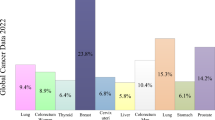
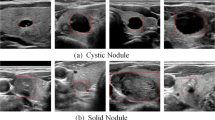
Abstract
Accurate diagnosis of thyroid nodules using ultrasonography heavily relies on the superb skills and rich experience of senior radiologists, considering the low contrast, high noise of the ultrasound image, and the diverse appearance of the nodules. Computer-aided diagnosis systems could diagnose thyroid nodules based on ultrasound characteristics to assist radiologists. However, the existing learning-based approaches for detecting and recognizing thyroid nodules have the problems of inaccurate localization and low recognition accuracy. In this study, we propose an Improved Cascade Mask R-CNN for effectively detecting and recognizing thyroid nodules. Firstly, a more effective detector is designed to better classify the ROIs and better correct the bounding boxes. Secondly, a more effective balanced L1 loss function is used to increase the gradient of the easy sample and solve the problem of imbalance between hard samples and easy samples during training. Finally, a more effective soft non-maximum suppression (Soft-NMS) method is used to set an attenuation function for adjacent bounding boxes, which solves the problem of possible missing detection in non-maximum suppression (NMS). The improved model is trained and verified by using real 1408 images collected from the known hospital. Under the localization accuracy of the IoU threshold of 0.5, the mAP reaches 87.1%, and the recognition accuracy reaches 98.67%. The experiment results show that the improved model is effective and highly valuable to help the doctors for the recognition of benign and malignant thyroid nodules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bibicu D, Moraru L, Biswas A (2013) Thyroid nodule recognition based on feature selection and pixel classification methods. J Digit Imaging 26(1):119–128
Bodla N, Singh B, Chellappa R, Davis LS (2017) Soft-NMS–improving object detection with one line of code. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 5561–5569
Cai Z, Vasconcelos N (2018) Cascade r-cnn: delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 6154–6162
Cai Z, Vasconcelos N (2019) Cascade R-CNN: high quality object detection and instance segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.09756
Chang CY, Chen SJ, Tsai MF (2010) Application of support-vector-machine-based method for feature selection and classification of thyroid nodules in ultrasound images. Pattern Recogn 43(10):3494–3506
Chi J, Yu X, Zhang Y (2018) Thyroid nodule malignant risk detection in ultrasound image by fusing deep and texture features. Journal of Image and Graphics 23(10):1582–1593
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 248-255
Ding J, Cheng H, Ning C, Huang J, Zhang Y (2011) Quantitative measurement for thyroid cancer characterization based on elastography. J Ultras Med 30(9):1259–1266
Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J (2014) Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 580–587
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 770–778
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp. 2961–2969
Ke W (2018) An ultrasonic image recognition method for papillary thyroid carcinoma based on depth convolution neural network. Dissertation, Guangdong University of Technology
Keramidas EG, Maroulis D, Iakovidis DK (2012) TND: a thyroid nodule detection system for analysis of ultrasound images and videos. J Med Syst 36(3):1271–1281
Lin TY, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K, Hariharan B, Belongie S (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 2117–2125
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu CY, Berg AC (2016) SSD: single shot multibox detector. In: European conference on computer vision. pp. 21–37
Liu Y, Guo Y, GeorgIoU T, Lew MS (2018) Fusion that matters: convolutional fusion networks for visual recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 77(22):29407–29434
Liu X, Ma X, Liu L (2019) Thyroid nodule detection method based on median filter and residual network. Computer Engineering and Applications 55(13):254–259
Liu T, Guo Q, Lian C, Ren X, Liang S, Yu J, Niu L, Sun W, Shen D (2019) Automated detection and classification of thyroid nodules in ultrasound images using clinical-knowledge-guided convolutional neural networks. Med Image Anal 58:101555
Ma J, Wu F, Jiang T, Zhu J, Kong D (2017) Cascade convolutional neural networks for automatic detection of thyroid nodules in ultrasound images. Med Phys 44(5):1678–1691
Ma J, Wu F, Zhu J, Xu D, Kong D (2017) A pre-trained convolutional neural network based method for thyroid nodule diagnosis. Ultrasonics 73:221–230
Neubeck A, Van Gool L (2006) Efficient non-maximum suppression. In: 18th international conference on pattern recognition. pp. 850-855
Pang J, Chen K, Shi J, Feng H, Ouyang W, Lin D (2019) Libra r-cnn: towards balanced learning for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 821–830
Peng W (2017) The study of thyroid nodule recognition based on CT images. Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2017) YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 7263–7271
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A (2016) You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 770–778
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp. 91–99
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556
Sipos JA (2009) Advances in ultrasound for the diagnosis and management of thyroid cancer. Thyroid 19(12):1363–1372
Tsantis S, Dimitropoulos N, Cavouras D, Nikiforidis G (2009) Morphological and wavelet features towards sonographic thyroid nodules evaluation. Comput Med Imag Grap 33(2):91–99
Uijlings JR, Van De Sande KE, Gevers T, Smeulders AW (2013) Selective search for object recognition. Int J Comput Vis 104(2):154–171
Wu Y, Chen Y, Yuan L, Liu Z, Wang L, Li H, Fu Y (2019) Double-head rcnn: rethinking classification and localization for object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.06493
Zhu C, Zheng T, Kilfoy BA, Han X, Ma S, Ba Y, Bai Y, Wang R, Zhu Y, Zhang Y (2009) A birth cohort analysis of the incidence of papillary thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973-2004. Thyroid 19(10):1061–1066
Funding
This work was supported by the Key R&D Program of JiangXi Province of China (Grant No.20181BBG70031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University approved our study. We retrospectively analyzed these data.
Informed consent
This articles does not contain patient data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Qin, L., Qiu, T. et al. Automated detection and recognition of thyroid nodules in ultrasound images using Improve Cascade Mask R-CNN. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 13253–13273 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10939-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10939-4