Abstract
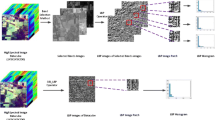
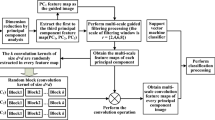
Hyperspectral images (HSIs) have been widely used to study earth surface phenomena. Traditionally, spectral features have been used to classify hyperspectral images, which result in noisy classified maps. Researchers have demonstrated that spatial information, such as local covariance matrix features, can enhance classification accuracy by providing complementary information. It can be proved that the covariance matrix is represented as the linear kernel function and can only model linear dependencies and does not contain any information about higher-order statistics that are important in HSI classification. To address this issue, this paper proposes a new method for classifying hyperspectral images based on weighted local kernel matrix features (WLKM) and improved binary grey wolf optimization (IBGWO). Spatial features, with the capability of modeling complicated nonlinear relationships between features, are first produced based on WLKM features. Then, the proposed method follows an improved binary grey wolf optimization algorithm based on a modified crossover operator to select the most informative features from spatial-spectral features vectors which are resulted from stacked WLKM and spectral features. Experiments on the three hyperspectral images named Indian Pines, Pavia University, and Salinas show that the proposed method can efficiently classify HSI and has better performance than some state-of-the-art spatial-spectral classification methods.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi SA, Mehrshad N (2020) Spectral-spatial feature extraction method for hyperspectral images classification using multiscale superpixel and covariance map. Geocarto Int:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1734874
Audebert N, Le Saux B, Lefèvre S (2019) Deep learning for classification of hyperspectral data: a comparative review. IEEE Geosci Remote Sensing Magazine 7(2):159–173. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2019.2912563
Beirami BA, Mokhtarzade M (2019) Spatial-spectral random patches network for classification of hyperspectral images. Traitement du Signal 36(5):399–406. https://doi.org/10.18280/ts.360504
Beirami B A, and Mokhtarzade M (2020) Spatial-spectral classification of hyperspectral images based on multiple fractal-based features. Geocarto International: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1713232
Cheng G, Yang C, Yao X, Guo L, Han J (2018) When deep learning meets metric learning: remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative CNNs. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(5):2811–2821. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2783902
Cheng G, Li Z, Han J, Yao X, Guo L (2018) Exploring hierarchical convolutional features for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(11):6712–6722. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2841823
Dalla Mura M, Atli Benediktsson J, Waske B, Bruzzone L (2010) Extended profiles with morphological attribute filters for the analysis of hyperspectral data. Int J Remote Sens 31(22):5975–5991. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2010.512425
Duan P, Ghamisi P, Kang X, Rasti B, Li S, Gloaguen R (2020) Fusion of dual spatial information for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(9):7726–7738. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.3031928
Emary E, Zawbaa HM, Hassanien AE (2016) Binary grey wolf optimization approaches for feature selection. Neurocomputing 172:371–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.06.083
Fang L, He N, Li S, Plaza AJ, Plaza J (2018) A new spatial–spectral feature extraction method for hyperspectral images using local covariance matrix representation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(6):3534–3546. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2801387
Faraki M, Harandi M T, and Porikli F (2015) Approximate infinite-dimensional region covariance descriptors for image classification. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2015.7178193
Faris H, Aljarah I, Al-Betar MA, Mirjalili S (2018) Grey wolf optimizer: a review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput & Applic 30(2):413–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3272-5
Ghamisi P, Souza R, Benediktsson JA, Rittner L, Lotufo R, Zhu XX (2016) Hyperspectral data classification using extended extinction profiles. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(11):1641–1645. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600244
Guan D, Xiang D, Tang X, Wang L, Kuang G (2019) Covariance of textural features: a new feature descriptor for SAR image classification. IEEE J Selected Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sensing 12(10):3932–3942. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2944943
Hao Q, Sun B, Li S, Crawford MM, Kang X (2021) Curvature filters-based multiscale feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3091860
He N, Paoletti ME, Haut JM, Fang L, Li S, Plaza A, Plaza J (2018) Feature extraction with multiscale covariance maps for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(2):755–769. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2860464
Hong D, Wu X, Ghamisi P, Chanussot J, Yokoya N, and Zhu, X.X (2020) Invariant attribute profiles: a spatial-frequency joint feature extractor for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58(6): 3791–3808. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2957251
Hu P, Pan JS, Chu SC (2020) Improved binary grey wolf optimizer and its application for feature selection. Knowl-Based Syst 195:105746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105746
Imani M, Ghassemian H (2020) An overview on spectral and spatial information fusion for hyperspectral image classification: current trends and challenges. Inform Fusion 59:59–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.01.007
Iyer P, Sriram A, Lal S (2021) Deep learning ensemble method for classification of satellite hyperspectral images. Remote Sensing Appl: Soc Environ 23:100580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100580
Ma B, Su Y, Jurie F (2014) Covariance descriptor based on bio-inspired features for person re-identification and face verification. Image Vis Comput 32(6–7):379–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2014.04.002
Malik MRS, Mohideen ER, Ali L (2015) Weighted distance grey wolf optimizer for global optimization problems. IEEE Int Conf Comput Intell Comput Res (ICCIC). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCIC.2015.7435714
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Moujahid A, Dornaika F (2020) Multi-scale multi-block covariance descriptor with feature selection. Neural Comput & Applic 32(10):6283–6294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04135-7
Niazmardi S (2019) A spatial-spectral classification strategy for very high-resolution images using region covariance descriptors and multiple kernel learning algorithms. Earth observation and geomatics. Engineering 3(2):92–98. https://doi.org/10.22059/eoge.2020.285999.1057
Pang Y, Yuan Y, Li X (2008) Gabor-based region covariance matrices for face recognition. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 18(7):989–993. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2008.924108
Sun Y, Fu Z, Fan L (2019) A novel hyperspectral image classification pattern using random patches convolution and local covariance. Remote Sens 11(16):1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11161954
Tuzel O, Porikli F, Meer P (2006) Region covariance: a fast descriptor for detection and classification. Eur Conf Comput Vision Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/11744047_45
Wang L, Zhang J, Zhou L, Tang C, Li W (2015) Beyond covariance: feature representation with nonlinear kernel matrices. Proceed IEEE Int Conf Comput Vision. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.519
Wei W, Jia Q, Feng Y, Chen G (2018) Emotion Recognition Based on Weighted Fusion Strategy of Multichannel Physiological Signals. Comput Intell Neurosci 2018: ID 5296523, 9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5296523
Xu Y, Du B, Zhang F, Zhang L (2018) Hyperspectral image classification via a random patches network. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 142:344–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.05.014
Yang W, Peng J, Sun W, Du Q (2019) Log-euclidean kernel-based joint sparse representation for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J Selected Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sensing 12(12):5023–5034. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2952408
Yue J, Zhao W, Mao S, Liu H (2015) Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral images using deep convolutional neural networks. Remote Sensing Letters 6(6):468–477. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2015.1047045
Zhang Y, Li S (2011) Gabor-LBP based region covariance descriptor for person re-identification. IEEE Sixth Int Conf Image Graphics. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIG.2011.40
Zhang J, Wang L, Zhou L, Li W (2021) Beyond covariance: Sice and kernel based visual feature representation. Int J Comput Vis 129(2):300–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01376-1
Zhao G, Li N, Tu B, Zhang G, He W (2019) Density peak covariance matrix for feature extraction of hyperspectral image. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 17(3):534–538. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2019.2926396
Zheng J, Feng Y, Bai C, Zhang J (2020) Hyperspectral image classification using mixed convolutions and covariance pooling. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(1):522–534. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.2995575
Zhou P, Han J, Cheng G, Zhang B (2019) Learning compact and discriminative stacked autoencoder for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(7):4823–4833. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2893180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beirami, B.A., Mokhtarzade, M. Optimized weighted local kernel features for hyperspectral image classification. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 21859–21885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12452-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12452-8