Abstract
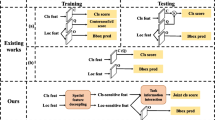
Leveraging the contextual information at instance-level can improve the accuracy in object detection. However, the-state-of-the-art object detection systems still detect each target individually without using contextual information. One reason is that contextual information is difficult to model. To solve this problem, the object relation module based on one-stage object detectors helps the object detectors learn the correlations between objects. It extracts and fuses the feature maps from various layers, including geometric features, categorical features, and appearance features, a transformation driven by visual attention mechanism are then performed to generate instance-level primary object relation features. Furthermore, a lightweight subnet is used to generate new feature prediction layer based on primary relation features and fused with the original detection layer to improve the detection ability. It does not require excessive amounts of computations and additional supervision and it can be easily ported to different one-stage object detection frameworks. The relation module is added to several one-stage object detectors (YOLO, Retinanet, and FCOS) as demonstrations and evaluate it on MS-COCO benchmark dataset after training. The results show that the relation module effectively improves the accuracy in one-stage object detection pipelines. Specifically, the relation module gives a 2.4 AP improvement for YOLOv3, 1.8 AP improvement for Retinanet and 1.6 AP improvement for FCOS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ba J, Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K (2014) Multiple Object recognition with visual attention[J]. Computer ence
Bochkovskiy A, Wang CY, Liao HYM (2020) Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934
Cai Z, Vasconcelos N (2017) Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality Object Detection[J]
Chen X , Gupta A . Spatial memory for context reasoning in Object Detection[J]. IEEE, 2017.
Divvala SK, Hoiem D, Hays J H, et al. (2009) An empirical study of context in object detection[J]. Proceedings / CVPR, IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1271–1278
Everingham M, Eslami S, Gool LV et al (2015) The Pascal visual Object classes challenge: a retrospective[J]. Int J Comput Vis 111(1):98–136
Felzenszwalb P (2010) F, et al. Object Detection with discriminatively trained part-based models.[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 32(9):1627–1645
Fu J , Zheng H, Tao M (2017) Look closer to see better: recurrent attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition[C]// IEEE conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE
Fu CY, Liu W, Ranga A, et al. (2017) DSSD : Deconvolutional single shot detector[J]
Galleguillos C , Rabinovich A , Belongie S (2008) Object categorization using co-occurrence, location and appearance[C]// 2008 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR 2008), 24–26 June 2008, Anchorage, Alaska, USA. IEEE
Gao Z, Zhang H, Dong S, et al. (2020) Salient Object Detection in the Distributed Cloud-Edge Intelligent Network[J]. IEEE Network, PP(99):1–9
Girshick R (2015) Fast R-CNN[J]. Computer Science
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 770–778
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. (2017) Mask r-cnn[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision 2961–2969.
Hu H , Gu J , Zhang Z , et al. Relation Networks for Object Detection[J]. 2018.
Huang J, Rathod V, Chen S, et al. (2016) Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors[J]. IEEE
Jie H , Li S , Gang S , et al. (2017) Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, PP(99).
Kong T, Sun F, Liu H, et al. (2020) FoveaBox: Beyound Anchor-Based Object Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing PP(99):1–1
Krishna R , Zhu Y , Groth O, Johnson J., Hata K., Kravitz J., Chen S., Kalantidis Y., Li L.J., Shamma D. A., Bernstein M. S., Fei-Fei L. Visual Genome: Connecting Language and Vision Using Crowdsourced Dense Image Annotations[J]. Int J Comput Vis, 2017, 123(1), 123, 123(73.
Law H, Deng J (2020) CornerNet: detecting objects as paired Keypoints[J]. Int J Comput Vis 128(3):642–656
LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker JS, Henderson D, Howard RE, Hubbard W, Jackel LD (1989) Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Comput 1(4):541–551
Lee SJ, Lee S, Cho SI, Kang SJ (2020) Object Detection-based video retargeting with spatial–temporal consistency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 30(12):4434–4439
Li J, Wei Y, Liang X, Dong J, Xu T, Feng J, Yan S (2016) Attentive contexts for object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 19(5):944–954
Li Y, Qi H, Dai J, et al. (2017) Fully convolutional instance-aware semantic segmentation[C]// Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S et al (2014) Microsoft COCO: common objects in context[J]. Springer International Publishing
Lin TY, Goyal P, Girshick R et al (2017) Focal loss for dense Object Detection[C]// IEEE transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence. IEEE:2999–3007
Lin TY, Dollar P, Girshick R, et al. (2017) Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection[J]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Liu W , Anguelov D , Erhan D, et al. (2016) SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]// European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham
Mottaghi R , Chen X , Liu X, et al. (2014) The role of context for Object Detection and semantic segmentation in the wild[C]// Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE
Oliva A, Torralba A, Castelhano MS, et al. (2003) Top-down control of visual attention in object detection[C]// International Conference on Image Processing. IEEE, :I-253-6
Redmon J , Farhadi A (2017) YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger[C]// IEEE. IEEE, 6517–6525.
Redmon J , Farhadi A (2018) YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement[J]. arXiv e-prints
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. (2016) You only look once: unified, real-time Object Detection[J]. Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time Object Detection with region proposal Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 39(6):1137–1149
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg AC, Fei-Fei L (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Shrivastava A, Sukthankar R, Malik J, et al. (2016) Beyond skip connections: top-down modulation for Object Detection[J]
Stewart R, Andriluka M, Ng AY (2016) End-to-end people detection in crowded scenes[C]// Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE
Tian Z, Shen C, Chen H, et al. (2020) FCOS: fully convolutional one-stage Object Detection[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE
Torralba A, Murphy KP, Freeman WT et al (2003) Context-based vision system for place and object recognition[C]//computer vision, IEEE international conference on. IEEE Computer Society 2:273–273
Tu Z (2008) Auto-context and its application to high-level vision tasks[C]// IEEE conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. (2017) Attention is all you need[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03762
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R et al (2015) Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention[J]. Computer Science:2048–2057
Zhang N , Donahue J , Girshick R, et al. (2014) Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category Detection[J]. European Conference on Computer Vision
Zhou X, Wang D, Krhenbühl P (2019) Objects as Points[J]
Zhu C, He Y, Savvides M (2019) Feature Selective Anchor-Free Module for Single-Shot Object Detection[C]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, W., Han, J. & Liu, G. Instance-level Object relation module for one-stage Object Detection. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 8617–8632 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12264-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12264-w