Abstract
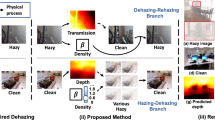
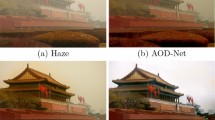
Deep learning technologies have been reshaping the research of image dehazing in recent years with superior performance. Due to the difficulty to obtain the real hazy and corresponding clear image pairs in the wild, most of the existed deep learning based methods utilize synthetic datasets for model training. As a result, the performance and robustness of those methods are compromised under the real-world complex scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel image dehazing method for unpaired data via cycle-consistent adversarial networks with a multi-scale hybrid encoder-decoder and global correlation loss. The requirement of paired training data is eliminated by combining two generators and discriminators into a cycle-consistent adversarial network. Moreover, to further improve the feature representation capability of the network for degraded images, a multi-scale hybrid encoder-decoder structure is introduced into the generators and multiple residual and dense blocks are constructed. Furthermore, to preserve more details of color and structure in generated dehazed images, a global correlation loss function is proposed. The task-specific haze-line prior is reformulated in the form of color loss constraint and incorporates with adversarial loss, cycle consistency loss, identity mapping loss, and perceptual consistency loss into a unified framework. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the favourable dehazing results of the proposed method compared with a number of state-of-the-art methods. The code will be made available on Github.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ancuti C, Ancuti CO, De Vleeschouwer C (2016) D-HAZY: a dataset to evaluate quantitatively dehazing algorithms. In: International conference on image processing, pp 2226–2230
Ancuti CO, Ancuti C, Timofte R, De Vleeschouwer C (2018) O-HAZE: a dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free outdoor images. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 867–8678
Berman D, Treibitz T, Avidan S (2016) Non-local image dehazing. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1674–1682
Cai B, Xu X, Jia K, Qing C, Tao D (2016) Dehazenet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(11):5187–5198
Chen Y, Li J, Xiao H, Jin X, Yan S, Feng J (2017) Dual path networks. In: International conference on neural information processing systems, pp 4470–4478
Dudhane A, Murala S (2020) RYF-Net: Deep fusion network for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:628–640
Engin D, Genc A, Ekenel HK (2018) Cycle-dehaze: Enhanced cyclegan for single image dehazing. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 938–9388
Gao Y, Li Q, Li J (2020) Single image dehazing via a dual-fusion method. Image Vis Comput 94:1–10
Guo F, Zhao X, Tang J, Peng H, Liu L, Zou B (2020) Single image dehazing based on fusion strategy. Neurocomputing 378:9–23
He K, Sun J, Tang X (2011) Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(12):2341–2353
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
He L, Kun L, Zhao J, Bi D (2019) Visibility restoration of single foggy images under local surface analysis. Neurocomputing 341:212–226
Hu H, Guo Q, Zheng J, Wang H, Li B (2019) Single image defogging based on illumination decomposition for visual maritime surveillance. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(6):2882–2897
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2261–2269
Isola P, Zhu J, Zhou T, Efros AA (2017) Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5967–5976
Ju M, Ding C, Guo YJ, Zhang D (2020) IDGCP: Image Dehazing based on gamma correction prior. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:3104–3118
Khan H, Sharif M, Bibi N, Usman M, Haider SA, Zainab S, Shah JH, Bashir Y, Muhammad N (2020) Localization of radiance transformation for image dehazing in wavelet domain. Neurocomputing 381:141–151
Kumar A, Jha RK, Nishchal NK (2021) An improved gamma correction model for image dehazing in a multi-exposure fusion framework. Visual Commun Image Represent 78:1–14
Kumar M, Jindal SR (2019) Fusion of rgb and hsv colour space for foggy image quality enhancement. Multimed Tools Appl 78(8):9791–9799
Li B, Peng X, Wang Z, Xu J, Feng D (2017) AOD-Net: All-in-one dehazing network. In: International conference on computer vision, pp 4780–4788
Li B, Ren W, Fu D, Tao D, Feng D, Zeng W, Wang Z (2019) Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(1):492–505
Li C, Guo J, Cong R, Pang Y, Wang B (2016) Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(12):5664–5677
Li R, Pan J, Li Z, Tang J (2018) Single image dehazing via conditional generative adversarial network. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8202–8211
Li Y, Miao Q, Liu R, Song J, Quan Y, Huang Y (2018) A multi-scale fusion scheme based on haze-relevant features for single image dehazing. Neurocomputing 283:73–86
Li Z, Tan P, Tan RT, Zou D, Zhou SZ, Cheong L (2015) Simultaneous video defogging and stereo reconstruction. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4988–4997
Mao X, Li Q, Xie H, Lau RYK, Wang Z, Smolley SP (2017) Least squares generative adversarial networks. In: International conference on computer vision, pp 2813–2821
Mehta A, Sinha H, Narang P, Mandal M (2020) Hidegan: a hyperspectral-guided image dehazing GAN. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 846–856
Park J, Han DK, Ko H (2020) Fusion of heterogeneous adversarial networks for single image dehazing. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:4721–4732
Ren W, Liu S, Zhang H, Pan J, Cao X, Yang M (2016) Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 154–169
Shen L, Zhao Y, Peng Q, Chan JC, Kong SG (2019) An iterative image dehazing method with polarization. IEEE Trans Multimedia 21 (5):1093–1107
Shrivastava A, Pfister T, Tuzel O, Susskind J, Wang W, Webb R (2017) Learning from simulated and unsupervised images through adversarial training. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2242–2251
Sim H, Ki S, Choi J, Kim SY, Seo S, Kim S, Kim M (2018) High-resolution image dehazing with respect to training losses and receptive field sizes. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 1025–10257
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: International conference on learning representations, pp 1–14
Sohn K, Lee H, Yan X (2015) Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models. In: International conference on neural information processing systems, pp 3483–3491
Wang J, Lu K, Xue J, He N, Shao L (2018) Single image dehazing based on the physical model and msrcr algorithm. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 28(9):2190–2199
Xiao J, Shen M, Lei J, Zhou J, Klette R, Sui H (2020) Single image dehazing based on learning of haze layers. Neurocomputing 389:108–122
Yang X, Xu Z, Luo J (2018) Towards perceptual image dehazing by physics-based disentanglement and adversarial training. In: Association for the advance of artificial intelligence, pp 7485–7492
Yang Y, Wang Z, Hong W, Yue H (2021) Single image dehazing algorithm based on double exponential attenuation model. Multimed Tools Appl 11 (1):1–18
Yao LP, Pan ZL (2021) The retinex-based image dehazing using a particle swarm optimization method. Multimed Tools Appl 80(1):3425–3442
Yin S, Wang Y, Yang Y (2020) A novel image-dehazing network with a parallel attention block. Pattern Recogn 102:1–11
Zhang H, Patel VM (2018) Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3194–3203
Zhao D, Xu L, Yan Y, Chen J, Duan LY (2019) Multi-scale optimal fusion model for single image dehazing. Signal Process Image Commun 74:253–265
Zhu J, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: International conference on computer vision, pp 2242–2251
Zhu Q, Mai J, Shao L (2015) A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3522–3533
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62001078) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3132020208). We would also like to thank Yuan Gao for carrying out more comparative experiments in the process of revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, T., Liang, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Single image dehazing via cycle-consistent adversarial networks with a multi-scale hybrid encoder-decoder and global correlation loss. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 12279–12301 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13772-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13772-5