Abstract
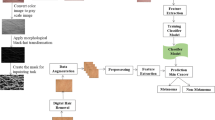
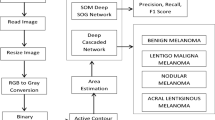
Melanoma is a lethal skin cancer disease affecting millions of people around the globe and has a high mortality rate. Dermatologists perform the manual inspection through visual analysis of pigmented skin lesions for melanoma identification at the early stage. However, manual inspection for melanoma detection is limited due to variable accuracy and lesser availability of dermatologists. Therefore, there exists an urgent need to develop automated melanoma detection methods that can effectively localize and classify skin lesions. Accurate localization and classification of the melanoma lesions is a challenging task due to the presence of low contrast information between the moles and skin part, the massive color similarity between the infected and non-infected skin portions, presence of noise, hairs, and tiny blood vessels, variations in color, texture, illumination, contrast, blurring, and melanoma size. To address these afore-mentioned challenges, we propose an effective and efficient melanoma detection method. The proposed method consists of three steps: i) image preprocessing, ii) employing Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (Faster-RCNN) for melanoma localization, and iii) application of Support Vector Machine (SVM) for the classification of localized melanoma region into benign and malignant classes. Performance of the proposed method is evaluated on the benchmark ISIC-2016 dataset launched by ISBI challenge-2016 that is diverse in terms of variations in illumination, color, texture, and size of melanoma, and presence of blurring, noise, hairs, and tiny blood vessels, etc. Moreover, we have also performed a cross-dataset validation over the ISIC-2017 dataset to show the efficacy of our method in real-world scenarios. Our experimental results illustrate that the proposed framework is efficient and able to effectively localize and classify the melanoma lesion than state-of-the-art techniques.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcón JF, Ciuhu C, Ten Kate W, Heinrich A, Uzunbajakava N, Krekels G, Siem D, de Haan G (2009) Automatic imaging system with decision support for inspection of pigmented skin lesions and melanoma diagnosis. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 3(1):14–25
Al-Masni MA, Kim D-H, Kim T-S (2020) Multiple skin lesions diagnostics via integrated deep convolutional networks for segmentation and classification. Comput Meth Prog Biomed 190:105351
Anthimopoulos M, Christodoulidis S, Ebner L, Christe A, Mougiakakou S (2016) Lung pattern classification for interstitial lung diseases using a deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1207–1216
Attia M, Hossny M, Nahavandi S, Yazdabadi A (2017) Skin melanoma segmentation using recurrent and convolutional neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), pp 292–296: IEEE
Badrinarayanan V, Handa A, Cipolla R (2015) Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for robust semantic pixel-wise labelling, arXiv preprint arXiv:.07293
Ballerini L, Fisher R B, Aldridge B, Rees J (2013) A color and texture based hierarchical K-NN approach to the classification of non-melanoma skin lesions. In: Color Medical Image Analysis: Springer, pp 63–86
Barata C, Ruela M, Francisco M, Mendonça T, Marques JS (2013) Two systems for the detection of melanomas in dermoscopy images using texture and color features. IEEE Syst J 8(3):965–979
Barata C, Celebi ME, Marques JS (2017) Development of a clinically oriented system for melanoma diagnosis. Pattern Recogn 69:270–285
Bi L, Kim J, Ahn E, Feng D, Fulham M (2017) Semi-automatic skin lesion segmentation via fully convolutional networks. In: 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), pp 561–564: IEEE
Burdick J, Marques O, Romero-Lopez A, Giró Nieto X, Weinthal J (2017) The impact of segmentation on the accuracy and sensitivity of a melanoma classifier based on skin lesion images. In: SIIM 2017 scientific program: Pittsburgh, PA, June 1–June 3, 2017, David L. Lawrence Convention Center, pp 1–6
Cavalcanti PG, Scharcanski J (2011) Automated prescreening of pigmented skin lesions using standard cameras. Comput Med Imaging Graph 35(6):481–491
Cavalcanti PG, Scharcanski J, Baranoski GV (2013) A two-stage approach for discriminating melanocytic skin lesions using standard cameras. Expert Syst Appl 40(10):4054–4064
Cheng Y, Swamisai R, Umbaugh SE, Moss RH, Stoecker WV, Teegala S, Srinivasan SK (2008) Skin lesion classification using relative color features. Skin Res Technol 14(1):53–64
Codella N C, Nguyen Q-B, Pankanti S, Gutman D A, Helba B, Halpern A C, Smith J R (2017) Deep learning ensembles for melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images. IBM J Res Dev 61, no4/5, pp. 5: 1–5: 15
Codella N C, Gutman D, Celebi M E, Helba B, Marchetti M A, Dusza S W, Kalloo A, Liopyris K, Mishra N, Kittler H (2018) Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the 2017 International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC), in 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp 168–172: IEEE
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Dollár P, Zitnick CL (2014) Fast edge detection using structured forests. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(8):1558–1570
Fukunaga K, Narendra PM (1975) A branch and bound algorithm for computing k-nearest neighbors. IEEE Trans Comput 100(7):750–753
Ganster H, Pinz P, Rohrer R, Wildling E, Binder M, Kittler H (2001) Automated melanoma recognition. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(3):233–239
Garnavi R, Aldeen M, Celebi ME, Bhuiyan A, Dolianitis C, Varigos G (2010) Automatic segmentation of dermoscopy images using histogram thresholding on optimal color channels. Int J Med Med Sci 1(2):126–134
Giotis I, Molders N, Land S, Biehl M, Jonkman MF, Petkov N (2015) MED-NODE: a computer-assisted melanoma diagnosis system using non-dermoscopic images. Expert Syst Appl 42(19):6578–6585
Girshick R (2015) Fast r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1440–1448
Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J (2014) Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 580–587
Gulati S, Bhogal R K (2019) Detection of Malignant Melanoma Using Deep Learning. In: International Conference on Advances in Computing and Data Sciences. Springer, pp 312–325
Gutman D, Codella N C, Celebi E, Helba B, Marchetti M, Mishra N, Halpern A (2016) Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC), arXiv preprint arXiv:.01397
Harangi B (2018) Skin lesion classification with ensembles of deep convolutional neural networks. J Biomed Inform 86:25–32
Hosny K M, Kassem M A, Foaud M M (2018) Skin Cancer Classification using Deep Learning and Transfer Learning. In: 2018 9th Cairo International Biomedical Engineering Conference (CIBEC), pp 90–93: IEEE
Hu K, Niu X, Liu S, Zhang Y, Cao C, Xiao F, Yang W, Gao X (2019) Classification of melanoma based on feature similarity measurement for codebook learning in the bag-of-features model. Biomed Signal Process Control 51:200–209
Lewis DD (1998) Naive (Bayes) at forty: The independence assumption in information retrieval, in European conference on machine learning. Springer, pp 4–15
Li Y, Shen L (2018) Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors 18(2):556
Liao P-S, Chen T-S, Chung P-C (2001) A fast algorithm for multilevel thresholding. J Inf Sci Eng 17(5):713–727
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440
Mahbod A, Schaefer G, Wang C, Ecker R, Ellinge I (2019) Skin lesion classification using hybrid deep neural networks, in ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp 1229–1233: IEEE
Nachbar F, Stolz W, Merkle T, Cognetta AB, Vogt T, Landthaler M, Bilek P, Braun-Falco O, Plewig G (1994) The ABCD rule of dermatoscopy: high prospective value in the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol 30(4):551–559
Nida N, Irtaza A, Javed A, Yousaf MH, Mahmood MT (2019) Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep region based convolutional neural network and fuzzy C-means clustering. Int J Med Inform 124:37–48
Nijeweme-d’Hollosy WO, van Velsen L, Poel M, Groothuis-Oudshoorn CG, Soer R, Hermens H (2018) Evaluation of three machine learning models for self-referral decision support on low back pain in primary care. Int J Med Inform 110:31–41
Okur E, Turkan M (2018) A survey on automated melanoma detection. Eng Appl Artif Intell 73:50–67
Polesel A, Ramponi G, Mathews VJ (2000) Image enhancement via adaptive unsharp masking. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(3):505–510
Rehman A, Khan MA, Mehmood Z, Saba T, Sardaraz M, Rashid M (2020) Microscopic melanoma detection and classification: a framework of pixel-based fusion and multilevel features reduction. Microsc Res Tech 83(4):410–423
Ridler T, Calvard S (1978) Picture thresholding using an iterative selection method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 8(8):630–632
Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, Coldiron BM (2015) Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol 151(10):1081–1086
Schaefer G, Krawczyk B, Celebi ME, Iyatomi H (2014) An ensemble classification approach for melanoma diagnosis. Memet Comput 6(4):233–240
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ, Meester RG, Barzi A, Jemal A (2017) Colorectal cancer statistics. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 67(3):177–193
Silveira M, Nascimento JC, Marques JS, Marçal AR, Mendonça T, Yamauchi S, Maeda J, Rozeira J (2009) Comparison of segmentation methods for melanoma diagnosis in dermoscopy images. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 3(1):35–45
Singh S, Alam M, Singh B (2020) Orthogonal moment feature extraction and classification of melanoma images. Journal of Information Optimization Sciences 41(1):195–203
Society A C (2016) Cancer facts & figures. American Cancer Society
Stanley RJ, Stoecker WV, Moss RH (2007) A relative color approach to color discrimination for malignant melanoma detection in dermoscopy images. Skin Res Technol 13(1):62–72
Tajbakhsh N, Shin JY, Gurudu SR, Hurst RT, Kendall CB, Gotway MB, Liang J (2016) Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning? IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1299–1312
Tan TY, Zhang L, Lim CP (2020) Adaptive melanoma diagnosis using evolving clustering, ensemble and deep neural networks. Knowl-Based Syst 187:104807
Uijlings JR, Van De Sande KE, Gevers T, Smeulders AW (2013) Selective search for object recognition. Int J Comput Vis 104(2):154–171
Uricchio T, Bertini M, Seidenari L, Bimbo A (2015) Fisher encoded convolutional bag-of-windows for efficient image retrieval and social image tagging. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp 9–15
Walter M (2016) Is this the end? machine learning and 2 other threats to radiologys future, goo. gIIM9X3SF, pp l3
Yang J, Xie F, Fan H, Jiang Z, Liu J (2018) Classification for dermoscopy images using convolutional neural networks based on region average pooling. IEEE Access 6:65130–65138
Yap J, Yolland W, Tschandl P (2018) Multimodal skin lesion classification using deep learning. Exp Dermatol 27(11):1261–1267
Yu L, Chen H, Dou Q, Qin J, Heng P-A (2016) Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images via very deep residual networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(4):994–1004
Yu Z, Jiang F, Zhou F, He X, Ni D, Chen S, Wang T, Lei B (2020) Convolutional descriptors aggregation via cross-net for skin lesion recognition. Appl Soft Comput:106281
Zhang J, Xie Y, Wu Q, Xia Y (2019) Medical image classification using synergic deep learning. Med Image Anal 54:10–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nawaz, M., Masood, M., Javed, A. et al. Melanoma localization and classification through faster region-based convolutional neural network and SVM. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 28953–28974 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11120-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11120-7