Abstract
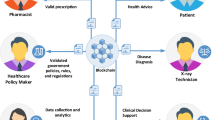
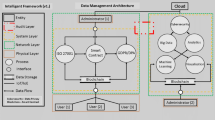
In the standard Electronic Health Record (EHR) management system, the medical service center supervises and dispenses the corresponding health records that are found to be a laborious process for sharing on several medical platforms. In recent years, blockchain technology has started gaining as one of the most favored possibilities based on dissimilar platforms to share EHRs. However, with the increased nature and size of the EHR storing data also involves a tedious process. The computation and communication cost are the challenges involved in accessing medical image information is not analyzed. The falsification rate for HER was not focused. To sort out this issue, the cloud computing (CC) environment is contemplated as an encouraging solution. Woefully, the EHR with CC environment is found to be susceptible to several attacks due to the sending of sensitive medical image data over a public channel. A secured method with Blind Digital Certificate and Lamport Merkle (BBDC-LM) Cloud-assisted Medical Image Sharing using Blockchain is proposed in our work. In the proposed BBDC-LM method, blockchain performs the task of access control and therefore ensuring security and minimum falsification of the entire process. Blind Digital Certificate is used for generating keys to contribute communication and computational cost. On the other hand, the cloud server stores and manages the patient’s five different classes of images (i.e., MRI, CT, X-ray, Annotated, and Ultrasound) to provide computationally efficient storage. The empirical results show that our proposed BBDC-LM method provides an efficient solution for reliable medical image data sharing between patients and medical analyzers in a secured manner. Lamport Merkle functions where the leaves from the authentication among patient and medical analyzer are performed by cloud server. The system evaluation and security analysis also demonstrate the performance improvements in minimum communication and computation cost with a minimum false positive rate compared to the existing medical image sharing methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso SG, Arambarri J, López-Coronado M, de la Torre Díez I, (2019) “Proposing New Blockchain Challenges in eHealth”, J Med Syst, Springer, 43
Benil T, Jasper J, (2020) “Cloud-based security on outsourcing using blockchain in E-health systems”, Computer Networks, Elsevier, [Elliptical Curve Certificateless Aggregate Cryptography Signature scheme (EC-ACS)] 178, 107344, 178
Boussif M, Aloui N, Cherif A (2017) Secured cloud computing for medical data based on watermarking and encryption. Inst Eng Technol 7:294–298
Chen Y, Ding S, Xu Z, Zheng H, Yang S (2018) Blockchain-Based Medical Records Secure Storage and Medical Service Framework. J Med Syst, Springer 33:43
Cheng W, WeiOu XY, Yan W, Liu D, Liu C (2020) A privacy-protection model for patients. Security Commun Netw Wiley 2:28–44
Chukwu E, Garg L (2020) A systematic review of Blockchain in healthcare: frameworks, prototypes, and implementations. IEEE Access 8:21196–21214
Huang H, Sun X, Xiao F, Zhu P, Wang W (2020) Blockchain-based eHealth system for auditable EHRs manipulation in cloud environments. J Parallel Distrib Comput Elsevier 148:46–57
Kleinaki A-S, Mytis-Gkometh P, Drosatos G, Efraimidis PS, Kaldoudi E (2018) A Blockchain-based notarization service for biomedical knowledge retrieval. Comput Struct Biotechnol J Elsevier 16:288–297
Liang H, Lee H-H (2020) A medical data privacy protection scheme based on Blockchain and cloud computing, Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. Wiley Publications
Meier P, Beinke JH, Fitte C, Jan Schulte to Brinke, Teuteberg F (2020) Generating design knowledge for blockchain-based access control to personal health records. Inform Syst e-Business Manag Springer 19:13–41
Nagasubramanian G, Sakthivel RK, Patan R, Gandomi AH, Sankayya M, Balusamy B (2018) Securing e-health records using keyless signature infrastructure blockchain technology in the cloud. Neural Comput Appl Springer 2:639–647
Nguyen DC, Pathirana PN, Ding M, Seneviratne A (2019) Blockchain for secure EHRs sharing of Mobile cloud-based E-health systems. IEEE Access 7:66792–66806
Nweke HF, Wah TY, Mujtab G, Al-garadi MA (2019) Data fusion and multiple classifier systems for human activity detection and health monitoring: Review and open research directions. Inf Fusion, Elsevier 46:147–170
Pournaghi SM, Bayat M, Farjami Y (2020) MedSBA: a novel and secure scheme to share medical data based on blockchain technology and attribute-based encryption. J Ambient Intell Human Comput, Springer, [Blockchain technology and attribute-based encryption MedSBA] 11:4613–4641
Rathee G, Sharma A, Saini H, Kumar R, Iqbal R (2019) A hybrid framework for multimedia data processing in IoT-healthcare using blockchain technology. Multim Tools Appl Springer 79:9711–9733
Roehrsa A, da Costa CA, da Rosa Righi R, da Silva VF, Goldim JR, Schmidt DC (2019) Analyzing the performance of a blockchain-based personal health record implementation. J Biomed Informat Elsevier 92:103140
Schrader L (2020) Advanced sensing and human activity recognition in early intervention and rehabilitation of elderly people. J Popul Ageing, Springer 13:139–165
Silva C-C A, Aquino Jr. GS, Melo SRM, Eg-dio DJB, (2019) “A Fog Computing-Based Architecture for Medical Records Management”, Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, Wiley, 19,1968960:1–1968960:16
Wang H, Song Y, (2018) “Secure Cloud-Based EHR System Using Attribute-Based Cryptosystem and Blockchain”, J Med Syst, Springer, 42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, C.E.J., Jagatheeswari, A. Secured blind digital certificate and Lamport Merkle cloud assisted medical image sharing using blockchain. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 9323–9342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13719-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13719-w