Abstract
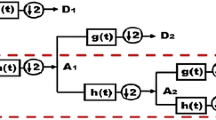
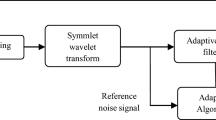
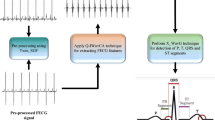
A retrospective aspect of prenatal complexities during pregnancy and advancements in technology shows the need for unscathed fetal ECG extraction from a single mother abdominal ECG (abdECG). The proposed work introduces a Non-invasive Single Channel Integration Technique (NSCIT) depicting a cumulative trapezoidal mathematical model with an LMS adaptive algorithm for mother and fetal ECG extraction with improved Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). Besides separation, fetal ECG (fECG) features are extracted, simulated, analyzed, and compared with standards to generate fetus cardiac growth during later Gestation Period (GP) of 21st to 40th week of pregnancy. The variants of the wavelet transform, such as Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DTCWT) for pre-processing and Maximal Overlap Discrete Wavelet Transform (MODWT) for post-processing, are exploited using a multi-resolution analysis. The NSCIT algorithm with LMS adaptive technique has shown 100% accuracy for detecting mother ECG and specific fetal ECG extraction channels. The improved accuracy using abdominal lead 4 is 96.36%, and overall abdominal mixed lead accuracy is 93.32% compared with recent existing literature. The maximum error in comparing Power Spectral Density (PSD) of actual and extracted fECG and mECG is significantly less. The calculated correlation coefficient between actual and extracted fetal QRS width, fetal R-peak intervals (R-R), and fetal heart rate (fHR) for Db1 are 0.70, 0.99, and 0.67, respectively. The research outcomes show that fECG SNR increases with GP, and it is maximum for the GP of 40th week. This fECG morphological analysis before childbirth will efficaciously contribute to sustainable fetal healthcare.
Highlights
• Cumulative trapezoidal with the least mean square (LMS) adaptive filter as the separation technique of mother and fetal ECG.
• Dual-tree complex wavelet transform (DTCWT) as a pre-processing technique.
• The influence of the Gestation Period (GP) on improved SNR of fetal ECG.
• Extracting and analyzing fetal morphological parameters using the maximal overlap discrete wavelet transform (MODWT).
• Research has verified in the Physiobank public databases, namely, Abdominal and Direct fetal ECG database(adfecgdb) and non-invasive Fetal ECG Database (nifecgdb).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas R, Hussain A J, Al-Jumeily D, Baker, Khattak A (2018) Classification of foetal distress and hypoxia using machine learning approaches. In: International Conference on Intelligent Computing 2018. Springer, Cham. 767–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95957-3_81
Almeida R, Gonçalves H, Bernardes J, Rocha AP (2014) Fetal QRS detection and heart rate estimation: a wavelet-based approach. Physiol Meas 35(8):1723–1735. https://doi.org/10.7863/jum.2012.31.3.389
Azzerboni B, La Foresta F, Mammone N, Morabito FC (2005) A new approach based on wavelet-ICA algorithms for fetal electrocardiogram extraction. In: ESANN 193–8
Behar J, Oster J, Clifford GD (2013) Non-invasive FECG extraction from a set of abdominal sensors. IEEE
Behar J, Johnson A, Clifford GD, Oster J (2014) A comparison of single channel fetal ECG extraction methods. Ann Biomed Eng 42(6):1340–1353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-0993-9
Behar J, Oster J, Clifford GD (2014) Combining and benchmarking methods of foetal ECG extraction without maternal or scalp electrode data. Physiol Meas 35(8):1569–1589. https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/35/8/1569
Bin Queyam A, Kumar Pahuja S, Singh D (2017) Quantification of feto-maternal heart rate from abdominal ECG signal using empirical mode decomposition for heart rate variability analysis. Technologies 5(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5040068
Castillo E, Morales DP, Botella G, Garcŕia A, Parrilla L, Palma AJ (2013) Efficient wavelet-based ECG processing for single-lead FHR extraction. Digit Signal Process 23(6):1897–1909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2013.07.010
Clifford GD, Silva I, Behar J, Moody GB (2014) Non-invasive fetal ECG analysis. Physiol Meas 35(8):1521–1536. https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/35/8/1521
Fergus P, Hussain A, Al-Jumeily D, Huang DS, Bouguila N (2017) Classification of caesarean section and normal vaginal deliveries using foetal heart rate signals and advanced machine learning algorithms. Biomed Eng Online 16(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-017-0378-z
Georgieva A, Payne SJ, Moulden M, Redman CW (2013) Artificial neural networks applied to fetal monitoring in labour. Neural Comput & Applic 22(1):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0743-y
Ghorat M, Gharehpetian GB, Latifi H, Hejazi MA (2018) A new partial discharge signal denoising algorithm based on adaptive dual-tree complex wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 67(10):2262–2272. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2018.2816438
Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng CK, Stanley HE (2000) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):e215–e220. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215
Gupta P, Sharma KK, Joshi SD (2016) Fetal heart rate extraction from abdominal electrocardiograms through multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Comput Biol Med 68:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.11.007
Gustafsson F (1996) Determining the initial states in forward-backward filtering. IEEE Trans Signal Process 44(4):988–992. https://doi.org/10.1109/78.492552
Hafez AG, Ghamry E (2012) Geomagnetic sudden commencement automatic detection via MODWT. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51(3):1547–1554. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCES.2009.5383235
Haver OT (2016) A pragmatic introduction to signal processing. Available: https://terpconnect.umd.edu/toh/spectrum/IntroToSignalProcessing.pdf. Accessed 5 Nov 2017
Haykin SS (2005) Adaptive filter theory. Pearson Education India. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420049701 ch37
Jezewski J, Matonia A, Kupka T, Roj D, Czabanski R (2012) Determination of fetal heart rate from abdominal signals: evaluation of beat-to-beat accuracy in relation to the direct fetal electrocardiogram. Biomed Tech Eng 57(5):383–394. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2011-0130
John RG, Ramachandran KI (2019) Extraction of foetal ECG from abdominal ECG by nonlinear transformation and estimations. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 175:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.04.022
Kahankova R, Jezewski J, Nedoma J, Jezewski M, Fajkus M, Kawala-Janik A et al (2017) Influence of gestation age on the performance of adaptive systems for fetal ECG extraction. Adv Electr Electron Eng 15(3):491–501. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2019.2938061
Kahankova R, Martinek R, Jaros R, Behbehani K, Matonia A, Jezewski M et al (2019) A review of signal processing techniques for non-invasive fetal electrocardiography. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.15598/aeee.v15i3.2207
Kaleem AM, Kokate RD (2019) Performance evaluation of fetal ECG extraction algorithms. In: Emerging Research in Electronics, Computer Science and Technology. Springer, pp 187–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5802-9_17
Khamene A, Negahdaripour S (2000) A new method for the extraction of fetal ECG from the composite abdominal signal. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 47(4):507–516. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.828150
Khandoker A, Ibrahim E, Oshio S, Kimura Y (2018) Validation of beat by beat fetal heart signals acquired from four-channel fetal phonocardiogram with fetal electrocardiogram in healthy late pregnancy. Sci Rep 8(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31898-1
Liu H, Chen D, Sun G (2019) Detection of fetal ECG R wave from single-lead abdominal ECG using a combination of RR time-series smoothing and template-matching approach. IEEE Access 7:66633–66643. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917826
Martinek R, Kahankova R, Nedoma J, Fajkus M, Skacel M (2018) Comparison of the LMS, NLMS, RLS, and QR-RLS algorithms for vehicle noise suppression. In: Proceedings of the 10th international conference on computer modeling and simulation. p. 23–7. https://doi.org/10.1145/3177457.3177502
Paarmann LD (2006) Design and analysis of analog filters: A signal processing perspective, vol 617. Springer Science & Business Media. ebooks.kluweronline.com
Panigrahy D, Sahu PK (2017) Extraction of fetal ECG signal by an improved method using extended Kalman smoother framework from single channel abdominal ECG signal. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 40(1):191–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0527-5
Percival DB, Mofjeld HO (1997) Analysis of subtidal coastal sea level fluctuations using wavelets. J Am Stat Assoc 92(439):868–880. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1997.10474042
Rooijakkers MJ, Rabotti C, de Lau H, Oei SG, Bergmans JWM, Mischi M (2015) Feasibility study of a new method for low-complexity fetal movement detection from abdominal ECG recordings. IEEE J Biomed Heal Informatics 20(5):1361–1368. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2015.2452266
Sana F, Ballal T, Shadaydeh M, Hoteit I, Al-Naffouri TY (2019) Fetal ECG extraction exploiting joint sparse supports in a dual dictionary framework. Biomed Signal Process Control 48:46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.08.023
Singh R, Rajpal N, Mehta R (2020) Dynamic ECG classification using shift-invariant DTCWT and discriminant analysis. In: Proceedings of ICETIT 2019. Springer, pp 490–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30577-2_43
Singh R, Rajpal N, Mehta R (2020) An empirical sequence to extract fetal electrocardiogram using the kernel and wavelet optimization. J Inf Optim Sci 41(1):107–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/02522667.2020.1715562
Spilka J, Frecon J, Leonarduzzi R, Pustelnik N, Abry P, Doret M (2016) Sparse support vector machine for intrapartum fetal heart rate classification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(3):664–671. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2546312
Stout MJ, Cahill AG (2011) Electronic fetal monitoring: past, present, and future. Clin Perinatol 38(1):127–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clp.2010.12.002
Su L, Wu H-T (2017) Extract fetal ECG from single-lead abdominal ECG by de-shape short time Fourier transform and nonlocal median. Front Appl Math Stat 3:2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fams.2017.00002
Sun Y, Thakor N (2015) Photoplethysmography revisited: from contact to noncontact, from point to imaging. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(3):463–477
Trivedi N, Levy D, Tarsa M, Anton T, Hartney C, Wolfson T, Pretorius DH (2012) Congenital cardiac anomalies: prenatal readings versus neonatal outcomes. J Ultrasound Med 31(3):389–399
Wang Y, He Z, Zi Y (2010) Enhancement of signal denoising and multiple fault signatures detecting in rotating machinery using dual-tree complex wavelet transform. Mech Syst Signal Process 24(1):119–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2009.06.015
Yu F, Ip HHS (2008) Semantic content analysis and annotation of histological images. Comput Biol Med 38(6):635–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2008.02.004
Yu Q, Guan Q, Li P, Liu T-B, Si J-F, Zhao Y et al (2017) Wavelet optimization for applying continuous wavelet transform to maternal electrocardiogram component enhancing. Chinese Phys B 26(11):118702. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/26/11/118702
Zarzoso V, Nandi AK (2001) Noninvasive fetal electrocardiogram extraction: blind separation versus adaptive noise cancellation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48(1):12–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.900244
Zarzoso V, Nandi AK, Bacharakis E (1997) Maternal and foetal ECG separation using blind source separation methods. Math Med Biol A J IMA 14(3):207–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/imammb/14.3.207
Zhang Y, Yu S (2020) Single-lead noninvasive fetal ECG extraction by means of combining clustering and principal components analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 58(2):419–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02087-7
Zhang N, Zhang J, Li H, Mumini OO, Samuel OW, Ivanov K, Wang L (2017) A novel technique for fetal ECG extraction using single-channel abdominal recording. Sensors 17(3):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030457
Zheng W, Liu H, He A, Ning X, Cheng J (2010) Single-lead fetal electrocardiogram estimation by means of combining R-peak detection, resampling and comb filter. Med Eng Phys 32(7):708–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.04.012
Zhong W, Liao L, Guo X, Wang G (2018) A deep learning approach for fetal QRS complex detection. Physiol Meas 39(4):45004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/aab297
Zhong W, Liao L, Guo X, Wang G (2019) Fetal electrocardiography extraction with residual convolutional encoder--decoder networks. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 42(4):1081–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-019-00805-x
Zhu L, Wang Y, Fan Q (2014) MODWT-ARMA model for time series prediction. Appl Math Model 38(5–6):1859–1865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2013.10.002
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their special gratitude to Dr. S.K. Gulati M.D.(Medicine), Bharat Nursing Home, Rohtak, Haryana, India, and Dr. Aditya Batra, M.D., D.M(Cardiology), Holy Heart Hospital, Rohtak, Haryana, India, and Dr. Gaurav Garg, MBBS, MD (Paediatrics), FNB (Pediatric Cardiology), Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi, India for their expert opinions and suggestions for the morphological analysis of fetal and maternal ECG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Rajpal, N. & Mehta, R. Non-invasive Single Channel integration model for fetal ECG extraction and sustainable fetal healthcare using wavelet framework. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 39669–39695 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13534-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13534-3