Abstract
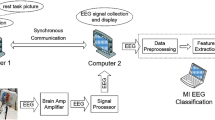
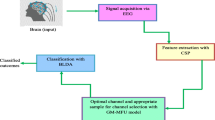
Multichannel Electroencephalography-based Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) systems facilitate a communicating medium between the human brain and the outside world. BCI systems aim to translate human intentions into computer-based control commands by decoding the respective brain patterns. Moreover, Electroencephalography (EEG) analysis involves high-dimensional features that increase the computational burden of applied signal processing approaches. To minimize this overload caused by a large set of channels, we propose an automatic EEG channel selection method for multiclass Motor-Imagery (MI) classification. In this study, we developed a hybrid channel ranking procedure using Fisher information and the objective Firefly Algorithm (FA). Firstly, the preprocessed neural signals are used to extract spatial-temporal features using the Regularized Common Spatial Pattern with Aggregation (RCSPA) method. Then, objective FA with two input variables (Spectral Entropy and Lyapunov exponent) is used to compute a weighted score for each channel in the neighborhood of a candidate solution. Finally, a novel Channel Set Relevance Index (CSRI) is developed to rank channels using their respective weighted score and Fisher information. The RCSPA features of highly ranked channels are employed to discriminate different MI-tasks using the Regularized Support Vector Machine (RSVM) classifier. The proposed approach is cross-validated on three publicly available BCI competition datasets (BCI Competition IV- 2008 - IIA, BCI Competition IV- dataset 1, BCI competition III - dataset IVa) with varying numbers of channels. The validation results show that the proposed method achieved a superior classification accuracy (83.97% on dataset 1, 80.85% on dataset 2, and 84.19% on dataset 3) with fewer channels than other baseline methods. In addition, our method significantly reduced the BCI preparation time, making it effective to conduct multiple experimental sessions for a large pool of subjects.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Rani A, Singh V, Mittal AP (2017) EEG signal enhancement using cascaded S-Golay filter. Biomed Signal Process Control 36:194–204
Alotaiby T, Abd El-Samie FE, Alshebeili SA, Ahmad I (2015) A review of channel selection algorithms for EEG signal processing. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2015(1):1–21
Alyasseri ZAA, Khader AT, Al-Betar MA, Alomari OA (2020) Person identification using EEG channel selection with hybrid flower pollination algorithm. Pattern Recogn 105:107393
Amin SU, Alsulaiman M, Muhammad G, Mekhtiche MA, Hossain MS (2019) Deep learning for EEG motor imagery classification based on multi-layer CNNs feature fusion. Futur Gener Comput Syst 101:542–554
Aydemir O, Ergün E (2019) A robust and subject-specific sequential forward search method for effective channel selection in brain computer interfaces. J Neurosci Methods 313:60–67
Baig MZ, Aslam N, Shum HP (2020) Filtering techniques for channel selection in motor imagery EEG applications: a survey. Artif Intell Rev 53(2):1207–1232
Bauer S, Nolte LP, Reyes M (2011, September) Fully automatic segmentation of brain tumor images using support vector machine classification in combination with hierarchical conditional random field regularization. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (pp. 354-361). Springer: Heidelberg
Bein B (2006) Entropy. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 20(1):101–109
Beraldo G, Antonello M, Cimolato A, Menegatti E, Tonin L (2018, May) Brain-computer Interface meets ROS: a robotic approach to mentally drive telepresence robots. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (pp. 4459-4464). IEEE
Blankertz B, Muller KR, Krusienski DJ, Schalk G, Wolpaw JR, Schlogl A, Pfurtscheller G, Millan JR, Schroder M, Birbaumer N (2006) The BCI competition III: validating alternative approaches to actual BCI problems. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehab Eng 14(2):153–159
Brunner C, Leeb R, Müller-Putz G, Schlögl A, Pfurtscheller G (2008) BCI competition 2008–Graz data set A. Institute for Knowledge Discovery (Laboratory of Brain-Computer Interfaces), Graz University of Technology, 16, 1–6
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 2(3):1–27
Chen Z, Wu C, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Ran B, Zhong M, Lyu N (2015) Feature selection with redundancy-complementariness dispersion. Knowl-Based Syst 89:203–217
Corsi MC, Chavez M, Schwartz D, Hugueville L, Khambhati AN, Bassett DS, De Vico Fallani F (2019) Integrating EEG and MEG signals to improve motor imagery classification in brain–computer interface. Int J Neural Syst 29(01):1850014
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134(1):9–21
Fauzi H, Shapiai MI, Abdullah SS, Ibrahim Z (2018, December) Automatic energy extraction methods for EEG channel selection. In: 2018 International Conference on Control, Electronics, Renewable Energy and Communications (ICCEREC) (pp. 70-75). IEEE
Feng JK, Jin J, Daly I, Zhou J, Niu Y, Wang X, Cichocki A (2019) An optimized channel selection method based on multifrequency CSP-rank for motor imagery-based BCI system. Comput Intell Neurosci 2019
Gaur P, Pachori RB, Wang H, Prasad G (2018) A multiclass EEG-based BCI classification using multivariate empirical mode decomposition based filtering and Riemannian geometry. Expert Syst Appl 95:201–211
Ghaemi A, Rashedi E, Pourrahimi AM, Kamandar M, Rahdari F (2017) Automatic channel selection in EEG signals for classification of left or right hand movement in brain computer interfaces using improved binary gravitation search algorithm. Biomed Signal Process Control 33:109–118
Gonzalez A, Nambu I, Hokari H, Wada Y (2014) EEG channel selection using particle swarm optimization for the classification of auditory event-related potentials. Sci World J (2014) 350270, https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/350270
Gorry PA (1990) General least-squares smoothing and differentiation by the convolution (Savitzky-Golay) method. Anal Chem 62(6):570–573
Hancer E, Xue B, Zhang M (2018) Differential evolution for filter feature selection based on information theory and feature ranking. Knowl-Based Syst 140:103–119
Handiru VS, Prasad VA (2016) Optimized bi-objective EEG channel selection and cross-subject generalization with brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Human-Mach Syst 46(6):777–786
Hastie T, Rosset S, Tibshirani R, Zhu J (2004) The entire regularization path for the support vector machine. J Mach Learn Res 5:1391–1415
Hsu H, Lachenbruch PA (2008) Paired t test. Wiley Encyclopedia of Clinical Trials, 1–3, https://doi.org/10.1002/0470011815.b2a15112
Joseph AFA, Govindaraju C (2019) Channel selection using glow swarm optimization and its application in line of sight secure communication. Clust Comput 22(5):10801–10808
Kantz H (1994) A robust method to estimate the maximal Lyapunov exponent of a time series. Phys Lett A 185(1):77–87
Kee CY, Ponnambalam SG, Loo CK (2015) Multiobjective genetic algorithm as channel selection method for P300 and motor imagery data set. Neurocomputing 161:120–131
Khaire UM, Dhanalakshmi R (2019) Stability of feature selection algorithm: a review. J King Saud Univ-Comput Inf Sci
Lan T, Erdogmus D, Adami A, Pavel M, Mathan S (2006, January) Salient EEG channel selection in brain computer interfaces by mutual information maximization. In: 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference (pp. 7064–7067). IEEE
Li Y, Pan J, Wang F, Yu Z (2013) A hybrid BCI system combining P300 and SSVEP and its application to wheelchair control. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(11):3156–3166
Chang C-C, Lin C-J (2001) LIBSVM a library for support vector machines. Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm
Lin X, Yang F, Zhou L, Yin P, Kong H, Xing W, Lu X, Jia L, Wang Q, Xu G (2012) A support vector machine-recursive feature elimination feature selection method based on artificial contrast variables and mutual information. J Chromatogr B 910:149–155
Liu J, Meng H, Li M, Zhang F, Qin R, Nandi AK (2018) Emotion detection from EEG recordings based on supervised and unsupervised dimension reduction. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 30(23):e4446
Lu H, Eng HL, Guan C, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2010) Regularized common spatial pattern with aggregation for EEG classification in small-sample setting. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(12):2936–2946
McKight PE, Najab J (2010) Kruskal–wallis test. In: The corsini encyclopedia of psychology, Wiley, New York, 1–1
Meisheri H, Ramrao N, Mitra S (2018) Multiclass common spatial pattern for EEG based brain computer interface with adaptive learning classifier. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.09046
Mohamed EA, Yusoff MZ, Malik AS, Bahloul MR, Adam DM, Adam IK (2018) Comparison of EEG signal decomposition methods in classification of motor-imagery BCI. Multimed Tools Appl 77(16):21305–21327
Politi A (2013) Lyapunov exponent. Scholarpedia 8(3):2722
Press WH, Teukolsky SA (1990) Savitzky-Golay smoothing filters. Comput Phys 4(6):669–672
Pudil P, Novovičová J, Kittler J (1994) Floating search methods in feature selection. Pattern Recogn Lett 15(11):1119–1125
Qiu Z, Jin J, Lam HK, Zhang Y, Wang X, Cichocki A (2016) Improved SFFS method for channel selection in motor imagery based BCI. Neurocomputing 207:519–527
Rissanen JJ (1996) Fisher information and stochastic complexity. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 42(1):40–47
Schröder M, Lal TN, Hinterberger T, Bogdan M, Hill NJ, Birbaumer N, Rosenstiel W, Schölkopf B (2005) Robust EEG channel selection across subjects for brain-computer interfaces. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2005(19):1–10
Schwemmer MA, Skomrock ND, Sederberg PB, Ting JE, Sharma G, Bockbrader MA, Friedenberg DA (2018) Meeting brain–computer interface user performance expectations using a deep neural network decoding framework. Nat Med 24(11):1669–1676
Shi B, Wang Q, Yin S, Yue Z, Huai Y, Wang J (2021) A binary harmony search algorithm as channel selection method for motor imagery-based BCI. Neurocomputing 443:12–25
Sreeja SR, Samanta D (2020) Distance-based weighted sparse representation to classify motor imagery EEG signals for BCI applications. Multimed Tools Appl 79(19):13775–13793
Su Y, Li Y, Wang S (2015, July) Filter ensemble regularized common spatial pattern for EEG classification. In: Seventh international conference on digital image processing (ICDIP 2015) (Vol. 9631, p. 963124). International Society for Optics and Photonics
Subhani AR, Mumtaz W, Kamil N, Saad NM, Nandagopal N, Malik AS (2017, December) MRMR based feature selection for the classification of stress using EEG. In: 2017 Eleventh International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST) (pp. 1-4). IEEE
Tangermann M, Müller KR, Aertsen A, Birbaumer N, Braun C, Brunner C, Leeb R, Mehring C, Miller KJ, Müller-Putz GR, Nolte G, Pfurtscheller G, Preissl H, Schalk G, Schlögl A, Vidaurre C, Waldert S, Blankertz B (2012) Review of the BCI competition IV. Front Neurosci 6:55
Tiwari A, Chaturvedi A (2019, November) A multiclass EEG signal classification model using spatial feature extraction and XGBoost algorithm. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (pp. 4169-4175). IEEE
Tiwari A, Chaturvedi A (2021) A Novel Channel selection method for BCI classification using Dynamic Channel relevance. IEEE Access 9:126698–126716
Wang L (2005) Support vector machines: theory and applications (Vol. 177). Springer Science & Business Media, 2005
Wang Y, Gao S, Gao X (2006, January) Common spatial pattern method for channel selelction in motor imagery based brain-computer interface. In: 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference (pp. 5392–5395). IEEE
Wang M, Qu W, Chen WY (2018) Hybrid sensing and encoding using pad phone for home robot control. Multimed Tools Appl 77(9):10773–10786
Wu SJ, Chow PT (1995) Steady-state genetic algorithms for discrete optimization of trusses. Comput Struct 56(6):979–991
Xue H, Chen S, Yang Q (2011) Structural regularized support vector machine: a framework for structural large margin classifier. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(4):573–587
Yang XS (2010) Firefly algorithm, stochastic test functions and design optimisation. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 2(2):78–84
Yang J, Singh H, Hines EL, Schlaghecken F, Iliescu DD, Leeson MS, Stocks NG (2012) Channel selection and classification of electroencephalogram signals: an artificial neural network and genetic algorithm-based approach. Artif Intell Med 55(2):117–126
Zgallai W, Brown JT, Ibrahim A, Mahmood F, Mohammad K, Khalfan M, ... & Hamood N (2019, March) Deep learning AI application to an EEG driven BCI smart wheelchair. In: 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET) (pp. 1–5). IEEE
Zhang A, Yang B, Huang L (2008, May) Feature extraction of EEG signals using power spectral entropy. In: 2008 International Conference on BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (Vol. 2, pp. 435-439). IEEE
Zhang Y, Zhou T, Wu W, Xie H, Zhu H, Zhou G, Cichocki A (2021) Improving EEG decoding via clustering-based multitask feature learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3053576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
For writing the article, the authors received academic infrastructure support from the Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi. Moreover, the authors also declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, A., Chaturvedi, A. Automatic EEG channel selection for multiclass brain-computer interface classification using multiobjective improved firefly algorithm. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 5405–5433 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12795-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12795-2