Abstract
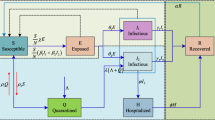
In this communication, a fractional order design and numerical form of the solutions are presented for numerical simulations of heterogeneous mosquito model. The use of the fractional order derivatives is exploited to observe more accurate and exhaustive performances of the numerical simulation of the model. The novel design of the fractional order heterogeneous mosquito differential system is analyzed with stochastic solver based on the internet of things (IoT) technologies, represented with four categories i.e., normal individuals, people with reflex behavior, panic behavior and controlled behavior based differential system. The solutions of the novel design of the fractional order system are presented by using the stochastic paradigm of artificial neural network (ANN) procedures along with the Scaled Conjugate Gradient (SCG), i.e., ANN-SCG, for learning of weights. In ANN-SCG implementation, the data statistics are picked as 78% for training, 11% for both authorization and testing samples to approximate the solutions. The accuracy of the ANN-SCG technique is seen by correlation of the determined outcomes and the information base on Adams-Bashforth-Moulton method based standard solutions. To achieve the capacity, legitimacy, consistent quality, fitness, and accuracy of the ANN-SCG strategy, the reproductions-based error histograms (EHs), MSE, regression, and state transitions (STs) are used for extensive experimentations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkawy MA, Sabir Z, Guirao JL, Saeed T (2020) Numerical investigations of a new singular second-order nonlinear coupled functional lane–Emden model. Open Phy 18(1):770–778
Afreen H, Bajwa IS (2021) An IoT-based real-time intelligent monitoring and notification system of cold storage. IEEE Access 9:38236–38253. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3056672
Akkilic AN, Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Bulut H (2022) Numerical treatment on the new fractional-order SIDARTHE COVID-19 pandemic differential model via neural networks. Eur Phys J Plus 137(3):1–14
Bukhari AH, Raja MAZ, Sulaiman M, Islam S, Shoaib M, Kumam P (2020) Fractional neuro-sequential ARFIMA-LSTM for financial market forecasting. IEEE Access 8:71326–71338
Cheng YJ, Hou M, Wang J (2020) An improved optimal trigonometric ELM algorithm for numerical solution to ruin probability of Erlang (2) risk model. Multimed Tools Appl 79(41):30235–30255
Dubey K, Sharma SC, Kumar M (2022) A secure IoT applications allocation framework for integrated fog-cloud environment. J Grid Comput 20(1):1–23
Durur H, Tasbozan O, Kurt A (2020) New analytical solutions of conformable time fractional bad and good modified Boussinesq equations. Appl Math Nonlinear Sci 5(1):447–454
Goel SS, Goel A, Kumar M, Moltó G (2021) A review of internet of things: qualifying technologies and boundless horizon. J Reliable Intel Environ 7(1):23–33
Guerrero-Sánchez Y, Umar M, Sabir Z, Guirao JL, Raja MAZ (2021) Solving a class of biological HIV infection model of latently infected cells using heuristic approach. Discre Cont Dyna Syst-S 14(10):3611
Hwang H-K, Yoon A-Y, Kang H-K, Moon S-I (2021) Retail electricity pricing strategy via an artificial neural network-based demand response model of an energy storage system. IEEE Access 9:13440–13450. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3048048
İlhan E, Kıymaz İO (2020) A generalization of truncated M-fractional derivative and applications to fractional differential equations. Appl Math Nonlinear Sci 5(1):171–188
Ilyas H, Ahmad I, Raja MAZ, Shoaib M (2021) A novel design of Gaussian WaveNets for rotational hybrid nanofluidic flow over a stretching sheet involving thermal radiation. Int Comm Heat Mass Transfer 123:105196
Ilyas H, Raja MAZ, Ahmad I, Shoaib M (2021) A novel design of Gaussian wavelet neural networks for nonlinear Falkner-Skan systems in fluid dynamics. Chin J Phys 72:386–402
Javeed A, Shah T (2020) Design of an S-box using Rabinovich-Fabrikant system of differential equations perceiving third order nonlinearity. Multimed Tools Appl 79(9):6649–6660
Junsawang P, Zuhra S, Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Shoaib M, Botmart T, Weera W (2022) Numerical simulations of vaccination and Wolbachia on dengue transmission dynamics in the nonlinear model. IEEE Access 10:31116–31144
Kiani AK et al (2021) Intelligent backpropagation networks with bayesian regularization for mathematical models of environmental economic systems. Sustainability 13(17):9537
Kumar M, Sharma SC, Goel S, Mishra SK, Husain A (2020) Autonomic cloud resource provisioning and scheduling using meta-heuristic algorithm. Neural Comput Applic 32(24):18285–18303
Li MW, Wang YT, Geng J, Hong WC (2021) Chaos cloud quantum bat hybrid optimization algorithm. Nonlinear Dynamics 103(1):1167–1193
Li MW, Xu DY, Geng J Hong WC (2022) A ship motion forecasting approach based on empirical mode decomposition method hybrid deep learning network and quantum butterfly optimization algorithm. Nonlinear dynamics, pp.1-21.
Malhotra P, Singh Y, Anand P, Bangotra DK, Singh PK, Hong WC (2021) Internet of things: evolution, concerns and security challenges. Sensors 21(0):1809
Mehmood A, Zameer A, Aslam MS, Raja MAZ (2020) Design of nature-inspired heuristic paradigm for systems in nonlinear electrical circuits. Neural Comput & Applic 32(11):7121–7137
Musanna F, Kumar S (2019) A novel fractional order chaos-based image encryption using fisher yates algorithm and 3-D cat map. Multimed Tools Appl 78(11):14867–14895
Naz S et al (2021) Neuro-intelligent networks for Bouc–wen hysteresis model for piezostage actuator. Eur Phys J Plus 136(4):1–20
Nuwairan ALM et al. 2022. An advance artificial neural network scheme to examine the waste plastic management in the ocean. AIP Adv, 12(4), 045211.
Sabir Z (2022) Stochastic numerical investigations for nonlinear three-species food chain system. Inter J Biomat 15(04):2250005
Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Guirao JL, Saeed T (2021) Meyer wavelet neural networks to solve a novel design of fractional order pantograph lane-Emden differential model. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 152:111404
Sabir Z, Umar M, Raja MAZ, Baskonus HM, Gao W (2021) Designing of Morlet wavelet as a neural network for a novel prevention category in the HIV system. Int J Biomat, p 2250012
Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Mahmoud SR, Balubaid M, Algarni A, Alghtani AH, Aly AA, Le DN (2022) A novel Design of Morlet Wavelet to solve the dynamics of nervous stomach nonlinear model. Int J Computa Intel Sys 15(1):1–15
Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Botmart T, Weera W (2022) A neuro-evolution heuristic using active-set techniques to solve a novel nonlinear singular prediction differential model. Fractal and Fractional 6(1):29
Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Guerrero Sánchez Y (2022) Solving an infectious disease model considering its anatomical variables with stochastic numerical procedures. J Healthcare Engin 2022:1–12
Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Umar M, Shoaib M, Baleanu D (2022) FMNSICS: fractional Meyer neuro-swarm intelligent computing solver for nonlinear fractional lane–Emden systems. Neural Comput & Applic 34(6):4193–4206
Shoaib M, Raja MAZ, Zubair G., Farhat, I., Nisar, K.S., Sabir, Z. and Jamshed, W., (2021) Intelligent computing with levenberg–marquardt backpropagation neural networks for third-grade nanofluid over a stretched sheet with convective conditions. Arabian journal for science and engineering, pp.1-19.
Ullah I, Fayaz M, Naveed N, Kim D (2020) ANN based learning to Kalman filter algorithm for indoor environment prediction in smart greenhouse. IEEE Access 8:159371–159388. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016277
Umar M, Raja MAZ, Sabir Z, Alwabli AS, Shoaib M (2020) A stochastic computational intelligent solver for numerical treatment of mosquito dispersal model in a heterogeneous environment. Eur Phys J Plus 135(7):1–23
Umar M, Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Baskonus HM, Yao SW, Ilhan E (2021) A novel study of Morlet neural networks to solve the nonlinear HIV infection system of latently infected cells. Results Phys 25:104235
Umar M, Sabir Z, Raja MAZ, Aguilar JG, Amin F, Shoaib M (2021) Neuro-swarm intelligent computing paradigm for nonlinear HIV infection model with CD4+ T-cells. Math Comput Simul 188:241–253
Yoon S, Cho J-H, Kim DS, Moore TJ, Free-Nelson F, Lim H (2020) Attack graph-based moving target defense in software defined networks. IEEE Trans Netw Service Manage 17(3):1653–1668. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2020.2987085
Zhang Z, Hong WC (2021) Application of variational mode decomposition and chaotic grey wolf optimizer with support vector regression for forecasting electric loads. Knowl-Based Syst 228:107297
Acknowledgements
The first author was supported by the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors describe that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Latif, S., Sabir, Z., Raja, M.A.Z. et al. IoT technology enabled stochastic computing paradigm for numerical simulation of heterogeneous mosquito model. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 18851–18866 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14270-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14270-4