Abstract
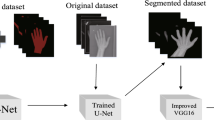
Bone age assessment investigates the ossification improvement for estimating the skeletal age of the pediatrics for analyzing their skeletal growth and forecast their future adult height. The main intent of this paper is to contribute a novel deep learning-based bone segmentation for bone age assessment. Here, the datasets are gathered from both the manual as well as the RSNA database. The segmentation of 5 regions “Distal Phalanx of thumb, middle phalanx, third metacarpal, radius, and ulna” is performed by the optimized U-Net model. As an improvement in the existing U-Net architecture, tuning of the activation function is adopted by the hybridization of two meta-heuristic algorithms such as Class Topper Optimization (CTO) and Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) termed as Whale-based Class Topper Optimization (W-CTO). This improved model is developed with the intention of solving the multi-objective segmentation that concerns the parameters like entropy and variance. Moreover, the effect of the proposed segmentation is analyzed by estimating the bone age with the deep Convolutional Neural Network (Deep CNN). From the analysis, the overall MASE of W-CTO-U-Net+CNN is 14.66%, 22.06%, and 5.53% higher than RNN, CNN, and NN, respectively, and RMSE of W-CTO-U-Net+CNN is 53.28%, 22.02%, and 32.87% better than RNN, CNN, and NN, respectively.. The performance comparison of the proposed segmentation model over the conventional approaches confirms its effective performance with relatively high accuracy.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshamrani K, Hewitt A, Offiah AC (2020) Applicability of two bone age assessment methods to children from Saudi Arabia. Clin Radiol 75(2):1561–1569
Baliarsingh SK, Vipsita S (2020) Chaotic emperor penguin optimised extreme learning machine for microarray cancer classification. IET Syst Biol 14(2):85–95
Baliarsingh SK, Vipsita S, Gandomi AH, Panda A, Bakshi S, Ramasubbareddy S (2020) Analysis of high-dimensional genomic data using MapReduce based probabilistic neural network. Comp Methods Programs Biomed, volume 195, pp 105625
Baliarsingh SK, Muhammad K, Bakshi S (2021) SARA: a memetic algorithm for high-dimensional biomedical data. Appl Soft Computing 101(4)
Berst MJ, Dolan L, Bogdanowicz MM, Stevens MA, Chow S, Brandser EA (2001) Effect of knowledge of chronologic age on the variability of pediatric bone age determined using the Greulich and Pyle standards. Am J Roentgenol 176(2):507–510
Birhade P, Khaparde A, Deshmukh S (2017) Performance analysis of snake algorithm for bone age assessment. 2017 International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, pp 1-5
Breen MA, Tsai A, Stamm A, Kleinman PK (2016) Bone age assessment practices in infants and older children among Society for Pediatric Radiology members. Pediatr Radiol 46:1269–1274
Bui TD, Lee J-J, Shin J (2018) Incorporated region detection and classification using deep convolutional networks for bone age assessment. Artif Intell Med 97:1–8
Bull R, Edwards P, Kemp P, Fry S, Hughes I (1999) Bone age assessment: a large scale comparison of the Greulich and Pyle, and tanner and Whitehouse (tw2) methods. Arch Dis Child 81(2):172–173
Chai HY, Wee LK, Swee TT, Salleh SH (2011) Adaptive crossed reconstructed (acr) k-mean clustering segmentation for computer-aided bone age assessment system. Int J Math Models Methods Appl Sci 5(3):628–635
Chan TF, Vese LA (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(2):266–277
Chaumoitre K, Colavolpe N (2006) Sayegh-Martin Y "reliability of the Sauvegrain and Nahum method to assess bone age in a contemporary population". J Radiol 87:1679–1682
Chen Y, Yang J, Qian J (2017) Recurrent neural network for facial landmark detection. Neurocomputing 219:26–38
Chowdhary CL, Patel PV, Kathrotia KJ, Attique M, Perumal K, Ijaz MF (2020) Analytical study of hybrid techniques for image encryption and decryption. Sensors 20(18):5162
Christoforidis A, Badouraki M, Katzos G, Athanassiou-Metaxa M (2007) Bone age estimation and prediction of final height in patients with β-thalassaemia major: a comparison between the two most common methods. Pediatr Radiol 37:1241–1246
Daneff M, Casalis C, Bruno CH (2015) Bone age assessment with conventional ultrasonography in healthy infants from 1 to 24 months of age. Pediatr Radiol 45:1007–1015
Das P, Kumar Das D, Dey S (2018) A new class topper optimization algorithm with an application to data clustering. IEEE Trans Emerg Topics Comput PP(99):1-1
Dwivedi S, Vardhan M, Tripathi S (2020) An effect of chaos grasshopper optimization algorithm for protection of network infrastructure. Comput Netw 176
Gertych A, Zhang A, Sayre J, Pospiech-Kurkowska S, Huang HK (2007) Bone age assessment of children using a digital hand atlas. Comput Med Imaging Graph 31:322–331
Giordano D, Kavasidis I, Spampinato C (2016) Modeling skeletal bone development with hidden markov models. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 124:138–147
Gomes GF, da Cunha SS, Ancelotti AC (2019) A sunflower optimization (SFO) algorithm applied to damage identification on laminated composite plates. Eng Comput 35(2):619–626
Gonzalez C, Escobar M, Daza L, Torres F, Triana G, Arbelaez P (2020) SIMBA: Specific identity markers for bone age assessment. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, Cham, pp 753-763
Halabi SS, Prevedello LM, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Mamonov AB, Bilbily A, Cicero M, Pan I, Pereira LA, Sousa RT, Abdala N, Kitamura FC (2019) The RSNA pediatric bone age machine learning challenge. Radiology 290(2):498–503
Hansen LK, Salamon P (1990) Neural network ensembles. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 12(10):993–1001
Harmsen M, Fischer B, Schramm H, Seidl T, Deserno TM (2012) Support vector machine classification based on correlation prototypes applied to bone age assessment. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 17(1):190–7
Hayyolalam V, Kazem AAP (2020) Black widow optimization algorithm: a novel meta-heuristic approach for solving engineering optimization problems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 87
Hsieh CW, Liu TC, Jong TL, Tiu CM (2010) A fuzzy-based growth model with principle component analysis selection for carpal bone-age assessment. Med Biol Eng Comput 48(6):579–588
Hu B, Shang L, Cheng F, Sheng H, Pan J, Yin D (2020) Bone age prediction method based on convolutional neural network. J Phys Conf Series 1646(1):012065
Iglovikov V, Rakhlin A, Kalinin AA, Shvets A (2018) Pediatric bone age assessment using deep convolutional neural networks. In: Deep learning in medical image analysis and multimodal learning for clinical decision support. Springer, Cham, 300–308
Ijaz MF, Alfian G, Syafrudin M, Rhee J (2018) Hybrid prediction model for type 2 diabetes and hypertension using DBSCAN-based outlier detection, synthetic minority over sampling technique (SMOTE), and random forest. Appl Sci 8(8):1325
Ijaz MF, Attique M, Son Y (2020) Data-driven cervical cancer prediction model with outlier detection and over-sampling methods. Sensors 20(10):2809
King DG, Steventon DM, O’Sullivan MP (1994) Reproducibility of bone ages when performed by radiology registrars: an audit of Tanner and Whitehouse II versus Greulich and Pyle methods. Br J Radiol 67(801):848–851
Liang B, Zhai Y, Tong C, Zhao J, Li J, He X, Ma Q (2019) A deep automated skeletal bone age assessment model via region-based convolutional neural network. Futur Gener Comput Syst 98:54–59
Liu J, Qi J, Liu Z, Ning Q, Luo X (2008) Automatic bone age assessment based on intelligent algorithms and comparison with TW3 method. Comput Med Imaging Graph 32:678–684
Liu B, Zhang Y, Chu M, Bai X, Zhou F (2019) Bone age assessment based on rank-monotonicity enhanced ranking CNN. IEEE Access 7:120976–120983
Marsaline Beno M, Valarmathi IR, Swamy SM, Rajakumar BR (2014) Threshold prediction for segmenting tumour from brain MRI scans. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 24(2):129–137
Merzban MH, Elbayoumi M (2019) Efficient solution of Otsu multilevel image thresholding: a comparative study. Expert Syst Appl 116:299–309
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67
Ng HP, Ong SH, Foong KWC, Goh PS, Nowinski WL (2006) Medical image segmentation using K-means clustering and improved watershed algorithm. 2006 IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation, Denver, pp 61-65
Ontell FK, Ivanovic M, Ablin DS (1996) Bone age in children of diverse ethnicity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167(6):1395–1398
Panigrahi R, Borah S, Bhoi AK, Ijaz MF, Pramanik M, Kumar Y, Jhaveri RH (2021) A consolidated decision tree-based intrusion detection system for binary and multiclass imbalanced datasets. Mathematics 9(7):751
Panigrahi R, Borah S, Bhoi AK, Ijaz MF, Pramanik M, Jhaveri RH, Chowdhary CL (2021) Performance assessment of supervised classifiers for designing intrusion detection systems: a comprehensive review and recommendations for future research. Mathematics 9(6):690
Pietka E, Gertych A, Pospiech S, Cao F, Huang H, Gilsanz V (2001) Computer-assisted bone age assessment: image preprocessing and epiphyseal/metaphyseal roi extraction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(8):715–729
Pietka E, Pospiech-Kurkowska S, Gertych A, Cao F (2003) Integration of computer assisted bone age assessment with clinical pacs. Comput Med Imaging Graph 27(2-3):217–228
Ren X, Li T, Yang X, Wang S, Ahmad S, Xiang L, Stone SR, Li L, Zhan Y (2019) Regression convolutional neural network for automated pediatric bone age assessment from hand radiograph. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(5):2030–2038
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Springer, Berlin, pp 234-241
Son SJ et al (2019) TW3-based fully automated bone age assessment system using deep neural networks. IEEE Access 7:33346–33358
Spampinato C, Palazzo S, Giordano D, Aldinucci M, Leonardi R (2017) Deep learning for automated skeletal bone age assessment in X-ray images. Med Image Anal 36:41–51
Tamang J, Nkapkop JDD, Ijaz MF, Prasad PK, Tsafack N, Saha A, Kengne J, Son Y (2021) Dynamical properties of ion-acoustic waves in space plasma and its application to image encryption. IEEE Access 9:18762–18782
Thodberg HH, Kreiborg S, Juul A, Pedersen KD (2009) The bonexpert method for automated determination of skeletal maturity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(1):52–66
Tong C, Liang B, Li J, Zheng Z (2018) A deep automated skeletal bone age assessment model with heterogeneous features learning. J Med Syst 42(12):249
Varma RK, Rahman SA, Atodaria V, Mohan S, Vanderheide T (2016) Technique for fast detection of short circuit current in PV distributed generator. IEEE Power Energy Technol Syst J 11
Zarie M, Jahedsaravani A, Massinaei M (2020) Flotation froth image classification using convolutional neural networks. Miner Eng 155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshmukh, S., Khaparde, A. Multi-objective segmentation approach for bone age assessment using parameter tuning-based U-net architecture. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 6755–6800 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11793-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11793-0