Abstract
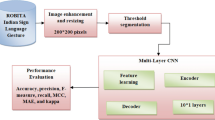
In the world, several sign languages (SL) are used, and BSL (Baby Sign Language) is the process of communication between the parents and baby using gestures. Communication by gestures is a non-verbal process that utilizes motion to pass on realities, expressions and feelings to people. SL is the communication mode in which the information is conveyed via movement of body parts like cheeks, eyebrows and head. Even though many research works based on SL are available, research in BSL remains a challenge. Hence, this paper presents an optimization-based automated recognition of the deep BSL system, which determines the gesture signalled by the kids. Initially, the image frames are extracted from the videos and data augmentation processes are performed. After pre-processing, the features are extracted from the frames using the Enhanced Convolution Neural Network (ECNN). The optimal characteristics are then selected by a new Life Choice Based Optimizer (LCBO). Finally, the classification is carried out by the Deep Long Short-Term Memory (DLSTM) scheme. The implementation is performed on the Python platform, and the performances are evaluated using several performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, kappa, f1-score and recall. The performance of the proposed approach (ECNN-DLSTM) is compared with several deep and machine learning approaches and obtains an accuracy of 99% and a kappa of 96%.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing does not apply to this article
References
Albanie S, Varol G, Momeni L, Afouras T, Chung JS, Fox N and Zisserman A (2020) BSL-1K: scaling up co-articulated sign language recognition using mouthing cues. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.12131
Aly W, Aly S, Almotairi S (2019) User-independent American sign-language alphabet recognition based on depth image and PCANet features. IEEE Access 7:123138–123150
Arora M, Mehta P, Mittal D, Bajaj P (2020) Word-level sign language gesture prediction under different conditions. In: international conference on innovative computing and communications. Springer, Singapore: pp. 427-435
Asadi-Aghbolaghi M, Clapés A, Bellantonio M, Jair Escalante H, Ponce-López V, Baró X, Guyon I, Kasaei S, Escalera S (2017) Deep learning for action and gesture recognition in image sequences: a survey. Gesture Recog:539–578
Bragg D, Koller O, Bellard M, Berke L, Boudreault P, Braffort A, Caselli N, Huenerfauth M, Kacorri H, Verhoef T and Vogler C (2019) Sign language recognition, generation, and translation: An Interdisciplinary Perspective Computers and Accessibility 16-31
Cai W, Liu D, Ning X, Wang C, Xie G (2021) Voxel-based three-view hybrid parallel network for 3D object classification. Displays 69:102076
Cui R, Liu H, Zhang C (2019) A deep neural framework for continuous sign language recognition by iterative training. IEEE Transac Multimed 21(7):1880–1891
Deng X, Yang S, Zhang Y, Tan P, Chang L, Wang H (2017) Hand3D: Hand Pose Estimation using 3D Neural Network. arXiv:1704.02224
Farooq U, Rahim MSM, Sabir N, Hussain A, Abid A (2021) Advances in machine translation for sign language: approaches, limitations, and challenges. Neural Comput Applic 33(21):14357–14399
Ferreira P, Cardoso J, Rebelo A (2019) On the role of multi-modal learning in the recognition of sign language. Multimed Tools Appl 78:10035–10056
Gao L, Li H, Liu Z, Liu Z, Wan L, Feng W (2021) RNN-transducer based Chinese sign language recognition. Neurocomputing 434:45–54
Guo H, Wang G, Chen X (2017) Towards good practices for deep 3D hand pose estimation. arXiv:1707.07248
Imran J, Raman B (2020) Deep motion templates and extreme learning machine for sign language recognition. Vis Comput 36(6):1233–1246
Kamruzzaman MM (2020) Arabic sign language recognition and generating Arabic speech using convolutional neural network. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 2020:1–9
Khatri A, Gaba A, Rana KPS and Kumar V (2019) A novel life choice-based optimizer. Soft computing 1-21
Koller O, Zargaran S, Ney H, Bowden R (2018) Deep sign: enabling robust statistical continuous sign language recognition via hybrid CNN-HMMs. Int J Comput Vis 126(12):1311–1325
Kowdiki M, Khaparde A (2021) Automatic hand gesture recognition using hybrid meta-heuristic-based feature selection and classification with dynamic time warping. Comput Sci Rev 39:100320
Li D, Rodriguez C, Yu X, Li H (2020) Word-level deep sign language recognition from video: a new large-scale dataset and methods comparison. Appl Comput Vis:1459–1469
Liao Y, Xiong P, Min W, Min W, Lu J (2019) Dynamic sign language recognition based on video sequence with BLSTM-3D residual networks. IEEE Access 7:38044–38054
Lim K, Tan A, Lee C, Tan S (2019) Isolated sign language recognition using convolutional neural network hand modelling and hand energy image. Multimed Tools Appl 78:19917–19944
Masood S, Srivastava A, Thuwal HC and Ahmad M (2018) Real-time sign language gesture (word) recognition from video sequences using CNN and RNN. In intelligent engineering informatics. Springer, Singapore 623-632
Nadgeri S, Kumar A (2019, July) An image texture based approach in understanding and classifying baby sign language. In 2019 2nd international conference on intelligent computing, instrumentation and control technologies (ICICICT). IEEE 1:854–858
Nadgeri S, Kumar D (2020) An analytical study of signs used in baby sign language using Mobilenet framework. In proceedings of the international conference on recent advances in computational techniques (IC-RACT)
Naranjo-Zeledón L, Peral J, Ferrández A, Chacón-Rivas M (2019) A systematic mapping of translation-enabling technologies for sign languages. Electronics 8(9):1047
Neiva DH, Zanchettin C (2018) Gesture recognition: a review focusing on sign language in a mobile context. Expert Syst Appl 103:159–183
Ning X, Gong K, Li W, Zhang L (2021) JWSAA: joint weak saliency and attention aware for person re-identification. Neurocomputing 453:801–811
Prietch SS, Pineda IO, Paim PDS, Calleros JMG, García JG, Resmin R (2019) Discussion on image processing for sign language recognition: an overview of the problem complexity. Res Develop Technol:112–127
Rao GA, Kishore PVV (2018) Selfie video based continuous Indian sign language recognition system. Ain Shams Eng J 9(4):1929–1939
Rastgoo R, Kiani K, Escalera S (2018) Multi-modal deep hand sign language recognition in still images using restricted Boltzmann machine. Entropy
Rastgoo R, Kiani K, Escalera S (2020) Sign language recognition: a deep survey. Expert systems with Applications113794
Saunders B, Camgoz NC, Bowden R (2021) Continuous 3d multi-channel sign language production via progressive transformers and mixture density networks. Int J Comput Vis 129(7):2113–2135
Sullivan AL, Thayer AJ, Farnsworth EM, Susman-Stillman A (2019) Effects of child care subsidy on school readiness of young children with or at-risk for special needs. Early Child Res Q 47:496–506
Wadhawan A, Kumar P (2020) Deep learning-based sign language recognition system for static signs. Neural computing and applications 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04691-y
Wang C, Wang X, Zhang J, Zhang L, Bai X, Ning X, Zhou J, Hancock E (2022) Uncertainty estimation for stereo matching based on evidential deep learning. Pattern Recogn 124:108498
Wangchuk K, Riyamongkol P, Waranusast R (2021) Real-time bhutanese sign language digits recognition system using convolutional neural network. ICT Express 7(2):215–220
Wei S, Chen X, Yang X, Cao S, Zhang X (2016) A component-based vocabulary-extensible sign language gesture recognition framework. Sensors 16(4):556
Wu F, Jing XY, Dong X, Hu R, Yue D, Wang L, Ji YM, Wang R, Chen G (2018) Intraspectrum discrimination and interspectrum correlation analysis deep network for multispectral face recognition. IEEE Transac Cyber 50(3):1009–1022
Yang S, Zhu Q (2017) Continuous Chinese sign language recognition with CNN-LSTM”, Proc. SPIE 10420, Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2017), 104200F. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2281671
Zheng L, Liang B, Jiang A (2017) Recent Advances of Deep Learning for Sign Language Recognition. 2017 International conference on digital image computing: techniques and applications (DICTA), Sydney, NSW, Australia
Funding
No funding is provided for the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Enireddy, V., Anitha, J., Mahendra, N. et al. An optimized automated recognition of infant sign language using enhanced convolution neural network and deep LSTM. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 28043–28065 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14428-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14428-8