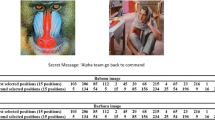
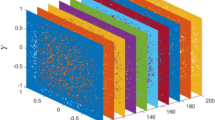
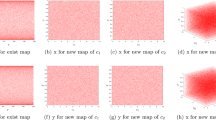
Abstract
The art of concealing information by embedding it in a seemingly “innocent” message is called steganography. An appropriate system for steganography is essential to guarantee the safety of the transfer file and, moreover, the size of the attached file is of great importance. Ergodic dynamical systems with confusion guarantee an acceptable level of security for cryptographic systems. Here, we suggest a new steganography algorithm based on a measurable dynamical system and a new chaotic S-box. We use two different chaotic maps at the same time to create the new S-box aimed at providing adequate key space and high security for the encryption. In the encryption stage, the message is encrypted with a new S-box. The capability of S-box and encryption has been confirmed by performance analysis. Our goal in adding this encryption step is to increase security and complicate the process to access the steganographic stage secret message. The pixel position of the cover color image is determined by using chaotic maps in the proposed algorithm, in which, a secret information bit can be hidden. By considering the key role in the security of cryptographic systems, an entropy calculation is presented to determine the chaotic area of the proposed system. The problems of the low security against some existing tests as well as the small key space may lead to the steganography failure, which can be fixed by the proposed algorithm. The contributions of the suggested steganography algorithm are as follows: (1) It allows us to use an ergodic coupled system that provides ample key space. (2) It uses an encryption step with new, well-performance S-boxes that provides high security. (3) The performance of the steganographic design performs better than previous works.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbdEl-Latif AA, Abd-El-Atty B, Elseuofi Sh, Khalifa HS, Alghamdi AS, Polat K, Amin M (2020) Secret images transfer in cloud system based on investigating quantum walks in steganography approaches, Physica a: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 541, pp 123687
Advanced encryption standard (aes), Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 197 Std
Agiza HN (2004) Chaos synchronization of lü dynamical system. Nonlinear analysis: Theory, Methods and Applications 58:11
Ahadpour S, Behnia S, Jafarizadeh MA, Ghasemi G (2009) Synchronization in pair-coupled maps with invariant measure. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simultions 14:2916
Ahadpour S, Hematpour N (2012) Quantum chaos in quantum dots coupled to bosons arXiv:1207.5590v1
Ali KM, Khan M (2019) Application based construction and optimization of substitution boxes over 2D mixed chaotic maps. Int J Theor Phys 58:3091–3117
Azoug SE, Bouguezel S (2016) A non-linear preprocessing for opto-digital image encryption using multiple-parameter discrete fractional Fourier transform. Opt Commun 359:85
Bai J, Ch Ch, Chang TS, Nguyen C, Zhu Y, Liu A (2017) High payload steganographic algorithm based on edge detection. Displays 46:42
Batool SI, Younas I, Khan M, Yaqoob N (2021) A new technique for the construction of confusion component based on inverse LA-semigroups and its application in steganography. Multimed Tools Appl, pp 1–21
Bender W, Gruhl D, Morimoto N, Lu A (1996) Techniques for data hiding. IBM Syst J 35:313
Biham E, Shamir A (1991) Differential cryptanalysis of des like cryptosystems. J. Cryptol. 4:3–72
Cavusoglu U, Kaçar S, Zengin A, Pehlivan I (2018) A novel hybrid encryption algorithm based on chaos and s-aes algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 91:939–956
Cheddad A, Condell J, Curran K, Mc Kevitt P (2010) Digital image steganography: Survey and analysis of current methods. Signal Process 90:727
Cui Q, Zhang Q, Qiu Z, Hu Z (2016) On the design of s-boxes. In: Conference on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques, chaos, solitons and fractals 87, pp. 158
Cusick T, Stanica P (2017) Cryptographic boolean functions and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Diaconu A-V (2016) Circular inter-intra pixels bit-level permutation and chaos-based image encryption. Inf Sci 355:314–327
Dorfman JR (1999) An introduction to chaos in nonequilibrium statistical mechanics Cambridge Lecture Notes in Physics
Gonzalez RC, Woods ER, Eddins SL (2010) Digital Image Processing Using Matlab, Prentice Hall Press, (Second Edition) 21, pp 797
Hakak S, Kamsin A, Tayan O, Idris MYI, Gilkar GA (2019) Approaches for preserving content integrity of sensitive online Arabic content: A survey and research challenges. Inf Process Manag 56:367–380
Hematpour N, Ahadpour S (2021) Execution examination of chaotic S-box dependent on improved PSO algorithm. Neural Comput & Applic 33 (10):5111–5133
Hematpour N, Ahadpour S, Behnia S (2021) Presence of dynamics of quantum dots in the digital signature using DNA alphabet and chaotic S-box. Multimed Tools Appl 80(7):10509–10531
Huang T, Zhang H (2016) Bifurcation, chaos and pattern formation in a space- and time-discrete predator-prey system Chaos. Solitons and Fractals 91:92
Hussain I, Tariq S, Muhammad A (2012) A novel approach for designing substitution-boxes based on nonlinear chaotic algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 70:1791–1794
Jafarizadeh MA, Behnia S (2002) Hierarchy of chaotic maps with an invariant measure. J Nonlinear Mathematical Phys 9:26
Jafarizadeh MA, Behnia S, Khorram S, Nagshara H (2001) Hierarchy of chaotic maps with an invariant measure. J Stat Phys 104:1013
Jafarizadeh MA, Foroutan M, Ahadpour S (2006) Hierarchy of rational order families of chaotic maps with an invariant measure. Pramana 67:1073–1086
Jithin K, Sankar S (2020) Colour image encryption algorithm combining, combining, Arnold map, DNA sequence operation, and a Mandelbrot set. J Inf Secur Appl 50:102428
Johnson NF, Jajodia S (1998) Exploring steganography: Seeing the unseen. IEEE Computer Journal 31:26
Kalita M, Tuithung TH, Majumder S (2019) A new steganography method using integer wavelet transform and least significant bit substitution. The Computer Journal 62:1639–1655
Kaneko K, Tsuda l (1996) Complex systems: Chaos and beyond: a construive approach with applications in life sdences, Fukuzatsukei no kaosu-teki shinario, The English edition righlS are granted by Asakura Publishing Co, Ltd., Tokyo
Kanso A, Ghebleh M (2017) An algorithm for encryption of secret images into meaningful images. Opt Lasers Eng 90:196
Kaur R, Singh B (2021) A novel approach for data hiding based on combined application of discrete cosine transform and coupled chaotic map. Multimed Tools Appl 80(10):14665–14691
Khan M, Shah T, Mahmood H, Asif M, Iqtadar G (2012) A novel technique for the construction of strong s-boxes based on chaotic lorenz systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 70:2303–2311
Kocarev L, Lian Sh (2011) Chaos-Based Cryptography theory, algorithms and applications, vol 397, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Kocarev L, Lian S (eds) (2011) Chaos-based cryptography: Theory, algorithms and applications (Vol. 354). Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin
Korba KA, Abed D, Fezari M (2021) Securing physical layer using new chaotic parametric maps. Multimed Tools Appl, pp 1–19
Laishram D, Tuithung T (2021) A novel minimal distortion-based edge adaptive image steganography scheme using local complexity. Multimed Tools Appl 80:831–854
Lambic D (2020) A new discrete-space chaotic map based on the multiplication of integer numbers and its application in s-box design. Nonlinear Dyn., pp 1–13
Lee CF, Huang YL (2012) An efficient image interpolation increasing payload in reversible data hiding. Expert Syst Appl 39:6712
Lee YP, Lee JCh, Chen WK, Chang KCh, Su IJ, Chang ChP (2012) High-payload image hiding with quality recovery using tri-way pixel-value differencing. Info Sci 191:214
Lee K, Westfeld A, Lee S (2007) Generalised category Attack—Improving Histogram-Based attack on JPEG LSB embedding. International Workshop on Information Hiding, p 378
Liu L, Xiao Sh, Zhang L, Bi M, Zhang Y, Fang J, Hu W (2017) Digital chaos-masked optical encryption scheme enhanced by two-dimensional key space. Opt Commun 398:62
Liu L, Zhang Q, Wei X (2012) A RGB image encryption algorithm based on DNA encoding and chaos map. Comput Electr Eng 38(5):1240–1248
Lv X, Liao X, Yang B (2018) A novel scheme for simultaneous image compression and encryption based on wavelet packet transform and multi-chaotic systems. Multimed Tools Appl 77(21):28633–28663
Matsui M (1993) Linear cryptanalysis method for des cipher, Workshop on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 386–397
Miri A, Faez K (2017) Adaptive image steganography based on transform domain via genetic algorithm. Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics 145:158
Mollaeefar M, Sharif A, Nazari M (2017) A novel encryption scheme for colored image based on high level chaotic maps. Multimed Tools Appl 76:607–629
Murugan G, Uthandipalayam Subramaniyam R (2020) Performance analysis of image steganography using wavelet transform for safe and secured transaction. Multimed Tools Appl 79:9101–9115
National Institute of Standards and Technology (1999) FIPS PUB 46-3: Data Encryption Standard (DES), Super-sedes FIPS 46-2
National institute of standard and technology statistical test (nist). http://www.nist.gov/
Nestor T, De Dieu NJ, Jacques K, Yves EJ, Iliyasu AM, El-Latif A, Ahmed A (2020) A multidimensional hyperjerk oscillator: dynamics analysis, analogue and embedded systems implementation, and its application as a cryptosystem. Sensors 20(1):83
Njitacke ZT, Isaac SD, Nestor T, Kengne J (2021) Window of multistability and its control in a simple 3D Hopfield neural network: application to biomedical image encryption. Neural Comput & Applic 33(12):6733–6752
Ozkaynak F, Yavuz S (2013) Designing chaotic S-boxes based on time-delay chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn. 74:551–557
Poornima R, Iswarya RJ (2013) An overview of digital image steganography. International Journal of Computer Science and Engineering Survey (IJCSES) 4:23
Pratt WK (2010) Digital image processing: Piks Scientific Inside, Wiley-Interscience, (4th edn.) pp 782
Ramalingam M, Isa NAM (2015) Fast retrieval of hidden data using enhanced hidden Markov model in video steganography. Appl Soft Comput 34:744
Ramalingam M, Isa NAM (2016) A data-hiding technique using scene-change detection for video steganography, Computers and Electrical Engineering. Comput Electr Eng 54:423
Reshma VK, Vinod Kumar RS (2020) Pixel Prediction-Based image steganography by support vector neural network. The Computer Journal bxaa017:1–18
Rukhin A, Soto J, Nechvatal J, Smid M, Barker E, Leigh S, Levenson M, Vangel M, Banks D, Heckert A, Dray J (2010) National institute of standards and technology (NIST) special publication 800-22. Revision 1a (NIST) 2010
Schneier B (2007) Applied cryptography: Protocols, algorithms, and source code in c Wiley
Scheinerman E (1996) Invitation to dynamical systems. Johns Hopkins university, Maryland
Shoeibi A, Ghassemi N, Alizadehsani R, Rouhani M, Hosseini-Nejad H, Khosravi A, Panahiazar M, Nahavandi S (2021) A comprehensive comparison of handcrafted features and convolutional autoencoders for epileptic seizures detection in EEG signals, Expert Systems with Applications, 163 p 113788
Shoeibi A, Khodatars M, Alizadehsani R, Ghassemi N, Jafari M, Moridian P, Khadem A, Sadeghi D, Hussain S, Zare A, Sani ZA (2020) Automated detection and forecasting of covid-19 using deep learning techniques:, A review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.10785
Shoeibi A, Khodatars M, Jafari M, Moridian P, Rezaei M, Alizadehsani R, Khozeimeh F, Gorriz JM, Heras J, Panahiazar M, Nahavandi S (2021) Applications of Deep Learning Techniques for Automated Multiple Sclerosis Detection Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Review. arXiv:2105.04881
Strogatz SH (2000) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos: with applications to physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering, vol 478. Westview Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Subhedar MS, Mankar VH (2016) Image steganography using redundant discrete wavelet transform and QR factorization. Comput Electr Eng 54:406–422
Tamang J, Nkapkop JDD, Ijaz MF, Prasad PK, Tsafack N, Saha A, Kengne J, Son Y (2021) Dynamical properties of ion-acoustic waves in space plasma and its application to image encryption. IEEE Access 9:18762–18782
Thanikaiselvan V, Arulmozhivarman P (2015) RAND—STEG: An integer wavelet transform domain digital image random steganography using knight’s tour. Secur Commun Netw 8:2374–2382
Trithemius J (1606) Steganographia. First printed edition, Frankfurt
Tsafack N, Kengne J, Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu AM, Hirota K, Abd EL-Latif AA (2020) Design and implementation of a simple dynamical 4-D chaotic circuit with applications in image encryption. Inf Sci 515:191–217
Tsafack N, Sankar S, Abd-El-Atty B, Kengne J, Jithin KC, Belazi A, Mehmood I, Bashir AK, Song OY, Abd El-Latif AA (2020) A new chaotic map with dynamic analysis and encryption application in internet of health things. IEEE Access 8:137731–137744
Wang X, Feng L, Zhao H (2019) Fast image encryption algorithm based on parallel computing system. Inf Sci 486:340–358
Wang X, Gao S (2020) Image encryption algorithm for synchronously updating boolean networks based on matrix semi-tensor product theory. Inf Sci 507:16–36
Wang ZX, Guo DR (1989) Special Functions, World Scientific Publishing, Singapour, New Jersey, London, Hong Kong, p 677
Webster A, Tavares S (1985) On the design of s-boxes. In: Conference on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques, springer, pp. 523-34
Wilf HS (1994) Algorithms and complexity. Summer., p 139
Wong KSh, Qi X, Tanaka K (2007) A DCT-based Mod4 steganographic method. Signal Process 87:1251
Yang F, Mou J, Ma Ch, Cao Y (2020) Dynamic analysis of an improper fractional-order laser chaotic system and its image encryption application, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 129, pp 106031
Yang ChH, Weng ChY, Wang ShJ, Sun HM (2010) Varied PVD + LSB evading detection programs to spatial domain in data embedding systems. J Syst Softw 83:1635
Zhang H, Ma T, Huang G, Wang Z (2009) Robust global exponential syn- chronization of uncertain chaotic delayed neural networks via dual-stage impulsive control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Part B Cybern 40:831–844
Zhang Y, Qin Ch, Zhang W, Liu F, Luo X (2018) On the fault-tolerant performance for a class of robust image steganography. Signal Process 146:99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A: The ratio of polynomials of degree N
\({{\varPhi }}_{N}^{(1,2)}(x,\alpha )\) are Chebyshev polynomials of type 1 and type 2 [74]. By considering:
where F is \(({T_{N}}(\sqrt x ))\) or \(({U_{N}}(\sqrt x ))\). These chaotic maps are defined in the interval [0, 1]. Considering the conjugate or isomorphic maps of this equation, we could extract the invariant measure and calculate the KS-entropy. The invertible map
(which maps I = [0, 1] into \([0,\infty )\)) transforms maps \({{\varPhi }}_{N}^{(1,2)}(x,\alpha )\) into \(\tilde {{\varPhi }}_{N}^{(1,2)}(x,\alpha )\), defined as [24]:
this is mean of conjugacy.
Appendix B: Proof of the ergodicity
The introduced pair coupled maps (2) at the synchronized state x = y, by considering the \([0,\infty )\) domain, is reduced to:
The definition of the invariant measure for the introduced hierarchy of chaotic maps (1) is [17]:
By considering the following invariant measure for the hierarchy of chaotic maps (19) [25]:
Simply one could find the following relation [4]:
Appendix C: KS-entropy
The definition of KS-entropy is [17]:
By considering the invariant measure, the KS-entropy for (2) can calculate, which leads to
The KS-entropy for pair coupled maps is computed in [4]:
where \(H=2{h_{KS}}(X = {((1 - \varepsilon )\alpha ^{p} + \varepsilon \beta ^{p})^{\frac {1}{p}}}ta{n^{2}}(N arc tan(\sqrt x )))\) is KS-entropy for one-dimensional map. The equality of KS-entropy and Lyapunov exponent for ergodic maps is implied by Birkohf ergodic theorem [17].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hematpour, N., Ahadpour, S., Sourkhani, I.G. et al. A new steganographic algorithm based on coupled chaotic maps and a new chaotic S-box. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 39753–39784 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12828-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12828-w