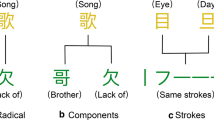
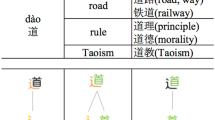
Abstract
As an important task in Asian language information processing, Chinese word embedding learning has attracted much attention recently. Based on either Skip-gram or CBOW, several methods have been proposed to exploit Chinese characters and sub-character components for learning Chinese word embeddings. Chinese characters are combinations of meaning, structure, and phonetic information (pinyin). However, previous works only cover the former two aspects and cannot effectively explore distinct semantics of characters. To address this issue, we develop a Pinyin-enhance Skip-gram model named rsp2vec, in addition to a radical and pinyin-enhanced Chinese word embedding (rPCWE) learning models based on CBOW. For our models, the phonetic information and semantic components of Chinese characters are encoded into embeddings simultaneously. Evaluations on word analogy reasoning, word relevance, text classification, named entity recognition, and case studies validate the effectiveness of our models.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/luyy9apples/PictophoneticZhEmb.
References
Baroni M, Dinu G, Kruszewski G (2014) In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 238–247
Bengio Y, Ducharme R, Vincent P, Jauvin C (2003) A neural probabilistic language model. J Mach Learn Res 3:1137
Cao S, Lu W, Zhou J, Li X (2018) In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 5053–5061
Chen X, Xu L, Liu Z, Sun M, Luan H (2015) In: Proceedings of the 24th international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1236–1242
Chen HY, Yu SH, Lin SD (2020) In: Proceedings of the 58th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 2865–2871
Fan RE, Chang KW, Hsieh CJ, Wang XR, Lin CJ (2008) Liblinear: a library for large linear classification. J Mach Learn Res 9:1871
Huang Z, Xu W, Yu K (2015) arXiv:1508.01991
Li Y, Li W, Sun F, Li S (2015) In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 829–834
Li H, Liu J, Liu RW, Xiong N, Wu K, hoon Kim T (2017) A dimensionality reduction-based multi-step clustering method for robust vessel trajectory analysis. Sensors 17(8):1792:1
Ma B, Qi Q, Liao J, Sun H, Wang J (2020) Learning chinese word embeddings from character structural information. Comput Speech Language 60:101031
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) In: Proceedings of the 27th annual conference on neural information processing systems, pp 3111–3119
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J (2013) In: Proceedings of the 1st international conference on learning representations
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning CD (2014) In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 1532–1543
Rubenstein H, Goodenough JB (1965) Contextual correlates of synonymy. Commun ACM 8(10):627
Schnabel T, Labutov I, Mimno D, Joachims T (2015) In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 298–307
Shi X, Zhai J, Yang X, Xie Z, Liu C (2015) In: Proceedings of the 53rd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics and the 7th international joint conference on natural language processing, pp 594–598
Su TR, Lee HY (2017) In: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp 264–273
Sun Z, Li X, Sun X, Meng Y, Ao X, He Q, Wu F, Li J (2021) In: Proceedings of the 59th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics and the 11th international joint conference on natural language processing, pp 2065–2075
Tang D, Wei F, Yang N, Zhou M, Liu T, Qin B (2014) In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 1555–1565
Wang S, Zhou W, Zhou Q (2020) Radical and stroke-enhanced chinese word embeddings based on neural networks. Neural Process Lett 52(2):1109
Wu M, Tan L, Xiong N (2015) A structure fidelity approach for big data collection in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 15(1):248
Yang Q, Xie H, Cheng G, Wang FL, Rao Y (2021) Pronunciation-enhanced chinese word embedding. Cogn Comput 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09850-9
Yang L, Sun M (2015) In: Proceedings of the 14th China national conference on chinese computational linguistics and natural language processing based on naturally annotated big data, pp 15–25
Yin R, Wang Q, Li P, Li R, Wang B (2016) In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 981–986
Yu J, Jian X, Xin H, Song Y (2017) In: Proceedings of the 2017 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 286–291
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhu J, Zheng Z, Liu X, Wang W, Chen Z, Zhai S (2019) Inproceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, pp 1011–1020
Zeng Y, Sreenan CJ, Sitanayah L, Xiong N, Park JH, Zheng G (2011) An emergency- adaptive routing scheme for wireless sensor networks for building fire hazard monitoring. Sensors 11(3):2899
Acknowledgements
The work described in this paper was fully supported by a grant from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (UGC/ FDS16/E01/19), the One-off Special Fund from Central and Faculty Fund in Support of Research from 2019/20 to 2021/22 (MIT02/19-20), the Research Cluster Fund (RG 78/2019-2020R), the Interdisciplinary Research Scheme of the Dean’s Research Fund 2019-20 (FLASS/ DRF/IDS-2) of The Education University of Hong Kong, and the Lam Woo Research Fund (LWI20011) of Lingnan University, Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F.L., Lu, Y., Cheng, G. et al. Learning Chinese word embeddings from semantic and phonetic components. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 42805–42820 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13488-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13488-6