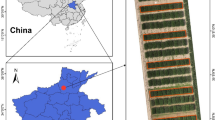
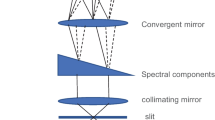
Abstract
Hyperspectral Images (HSI) generally have high spectral resolution when compared with multispectral and panchromatic images. On the other hand, hyperspectral images are redundant in nature and to prevent this band selection technique is adopted which is efficient to decrease the hyperspectral data size. Multi-Verse Optimizer (MVO) is a novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm, and it is based on the theory of multiverse in astrophysics. MVO is used to select optimal features and the effectiveness is proved through selective bands verification by classification algorithms such as: Random Forest (RF), and Support Vector Machine (SVM). It was observed from the literature that the existing works on hyperspectral band selection lacks in convergence rate and optimal fitness value. The proposed work aims to develop an efficient algorithm for optimal band selection for hyperspectral image data and it can be further used for agricultural applications. As a pilot study, the MVO algorithm is applied on two available hyperspectral image datasets such as: Pavia university and Indian Pines. To verify the results, MVO is compared with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Hybrid PSO-MVO (HPSO-MVO) and Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA). Fusion of PSO-MVO algorithm was attempted in this work and the effectiveness of hyperspectral band selection was found to be improved in terms of its execution time and convergence analysis. From the experimental results it was observed that the proposed algorithm gives the average accuracy of 92.5% for MVO, 90% for PSO and 91% for HPSO -MVO respectively using SVM. In addition, RF classifier is also performed which gives the average accuracy of 89.5% for MVO, 87.5% for PSO, 89% for HPSO - MVO and 88% for SSA respectively.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HSI:
-
Hyperspectral Images
- MVO:
-
Multi-Verse Optimizer
- RF:
-
Random Forest
- SVM:
-
Support Vector Machine
- PSO:
-
Particle Swarm Optimization
- HPSO-MVO:
-
Hybrid PSO-MVO
- CART:
-
Classification and Regression Tree
- WEP:
-
Worm hole Existence Probability
- TDR:
-
Traveling Distance Rate
- MA:
-
Memetic Algorithm
- SSA:
-
Sparrow Search Algorithm
References
Alturki A, Bchir O (2017) Clustering hyperspectral data. In: Computer Science & Information Technology (CS & IT)
Anand R, Veni S, Aravinth J (2021) Robust classification technique for hyperspectral images based on 3D-discrete wavelet transform. Remote Sens 13(7):1255
Aravinth J, Roopa S (2017) Identifying traces of copper in basavakote, Karnataka using hyperspectral remote sensing. 2018 Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Technological Advancements in Power and Energy: Exploring Energy Solutions for an Intelligent Power Grid, TAP Energy. pp. 1–6
Archibald R, Fann G (2007) Feature Selection and Classification of Hyperspectral Images with Support Vector Machines. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 4(4):674–677. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2007.905116
Author (n.d.) Science and Ultimate Reality: Quantum Theory, Cosmology, and Complexity. Edited by John D Barrow, Paul C W Davies, and Charles L Harper, Jr. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press.; index. ISBN: 0–521–83113–X. 2004. The Quarterly Review of Biology, vol. 79, no. 4, pp. 405–405, 2004. 10.1086/428147.
Borzov SM, Potaturkin OI (2018) Spectral-spatial methods for hyperspectral image classification. Review. Autometry 54(6):582–599. https://doi.org/10.15372/aut20180607
Breiman L (2001) Random Forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Chang Y, Liu J, Chen Y, Chang W, Hsieh T, Huang B (2014) Hyperspectral band selection based on parallel particle swarm optimization and impurity function band prioritization schemes. J Appl Remote Sens 8(1):084798. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jrs.8.084798
Clerici N, Weissteiner CJ, Gerard F (2012) Exploring the use of MODIS NDVI-based phenology indicators for classifying forest general habitat categories. Remote Sens 4:1781–1803
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511801389
Davies P (1978) Thermodynamics of black holes. Rep Prog Phys 41(8):1313–1355. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/41/8/004
Ding S, Chen L (2012) Spectral and spatial feature classification of hyperspectral images based on particle swarm optimisation. Int J Innov Comput Appl 4(34):233. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijica.2012.050052
Eardley D (1974) Death of White Holes in the Early Universe. Phys Rev Lett 33(7):442–444. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.33.442
Faris H, Hassonah M, Al-Zoubi A, Mirjalili S, Aljarah I (2017) A multi-verse optimizer approach for feature selection and optimizing SVM parameters based on a robust system architecture. Neural Comput & Applic 30(8):2355–2369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2818-2
Feng L, Tan A-H, Lim M-H, Jiang SW (2014) Band selection for hyperspectral images using probabilistic memetic algorithm. Soft Comput 20(12):4685–4693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1508-1
George JE, Aravinth J (2018) Estimating pollution contents in an urban area using airborne hyperspectral thermal data. 2018 international conference on wireless communications, Signal Processing and Networking, WiSPNET. 8538681
Guth A (2007) Eternal inflation and its implications. J Phys A Math Theor 40(25):6811–6826. https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/40/25/s25
Hongjun S, Qian D, Chen G, Peijun D (June 2014) Optimized Hyperspectral Band Selection Using Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7(6):2659–2670
Jangir P, Parmar S, Trivedi I, Bhesdadiya R (2017) A novel hybrid Particle Swarm Optimizer with multi verse optimizer for global numerical optimization and Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch problem. Eng Sci Technol Int J 20(2):570–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2016.10.007
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization," Proceedings of ICNN'95 - International Conference on Neural Networks, vol.4, pp. 1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Khoury, Ovrut B, Seiberg N, Steinhardt P, Turok N (2002) From big crunch to big bang. Physical Review D 65(8). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevd.65.086007
Landgrebe D (2002) Hyperspectral image data analysis. IEEE Signal Process Mag 19(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1109/79.974718
Liu D, Tan KC, Goh CK, Ho WK (2007) A multiobjective memetic algorithm based on particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B 37(1):42–50
Ma A, Filippi A, Wang Z, Yin Z (2019) Hyperspectral image classification using similarity measurements-based deep recurrent neural networks. Remote Sens 11(2):194
Main-Knorn M, Moisen GG, Healey SP, Keeton WS, Freeman EA, Hostert P (2011) Evaluating remote sensing and inventory-based estimation of biomass in the western carpathians. Remote Sens 3:1427–1446
Melgani F, Bruzzone L (2004) Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(8):1778–1790. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2004.831865
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S, Hatamlou A (2015) Multi-Verse Optimizer: a nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput & Applic 27(2):495–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1870-7
Morris M, Thorne K (1988) Wormholes in spacetime and their use for interstellar travel: A tool for teaching general relativity. Am J Phys 56(5):395–412. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.15620
Moughal T (2013) Hyperspectral image classification using support vector machine. J Phys Conf Ser 439:012042
Nidhin Prabhakar TV, Geetha P (2015) Empirical wavelet transform for improved hyperspectral image classification. In: Intelligent systems technologies and applications, pp 393–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23036-8_34
Reshma S, Veni S (2018-January) “Comparative analysis of classification techniques for crop classification using airborne hyperspectral data” 2018 Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking, WiSPNET, pp. 2272–2276
Rodriguez-Galiano VF, Ghimire B, Rogan J, Chica-Olmo M, Rigol-Sanchez JP (2012) An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sensing 67:93–104
Sawant SS, Prabukumar M, Samiappan S (n.d.) A Band Selection Method for Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Cuckoo Search Algorithm with Correlation Based Initialization. 2019 10th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS) https://doi.org/10.1109/WHISPERS.2019.8920950
Serpico S, Bruzzone L (2001) A new search algorithm for feature selection in hyperspectral remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39(7):1360–1367. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.934069
Steinhardt P, Turok N (2005) The cyclic model simplified. New Astron Rev 49(2–6):43–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newar.2005.01.003
Su H, Du Q, Chen G, Du P (2014) Optimized Hyperspectral Band Selection Using Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7(6):2659–2670. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstars.2014.2312539
Tang K, Wu J, Zhao J (2013) Adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm based on diversity feedback. J Comput Appl 33(12):3372–3374. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1087.2013.03372
Vapnik V (1995) the Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer-Verlag, New York
Xu M, Shi J, Chen W, Shen J, Gao H, Zhao J (2018) A band selection method for hyperspectral image based on particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamic sub-swarms. J Signal Process Systems 90:1269–1279
Zhang M, Ma J, Gong M (2017) Unsupervised Hyperspectral Band Selection by Fuzzy Clustering with Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(5):773–777. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2017.2681118
Zhong Z, Fan B, Duan J, Wang L, Ding K, Xiang S et al (2017) Discriminant tensor spectral–spatial feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(5):1028–1032
Zhong Z, Li J, Luo Z, Chapman M (2018) Spectral–Spatial Residual Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification: A 3-D Deep Learning Framework. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(2):847–858. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2017.2755542
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
J, A., S, V., R, D. et al. Optimal hyperspectral band selection using robust multi-verse optimization algorithm. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 14663–14687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13956-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13956-z