ambiguities among the tissues of the white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) of the infant’s brain MRI. The BRATS 2018, BRATS 2019, and iSeg-2019 datasets are used on different evaluation metrics to validate the RD2A. In the BRATS 2018 validation dataset, the proposed model achieves the average dice scores of 90.88, 84.46, and 78.18 for the whole tumor, the tumor core, and the enhancing tumor, respectively. We also evaluated on iSeg-2019 testing set, where the proposed approach achieves the average dice scores of 79.804, 77.925, and 80.569 for the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the gray matter (GM), and the white matter (WM), respectively. Furthermore, the presented work also obtains the mean dice scores of 90.35, 82.34, and 71.93 for the whole tumor, the tumor core, and the enhancing tumor, respectively on the BRATS 2019 validation dataset. Experimentally, it is found that the proposed approach is ideal for exploiting the full contextual information of the 3D brain MRI datasets.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
BRATS 2018 datasets
The description of the datasets and procedures to download them can be accessedFootnote 4.
BRATS 2019 datasets
The description of the datasets and procedures to download them can be accessedFootnote 5.
iSeg-2019 datasets
The description of the datasets and procedures to download them can be accessedFootnote 6.
References
Ahmad P, Qamar S, Hashemi SR, Shen L (2020) Hybrid labels for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 158–166
Albiol A, Albiol A, Albiol F (2019) Extending 2D deep learning architectures to 3D image segmentation problems. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 73–82
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J, Freymann J, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-GBM collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive (2017)
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J, Freymann J, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-LGG collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive 286
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J, Freymann JB, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci Data 4:170117. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.117
Bakas S, Reyes M, Jakab A, Bauer S, Rempfler M, Crimi A, Shinohara RT, Berger C, Ha SM, Rozycki M, Prastawa M, Alberts E, Lipková J, Freymann JB, Kirby J, Bilello M, Fathallah-Shaykh HM, Wiest R, Kirschke J, Wiestler B, Colen RR, Kotrotsou A, LaMontagne P, Marcus DS, Milchenko M, Nazeri A, Weber M, Mahajan A, Baid U, Kwon D, Agarwal M, Alam M, Albiol A, Albiol A, Varghese A, Tuan TA, Arbel T, Avery ABP, Banerjee S, Batchelder T, Batmanghelich K, Battistella E, Bendszus M, Benson E, Bernal J, Biros G, Cabezas M, Chandra S, Chang YJ et al (2018) Identifying the Best Machine Learning Algorithms for Brain Tumor Segmentation, Progression Assessment, and Overall Survival Prediction in the {BRATS} Challenge. CoRR arXiv:1811.02629
Carver E, Liu C, Zong W, Dai Z, Snyder JM, Lee J, Wen N (2019) Automatic brain tumor segmentation and overall survival prediction using machine learning algorithms. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 406–418
Chandra S, Vakalopoulou M, Fidon L, Battistella E, Estienne T, Sun R, Robert C, Deutsch E, Paragios N (2019) Context Aware 3D CNNs for Brain Tumor Segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 299–310
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2017) Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1706.05587
Chen W, Liu B, Peng S, Sun J, Qiao X (2019) S3d-UNet: Separable 3D U-Net for Brain Tumor Segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 358–368
Devalla SK, Renukanand PK, Sreedhar BK, Perera SA, Mari JM, Chin KS, Tun TA, Strouthidis NG, Aung T, Thiery AH, Girard MJA (2018) {DRUNET:}{A} Dilated-Residual U-Net Deep Learning Network to Digitally Stain Optic Nerve Head Tissues in Optical Coherence Tomography Images. CoRR arXiv:1803.00232
Dolz J, Ayed IB, Desrosiers C (2018) Dense Multi-path U-Net for Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation in Multiple Image Modalities. CoRR arXiv:1810.07003
Dolz J, Xu X, Rony J, Yuan J, Liu Y, Granger E, Desrosiers C, Zhang X, Ayed IB, Lu H (2018) Multi-region segmentation of bladder cancer structures in {MRI} with progressive dilated convolutional networks. CoRR arXiv:1805.10720
Feng X, Tustison N, Meyer C (2019) Brain tumor segmentation using an ensemble of 3D U-Nets and overall survival prediction using radiomic features. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 279–288
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. CoRR arXiv:1512.03385
Heller N, Sathianathen N, Kalapara A, Walczak E, Moore K, Kaluzniak H, Rosenberg J, Blake P, Rengel Z, Oestreich M et al (2019) The kits19 challenge data: 300 kidney tumor cases with clinical context, ct semantic segmentations, and surgical outcomes. arXiv:1904.00445
Hu Y, Liu X, Wen X, Niu C, Xia Y (2019) Brain Tumor Segmentation on Multimodal MR Imaging Using Multi-level Upsampling in Decoder. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 168–177
Hua R, Huo Q, Gao Y, Sun Y, Shi F (2019) Multimodal brain tumor segmentation using cascaded V-Nets. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 49–60
Huang G, Liu Z, Weinberger KQ (2016) Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. CoRR arXiv:1608.06993
Isensee F, Kickingereder P, Wick W, Bendszus M, Maier-Hein KH (2018) Brain Tumor Segmentation and Radiomics Survival Prediction: Contribution to the {BRATS} 2017 Challenge. CoRR arXiv:1802.10508
Isensee F, Kickingereder P, Wick W, Bendszus M, Maier-Hein KH (2019) No New-Net. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, pp 234–244
Jégou S, Drozdzal M, Vázquez D, Romero A, Bengio Y (2016) The One Hundred Layers Tiramisu: Fully Convolutional DenseNets for Semantic Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1611.09326
Kamnitsas K, Bai W, Ferrante E, McDonagh SG, Sinclair M, Pawlowski N, Rajchl M, Lee MCH, Kainz B, Rueckert D, Glocker B (2017) Ensembles of Multiple Models and Architectures for Robust Brain Tumour Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1711.01468
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VFJ, Simpson JP, Kane AD, Menon DK, Rueckert D, Glocker B (2017) Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36:61–78
Kao PY, Ngo T, Zhang A, Chen JW, Manjunath BS (2019) Brain tumor segmentation and tractographic feature extraction from structural MR images for overall survival prediction. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 128–141
Kermi A, Mahmoudi I, Khadir MT (2019) Deep convolutional neural networks using U-Net for automatic brain tumor segmentation in multimodal MRI volumes. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 37–48
Kori A, Soni M, Pranjal B, Khened M, Alex V, Krishnamurthi G (2019) Ensemble of fully convolutional neural network for brain tumor segmentation from magnetic resonance images. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 485–496
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Liu L, Cheng J, Quan Q, Wu FX, Wang YP, Wang J (2020) A survey on U-shaped networks in medical image segmentations. Neurocomputing 409:244–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.070. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231220309218
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2014) Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1411.4038
Luo W, Li Y, Urtasun R, Zemel RS (2017) Understanding the Effective Receptive Field in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. CoRR arXiv:1701.04128
Ma J, Yang X (2019) Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation by Exploring the Multi-modality Complementary Information and Cascaded 3D Lightweight CNNs. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 25–36
Marcinkiewicz M, Nalepa J, Lorenzo PR, Dudzik W, Mrukwa G (2019) Segmenting Brain Tumors from MRI Using Cascaded Multi-modal U-Nets. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 13–24
Mehta R, Arbel T (2019) 3D U-Net for brain tumour segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 254–266
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, Burren Y, Porz N, Slotboom J, Wiest R, Lanczi L, Gerstner E, Weber M, Arbel T, Avants BB, Ayache N, Buendia P, Collins DL, Criminisi A (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993–2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA (2016) V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1606.04797
Nuechterlein N, Mehta S (2019) 3d-ESPNet with Pyramidal Refinement for Volumetric Brain Tumor Image Segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 245–253
Rezaei M, Yang H, Meinel C (2019) voxel-GAN: Adversarial Framework for Learning Imbalanced Brain Tumor Segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 321–333
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1505.04597
Roy Choudhury A, Vanguri R, Jambawalikar SR, Kumar P (2019) Segmentation of Brain Tumors Using DeepLabv3+. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 154–167
Samanta A, Saha A, Satapathy SC, Fernandes SL, Zhang YD (2020) Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using convolutional neural networks on a small dataset. Pattern Recogn Lett 135:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.04.026. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167865520301483
Sarker MMK, Rashwan HA, Akram F, Banu SF, Saleh A, Singh VK, Chowdhury FUH, Abdulwahab S, Romani S, Radeva P, Puig D (2018) SLSDeep: Skin Lesion Segmentation Based on Dilated Residual and Pyramid Pooling Networks. CoRR arXiv:1805.10241
Sun L, Zhang S, Luo L (2019) Tumor segmentation and survival prediction in glioma with deep learning. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 83–93
Sun Y, Gao K, Wu Z, Lei Z, Wei Y, Ma J, Yang X, Feng X, Zhao L, Phan TL, Shin J, Zhong T, Zhang Y, Yu L, Li C, Basnet R, Ahmad MO, Swamy MNS, Ma W, Dou Q, Bui TD, Noguera CB, Landman B, Gotlib IH, Humphreys KL, Shultz S, Li L, Niu S, Lin W, Jewells V, Li G, Shen D, Wang L (2020) Multi-Site Infant Brain Segmentation Algorithms: The iSeg-2019 Challenge
Tuan TA, Tuan TA, Bao PT (2019) Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Bit-plane and UNET. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 466–475
Wang G, Li W, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T (2017) Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation using Cascaded Anisotropic Convolutional Neural Networks. CoRR arXiv:1709.00382
Wang G, Li W, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T (2019) Automatic brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks with test-time augmentation. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol 11384 LNCS. Springer, pp 61–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11726-9_6
Wang P, Chen P, Yuan Y, Liu D, Huang Z, Hou X, Cottrell GW (2017) Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1702.08502
Weninger L, Rippel O, Koppers S, Merhof D (2019) Segmentation of Brain Tumors and Patient Survival Prediction: Methods for the braTS 2018 Challenge. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 3–12
Xie S, Sun C, Huang J, Tu Z, Murphy K (2017) Rethinking Spatiotemporal Feature Learning For Video Understanding. CoRR arXiv:1712.04851
Xu Y, Gong M, Fu H, Tao D, Zhang K, Batmanghelich K (2019) Multi-scale Masked 3-D U-Net for Brain Tumor Segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 222–233
Yang M, Yu K, Zhang C, Li Z, Yang K (2018) DenseASPP for Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3684–3692
Yu F, Koltun V (2016) Multi-scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. coRR arXiv:1511.0
Yu F, Koltun V, Funkhouser TA (2017) Dilated Residual Networks. CoRR arXiv:1705.09914
Zhang J, Jin Y, Xu J, Xu X, Zhang Y (2018) MDU-Net: Multi-scale Densely Connected U-Net for biomedical image segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1812.00352
Zhou Z, Siddiquee MMR, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) UNet++: {A} Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. CoRR arXiv:1807.10165
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.61672250 and the Hubei Provincial Development and Reform Commission Project in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest/competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, P., Jin, H., Qamar, S. et al. RD2A: densely connected residual networks using ASPP for brain tumor segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 27069–27094 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10915-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10915-y