Abstract
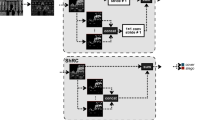
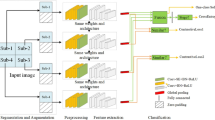
In recent years, many deep neural network models are used in steganalysis. However, the deep neural network models on steganalysis usually use the single scale channel for detection. When the number of convolution kernels reaches a certain limit, the improvement of detection accuracy is very weak by increasing the number of convolution kernels. In this paper, we try to establish a wider range of image region correlation extraction, and propose a multi-scale deep neural network model. The model is based on the deep residual network and adopts end-to-end design. Different local receptive fields in the same layer were selected to generate the characteristic channels. By the channel recognition, variety of image steganographic features were achieved from different scale channels. Experiments show that the multi-scale residual network can further improve the accuracy of steganography detection more than the networks of the single scale channel.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avcibas I, Memon N, Sankur B (2001) Steganalysis of watermarking techniques using image quality metrics. Proc SPIE 4314:523–531
Avcibas I, Memon N, Sankur B (2002) Image steganalysis with binary similarity measures. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. Iiage process., vol 3. Rochester, NY, USA, pp 645–648
Bas P, Filler T, Pevný T (2011) ‘Break our steganographic system’: the ins and outs of organizing BOSS. Proc. 13th int. conf. inf. hiding in lecture notes in computer science
Bas P, Furon T (2007) BOWS-2. http://bows2.ec-lille.fr
Boroumand M, Chen M, Fridrich J (2019) Deep residual network for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 14(5):1181–1193
Chen M, Sedighi V, Boroumand M, Fridrich J (2017) JPEG-phaseaware convolutional neural network for steganalysis of JPEG images. In: Proc. 5th ACM workshop
Denemark TD, Boroumand M, Fridrich J (2016) Steganalysis features for content-adaptive JPEG steganography. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 11(8):1736–1746
Denemark T, Fridrich J, Comesaña-Alfaro P (2016) Improving selectionchannel-aware steganalysis features. Electronic Imaging Issue Date 2016:1–8
Denemark T, Sedighi V, Holub V, Cogranne R, Fridrich J (2014) Selection-channel-aware rich model for steganalysis of digital images. In: Proc. IEEE int. workshop inf. forensics secur, Atlanta, GA, USA, pp 48–53
Fridrich J, Kodovský J (2011) Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 7(3):868–882
Guo L, Ni J, Shi YQ (2014) Uniform embedding for efficient JPEG steganography. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 9(5):814–825
Guo L, Ni J, Su W, Tang C, Shi Y (2015) Using statistical image model for JPEG steganography: Uniform embedding revisited. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 10(12):2669–2680
Guo L, Ni J, Shi Y (2012) An efficient JPEG steganographic scheme using uniform embedding. In: Proc. IEEE int. workshop inf. forensics secur., pp 169–174
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc. IEEE conf. comput. vis. pattern recognit. (CVPR), pp. 770–778
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: ECCV 2016: computer vision, pp 630–645
Holub V, Fridrich J, Denemark T (2014) Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. EURASIP J Inf Secur 2014:1
Holub V, Fridrich J (2012) Designing steganographic distortion using directional filters. In: Proc. IEEE int. workshop inf. forensics secur., pp 234–239
Kim J, Park H, Park J (2020) CNN-based image steganalysis using additional data embedding. Multimedia Tools and Applications 79(1):1355–1372
Kodovsky J, Fridrich J, Holub V (2012) Ensemble classifiers for steganalysis of digital media. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 7:432–444
Li L, Zhang W, Chen K, Yu N (2020) Steganographic security analysis from side channel steganalysis and its complementary attacks. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 22(10):2526–2536
Li B, Wang M, Huang J, Li X (2014) A new cost function for spatial image steganography. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. image process., pp 4206–4210
Lyu S, Farid H (2002) Detecting hidden messages using higher-order statistics and support vector machines. In: Proc. 5th Int. workshop inf. hiding, vol 2578, pp 340–354
Petitcolas F, Anderson R, Kuhn M (1999) Information hiding-A survey. Proc IEEE 87(7):1062–1078
Pevný T, Filler T, Bas P (2010) Using high-dimensional image models to perform highly undetectable steganography. In: Proc. int. workshop inf. hiding. Springer, Calgary, AB, Canada, pp 161–177
Provos N (2001) Defending against statistical steganalysis. Proc Usenix Secur Symp 10:323–336
Qian Y, Dong J, Wang W, Tan T (2015) Deep learning for steganalysis via convolutional neural networks. Proc SPIE 9409:94090
Sallee P (2004) Model-based steganography. In: Digital watermarking. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 154–167
Sedighi V, Cogranne R, Fridrich J (2016) Content-adaptive steganography by minimizing statistical detectability. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 11(2):221–234
Singh B, Chhajed M, Sur A, Mitra P (2021) Steganalysis using learned denoising kernels. Multimedia Tools and Applications 80(4):4903–4917
Tang W, Li H, Luo W, Huang J (2016) Adaptive steganalysis based on embedding probabilities of pixels. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 11(4):734–745
Tang W, Li H, Luo W, Huang J (2014) Adaptive steganalysis against WOW embedding algorithm. In: Katzenbeisser S, Kwitt R, Piva A, (eds) Proc. 2nd ACM workshop inf. hiding multimedia secur., ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 91–96
Wang P, Liu F, Yang C, Luo X (2019) Steganalysis aided by fragile detection of image manipulations. Multimedia Tools and Applications 78(16):23309–23328
Westfeld A (2001) F5-A steganographic algorithm. In: Information hiding. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 289–302
Xu G (2017) Deep convolutional neural network to detect J-UNIWARD. In: Stamm M, Kirchner M (eds)Proc. 5th ACM workshop inf. hiding multimedia secur., Philadelphia, PA, USA, pp 67–73
Xu G, Wu H, Shi Y (2016) Structural design of convolutional neural networks for steganalysis. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23(5):708–712
Xu G, Wu H, Shi Y (2016) Ensemble of CNNs for steganalysis: an empirical study. In: Proc. 4th ACM workshop
Ye J, Ni J, Yi Y (2017) Deep learning hierarchical representations for image steganalysis. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 12(11):2545–2557
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 61471141, 61361166006, 61301099]; Key Technology Program of Shenzhen, China, [grant number JSGG20160427185010977]; Basic Research Project of Shenzhen, China [grant number JCYJ20150513151706561]. The authors would like to thank the Digital Data Embedding Laboratory sharing code on the website, and Institute of Information Countermeasures Technology providing deep learning servers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Han, Q., Li, Q. et al. Image steganalysis with multi-scale residual network. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 22009–22031 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11611-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11611-7