Abstract
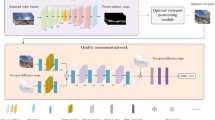
360-degree videos, also known as omnidirectional or panoramic videos, provide the user an immersive experience that 2D videos cannot provide. It is crucial to access the perceived quality of the 360-degree video. 2D video quality assessment (VQA) methods are unsuitable for 360-degree videos. There are few 360-degree video quality assessment (360VQA) methods. This paper proposes a multi-viewport based 3D convolutional neural network for 360VQA (3D-360VQA). First, it is easy to divide the 2D planar video into rectangular blocks as video patches in order to adapt to a deep neural network. The way to form the video patch in a 2D planar video is unsuitable for a 360-degree video. Thus, a multiple viewports based video patch forming method is proposed. Second, although the deep neural networks have achieved great success in image quality assessment (IQA), there are few deep neural networks for 360VQA. A 3D convolution based deep neural network is proposed to predict the perceived quality of 360-degree videos. The publicly available 360-degree videos datasets are used to evaluate the proposed method. The experimental results show that the proposed method is suitable for the 360-degree video and outperforms other existing methods, which verifies the effectiveness of our network architecture.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosse S, Maniry D, Müller KR, Wiegand T, Samek W (2018) Deep neural networks for no-reference and full-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(1):206–219
Chen D, Wang Y, Gao W (2020) No-reference image quality assessment: an attention driven approach. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:6496–6506
Chen S, Zhang Y, Li Y, Chen Z, Wang Z (2018) Spherical structural similarity index for objective omnidirectional video quality assessment. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Multimedia Expo (ICME), San Diego, California, United States, pp 1–6
Chen Z, Liao N, Gu X, Wu F, Shi G (2016) Hybrid distortion ranking tuned bitstream-layer video quality assessment. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 26(6):1029–1043
Daly SJ (1992) Visible differences predictor: an algorithm for the assessment of image fidelity. In: Rogowitz BE (ed) Human vision, visual processing, and digital display III, vol 1666. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE, San Jose, CA, United States, pp 2–15
Dinh KQ, Lee J, Kim J, Park Y, Choi KP, Park J (2018) Only-reference video quality assessment for video coding using convolutional neural network. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Image Process (ICIP), Athens, Greece, pp 2496–2500
Ferzli R, Karam LJ (2009) A no-reference objective image sharpness metric based on the notion of just noticeable blur (JNB). IEEE Trans Image Process 18(4):717–728
Final report from the video quality experts group on the validation of objective models of video quality assessment, Phase I (FR-TV1) (2000)
Gao F, Yu J, Zhu S, Huang Q, Tian Q (2018) Blind image quality prediction by exploiting multi-level deep representations. Pattern Recogn 81:432–442
Girod B (1993) What’s Wrong with Mean-Squared Error?. MIT Press, Cambridge
Golestaneh SA, Chandler DM (2014) No-reference quality assessment of JPEG images via a quality relevance map. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(2):155–158
Hu S, Jin L, Wang H, Zhang Y, Kwong S, Kuo CCJ (2017) Objective video quality assessment based on perceptually weighted mean squared error. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27(9):1844–1855
Jiang Q, Shao F, Lin W, Jiang G (2019) BLIQUE-TMI: Blind Quality evaluator for tone-mapped images based on local and global feature analyses. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(2):323–335
Kang L, Ye P, Li Y, Doermann D (2014) Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment. In: Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit (CVPR), Columbus, OH, United States, pp 1733–1740
Kelly DH (1979) Motion and vision. II. Stabilized spatio-temporal threshold surface. J Opt Soc Am 69(10):1340–1349
Kim H, Kim J, Oh T, Lee S (2017) Blind sharpness prediction for ultra high-definition video based on human visual resolution. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27(5):951–964
Kim J, Nguyen AD, Lee S (2019) Deep CNN-based blind image quality predictor. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(1):11–24
Kim J, Zeng H, Ghadiyaram D, Lee S, Zhang L, Bovik AC (2017) Deep convolutional neural models for picture-quality prediction: Challenges and solutions to data-driven image quality assessment. IEEE Signal Process Mag 34 (6):130–141
Kim MC (2016) Fourier-domain analysis of display pixel structure for image quality. J Display Technol 12(2):185–194
Laparra V, Muñoz-Marí J, Malo J (2010) Divisive normalization image quality metric revisited. J Opt Soc Am A 27(4):852–864
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Orr GB, Müller KR (1998) Efficient BackProp. Springer, Berlin, pp 9–50
Lee S, Pattichis MS, Bovik AC (2002) Foveated video quality assessment. IEEE Trans Multimedia 4(1):129–132
Li L, Lin W, Wang X, Yang G, Bahrami K, Kot AC (2016) No-reference image blur assessment based on discrete orthogonal moments. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(1):39–50
Li S, Ma L, Ngan KN (2012) Full-reference video quality assessment by decoupling detail losses and additive impairments. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 22(7):1100–1112
Li Y, Po LM, Feng L, Yuan F (2016) No-reference image quality assessment with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Digit Signal Process (DSP), Beijing, China, pp 685–689
Liu H, Heynderickx I (2009) A perceptually relevant no-reference blockiness metric based on local image characteristics. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2009 (263540):1–14
Liu H, Heynderickx I (2011) Visual attention in objective image quality assessment: based on eye-tracking data. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 21 (7):971–982
Liu H, Klomp N, Heynderickx I (2010) A no-reference metric for perceived ringing artifacts in images. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 20 (4):529–539
Liu Y, Gu K, Zhai G, Liu X, Zhao D, Gao W (2017) Quality assessment for real out-of-focus blurred images. J Vis Commun Image Represent 46:70–80
Masry M, Hemami SS, Sermadevi Y (2006) A scalable wavelet-based video distortion metric and applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 16(2):260–273
Narvekar ND, Karam LJ (2011) A no-reference image blur metric based on the cumulative probability of blur detection (CPBD). IEEE Trans Image Process 20(9):2678–2683
Oh T, Park J, Seshadrinathan K, Lee S, Bovik AC (2014) No-reference sharpness assessment of camera-shaken images by analysis of spectral structure. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(12):5428–5439
Po LM, Liu M, Yuen WYF, Li Y, Xu X, Zhou C, Wong PHW, Lau KW, Luk HT (2019) A novel patch variance biased convolutional neural network for no-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(4):1223–1229
Roodaki H, Hashemi MR, Shirmohammadi S (2012) A new methodology to derive objective quality assessment metrics for scalable multiview 3D video coding. ACM Trans Multimedia Comput Commun Appl 8(3s):44:1–44:25
Saha A, Wu QMJ (2015) Utilizing image scales towards totally training free blind image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(6):1879–1892
Seshadrinathan K, Bovik AC (2010) Motion tuned spatio-temporal quality assessment of natural videos. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(2):335–350
Sheikh HR, Bovik AC, Cormack L (2005) No-reference quality assessment using natural scene statistics: JPEG2000. IEEE Trans Image Process 14 (1):1918–1927
Sinno Z, Bovik AC (2019) Large-scale study of perceptual video quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(2):612–627
Su YC, Grauman K (2018) Learning compressible 360° video isomers. In: Proc. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recognit (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, pp 7824–7833
Sun W, Gu K, Luo W, Min X, Zhai G, Ma S, Yang X (2019) MC360IQA: A multi-channel CNN for blind 360-degree image quality assessment. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Circuits Syst. (ISCAS), Sapporo, Japan, pp 1–5
Sun Y, Lu A, Yu L (2016) AHG8: WS-PSNR For 360 video objective quality evaluation. In: Document JVET-d0040, 4th JVET meeting. Chengdu, CN
Sun Y, Lu A, Yu L (2017) Weighted-to-spherically uniform quality evaluation for omnidirectional video. IEEE Signal Process Lett 24(9):1408–1412
Tang Z, Zheng Y, Gu K, Liao K, Wang W, Yu M (2019) Full-reference image quality assessment by combining features in spatial and frequency domains. IEEE Trans Broadcast 65(1):138–151
Tran D, Bourdev L, Fergus R, Torresani L, Paluri M (2015) Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, pp 4489–4497
Wang S, Jin K, Lu H, Cheng C, Ye J, Qian D (2016) Human visual system-based fundus image quality assessment of portable fundus camera photographs. IEEE Trans Med Imag 35(4):1046–1055
Wang Y, Shuai Y, Zhu Y, Zhang J, An P (2019) Jointly learning perceptually heterogeneous features for blind 3D video quality assessment. Neurocomputing 332:298–304
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Evans BL (2000) Blind measurement of blocking artifacts in images. In: Proc. IEEE Int Conf Image Process (ICIP), vol 3, Chengdu, CN, pp 981–984
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Lu L, Kouloheris JL (2001) Foveated wavelet image quality index. In: Tescher AG (ed) Applications of Digital Image Processing XXIV, vol 4472. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE, San Diego, CA, United States, pp 42–52
Wu Q, Li H, Meng F, Ngan KN, Luo B, Huang C, Zeng B (2016) Blind image quality assessment based on multichannel feature fusion and label transfer. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 26(3):425–440
Xu M, Li C, Chen Z, Wang Z, Guan Z (2019) Assessing visual quality of omnidirectional videos. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29 (12):3516–3530
Xu M, Li C, Liu Y, Deng X, Lu J (2017) A subjective visual quality assessment method of panoramic videos. In: Proc. IEEE Int Conf Multimedia Expo (ICME), Hong Kong, pp 517–522
Yan Q, Gong D, Zhang Y (2019) Two-stream convolutional networks for blind image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(5):2200–2211
You J, Ebrahimi T, Perkis A (2014) Attention driven foveated video quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(1):200–213
Yu M, Lakshman H, Girod B (2015) A framework to evaluate omnidirectional video coding schemes. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Mixed Augment. Real. (ISMAR), Fukuoka, Japan, pp 31–36
Zakharchenko V, Choi KP, Park JH (2016) Quality metric for spherical panoramic video. In: Iftekharuddin KM, Awwal AAS, Vázquez MG, Márquez A, Matin MA (eds) Optics and Photonics for Information Processing X, vol 9970. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE, San Diego, CA, United States, pp 57–65
Zhang F, Bull DR (2016) A perception-based hybrid model for vdeo quality assessment. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 26(6):1017–1028
Zhang F, Lin W, Chen Z, Ngan KN (2013) Additive log-logistic model for networked video quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 22 (4):1536–1547
Zhang L, Shen Y, Li H (2014) VSI: A visual saliency-induced index for perceptual image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(10):4270–4281
Zhang W, Borji A, Wang Z, Callet PL, Liu H (2016) The application of visual saliency models in objective image quality assessment: a statistical evaluation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(6):1266–1278
Zhang W, Ma K, Yan J, Deng D, Wang Z (2020) Blind image quality assessment using a deep bilinear convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30(1):36–47
Zhou C, Li Z, Osgood J, Liu Y (2018) On the effectiveness of offset projections for 360-degree video streaming. ACM Trans Multimedia Comput Commun Appl 14(3s):62:1–62:24
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China under Grant 2019J01046.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Huang, L. & Chien, WC. Multi-viewport based 3D convolutional neural network for 360-degree video quality assessment. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 16813–16831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12073-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12073-1