Abstract
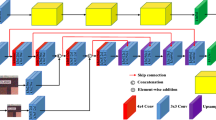
In digital image analysis and processing field of study, noise reduction and suppression have been stated as a common query. However, it is mostly essential issue to demesne the fine edges and ridges and tiny texture while suppressing the noise in processing of the digital images. In order to avoid causing “Over-strangling” phenomenon, semi-soft thresholding model is exploited to classify the sharp edges of the contaminated images. In this study, a self-adjusting generative adversarial network GAN is utilized. This procedure is used to extract the fine edge of the noised digital images in order to improve the actual signal in the high frequency components where the main parts of the clean pixels may consider as noise pixels, and as a result delete the unwanted noise from the tested image that might cause over smoothing to the resulted images. In order to further denoise the contaminated digital image, adaptive learning GAN model throughout scoring machine is exploited. Therefore, it preserves the information of input image and feature maps, learns the correlation between global and local features, improves image restoration performance, and suppresses phenomena such as over-smoothing that tend to occur in wavelets-based denoising. The proposed method is an end-to-end network structure with CNN-based preprocessing methods. Experimental results demonstrate that, in comparison with state-of-the-art noise removal techniques, the proposed method has better visual quality, and the proposed method improves PSNR by 2.27 dB and 0.85 dB on average compared with state-of-the-art- denoising methods. In addition, the proposed method could shorten the processing time noticeably.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao Y, Jia L, Chen Y et al (2018) Review of computer vision based on generative adversarial networks. J Image and Graph 23(10):1433–1449
Chauhan S, Singh M, Aggarwal AK (2021) Data science and data analytics: artificial intelligence and machine learning integrated based approach. Data Science and Data Analytics: Opportunities and Challenges
Chen H, Zhou C, Wang S (2004) Research Based on Mathematics Morphology Image Chirp Method. J Eng Graph 02:116–119
Dantas FC, Costa MN, Lopes RR (2017) Learning dictionaries as a sum of kronecker products. IEEE Signal Process Lett 24(5):559–563
GAO W, LI Z, KANG Q (2011) A hybrid mesh Denoising algorithm based on the mean Normal filter. J Eng Graph 32(04):84–89
Gu SL Zhang WZ, Feng X (2014) Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising. In: 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Guo T, Seyed Mousavi H, Huu Vu T, Monga V (Jul. 2017) Deep wavelet prediction for image superresolution. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Workshops (CVPRW). pp. 1100–1109
He Y, Yang M (2021) OCT image Denoising method based on generative confrontation network. Modern Comput 12:87–91
Hsieh SH, Lu CS, Pei SC (2014) 2D sparse dictionary learning via tensor decomposition. In: IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), pp. 492–496
Irofti P, Dumitrescu B (2019) Pairwise approximate k-svd. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). pp. 3677–3681. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683788
Jin H-Y, Jiao L-C, Liu F (2007) SAR Image De-noising Based on Curvelet Domain Hidden Markov Tree Models. Chin J Comput 03:491–497
Jing B, Biao H, Wang S, Licheng J (2008) SAR image Denoising based on lifting Directionlet domain Gaussian scale mixtures model. Chin J Comput 07:1234–1241
Jurovic DI (2016) BM3D filter in salt-and-pepper noise removal. EURASIP J Image Video Proc 13:1–11
Khmag A (2022) Digital image noise removal based on collaborative filtering approach and singular value decomposition. Multimed Tools Appl 81:16645–16660
Khmag A, Ramli AR, bin Hashim SJ, Al Haddad SAR (2017) Additive noise reduction in natural images using second-generation wavelet transform hidden Markov models. IEEJ Trans Electr Electron Eng 11(3):339–347
Khmag A, Al Haddad SAR, Suhimi Y, Kamarudin N (2017) Denoising of natural images through robust wavelet thresholding and genetic programming. Vis Comput 33(9):1141–1154
Khmag A, Al Haddad SAR, Ramlee RA, Kamarudin N, Malallah FL (2018) Natural image noise removal using nonlocal means and hidden Markov models in transform domain. Vis Comput 34(12):1661–1675
Khmag A, Al Haddad SAR, Kalantr B (2018) Single dehazing using second generation wavelet transformas and the mean vector L2-norm. Vis Comput 34(5):675–688
Liu K, Ma R, Pang Y (2018) A detail enhancement and Denoising algorithm of high dynamic range infrared image based on double guided image filter. J Graph 39(06):1048–1054
Liu P, Zhang H, Lian W, Zuo W (2019) Multi-level wavelet convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 7:74973–74985
Meng Y, Zhang J (2022) An image Denoising method using symmetric dilation residual network in the high noise level environment. IEEE Access 10:49657–49676
Park B, Jeong J (2019) Color filter array demosaicking using densely connected residual network. IEEE Access 7:128076–128085
Roth S, Black MJ (2009) Fields of experts. Int J Comput Vis 82(2):205–229 Article (CrossRef Link)
Sailaja R, Rupa C, Chakravarthy ASN (2017) Robust and indiscernible multimedia watermarking using light weight mutational methodology. J Citation Rep 34:45–55
Seghouane AK, Iqbal A (2018) Consistent adaptive sequential dictionary learning. Signal Process 153:300–310
Shi K (2021) Image denoising by nonlinear nonlocal diffusion equations. J Comput Appl Math 395(7):113605
Shitong Y (2014) Image enhancement algorithm combining with threshold De-noising and edge optimization. J Graph 35(04):571–576
Srivastava A, Singhal V, Aggarawal AK (2017) Comparative analysis of multimodal medical image fusion using PCA and wavelet transforms. Int J Latest Technol Eng Manag Appl Sci (IJLTEMAS) VI
Tan ET, Queler SC, Lin B (2021) Improved nerve conspicuity with water weighting and denoising in two-point Dixon magnetic resonance neurography. Magn Reson Imaging 79:103–111
Thukral R, Kumar A, Arora AS (2019, September) Effect of different thresholding techniques for Denoising of EMG signals by using different wavelets. In 2019 2nd international IEEE conference on intelligent communication and computational techniques (ICCT). pp. 161-165
Thukral R, Arora AS, Kumar, A. (2022). Denoising of thermal images using deep neural network. In: Proceedings of international conference on recent trends in computing. Springer, Singapore. pp. 827–833
Ubhi JS, Aggarwal AK (2022) Neural style transfer for image within images and conditional GANs for destylization. J Vis Commun Image Represent 85:103483
Wang X-H, Zhu Y-H, Lv F, Su X, Song C-M (2018) Cauchy distribution NSST-HMT model and its applications in image Denoising. Chin J Comput 41(11):2496–2508
Wang H, Yang X, Jiang Y, Wang Z (2021) Image denoising algorithm based on multi-channel GAN. J Commun 42(03):229–237
Xinxin C, Shiyu Z, Qiang C, Yunjie C, Wu M (2020) Structure preservation generative adversarial network for noise reduction in SD-OCT images. J Comput-Aided Des Comput Graph 32(05):751–758
Yang C, Luo Y, Yang S (2009) Hybrid linear model based image Denoising. Chin J Comput 32(11):2260–2264
Yu J, Liu G (2021) Extracting and inserting knowledge into stacked denoising auto-encoders. Neural Netw 137:31–42
Zhang K, Zuo W, Chen Y, Meng D, Zhang L (July 2017) Beyond a gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans Img Proc 26(7):3142–3155
Zhang Y, Tian Y, Kong Y, Zhong B, Fu Y (2018) Residual dense network for image superresolution, arXiv:1802.08797. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.08797
Zhou Y, Chen R, Zhao Y (2021) Point cloud denoising using non-local collaborative projections. Pattern Recogn 120(81):108–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Data availability
All the data are available on request.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khmag, A. Additive Gaussian noise removal based on generative adversarial network model and semi-soft thresholding approach. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 7757–7777 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13569-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13569-6