Abstract
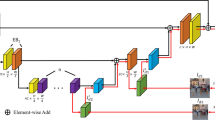
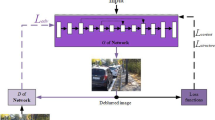
In the field of computer vision, image deblurring is a crucial and difficult task. By learning features from receptive fields, existing image deblurring algorithms have progressed. However, non-local feature representations, which depict the global data distribution of blurry images are not taken into account. As a result, in the local receptive field, combining the reliance of global space and the interaction of neighborhood space. For non-uniform deblurring, we develop a multi-path attention block (MPAB). To fuse several multi-path attention blocks, we offer an improved one-shot aggregation (IOSA). In addition, multiple loss functions are proposed to enhance network training and encourage convergence. Subjective and objective comparison experiments on various datasets are done to illustrate the efficiency of the suggested strategy. On synthetic datasets and real photos, our technique outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berahmand K, Bouyer A, Samadi N (2020) A new local and multidimensional ranking measure to detect spreaders in social networks. Computing 101 (11):1711–1733
Chakrabarti A (2016) A neural approach to blind motion deblurring. In: ECCV, pp 221–235
Cho S, Lee S (2009) Fast motion deblurring. ACM SIGGRAPH Asia, 1–8
Gong D, Yang J, Liu L, Zhang Y et al (2017) From motion blur to motion flow: a deep learning solution for removing heterogeneous motion blur. In: CVPR, pp 3806–3815
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: NIPS, pp 2672–2680
Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M et al (2017) Improved training of Wasserstein GANs. ArXiv, arXiv:1704.00028
Hradiš M, Kotera J, Zemcík P, Šroubek F (2015) Convolutional neural networks for direct text deblurring. Proceedings of BMVC, 10(2)
Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S et al (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR, pp 7132–7141
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: CVPR, pp 2261–2269
Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou T, Efros AA (2017) Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR, pp 1125–1134
Jin M, Hirsch M, Favaro P (2018) Learning face deblurring fast and wide. In: CVPR workshops, pp 745–753
Johnson J, Alahi A, Fei-Fei L (2016) Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: ECCV, pp 694–711
Kim TH, Ahn B, Lee KM (2013) Dynamic scene deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 3160–3167
Kim TH, Lee KM (2014) Segmentation-free dynamic scene deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 2766–2773
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Köhler R, Hirsch M, Mohler B, Schölkopf B, Harmeling S (2012) Recording and playback of camera shake: benchmarking blind deconvolution with a real-world database. In: ECCV, pp 27–40
Kupyn O, Budzan V, Mykhailych M, Mishkin D, Matas J (2018) Deblurgan: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR, pp 8183–8192
Kupyn O, Martyniuk T, Wu J, Wang ZY (2019) DeblurGAN-v2: deblurring (Orders-of-Magnitude) Faster and Better. In: ICCV, pp 8878–8887
Lai WS, Huang JB, Hu Z, Ahuja N, Yang MH (2016) A comparative study for single image blind deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 1701–1709
Lee Y, Hwang J, Lee S et al (2019) An energy and gpu-computation efficient backbone network for real-time object detection. In: CVPR
Li C, Anwar S, Porikli F (2020) Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement. Pattern Recog 98:107038
Li C, Cong R, Hou J, Zhang S, Qian Y, Kwong S (2019) Nested network with twostream pyramid for salient object detection in optical remote sensing images. arXiv:1906.08462
Li C, Guo J, Guo C (2018) Emerging from water: underwater image color correction based on weakly supervised color transfer. SPL 25:323–327
Li C, Guo C, Guo J, Han P, Fu H, Cong R (2016) Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(12):5664–5677
Li C, Guo C, Guo JC, Han P, Fu HZ, Cong R (2020) PDR-Net: perception-inspired single image Dehazing network with refinement. IEEE Trans Multimed 22:704–716
Li C, Guo C, Ren W, Cong R, Hou J, Kwong S, Tao D (2019) An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond. arXiv:1901.05495
Li Y, Luo Y, Lu J (2021) Single image deblurring using bi-attention network. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp 5333–5339
Maas AL, Hannun AY, Ng AY (2013) Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: ICML, p 3
Mao X, Shen C, Yang YB (2016) Image restoration using very deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks with symmetric skip connections. In: NIPS, pp 2802–2810
Mustaniemi J, Kannala J, Sarkka S et al (2018) Gyroscope-aided motion deblurring with deep networks. arXiv:1810.00986. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Nah S, Kim TH, Lee KM (2017) Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 257–265
Nimisha TM, Sunil K, Rajagopalan A (2018) Unsupervised class-specific deblurring. In: ECCV, pp 353–369
Pan J, Hu Z, Su Z, Lee H-Y, Yang M-H (2016) Soft-segmentation guided object motion deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 459–468
Pan J, Sun D, Pfister H, Yang MH (2016) Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior. In: CVPR, pp 1628-1636
Qi Q, Guo J, Jin W (2020) attention network for non-Uniform Deblurring. IEEE Access 8:100044–100057
Qing Q (2021) Image fine-grained for non-uniform scenes deblurring. Artif Intell Commun Netw 101(11):1C13
Ren W, Cao X, Pan J, Guo X, Zuo W, Yang MH (2016) Image deblurring via enhanced low-rank prior. TIP 25:3426–3437
Rostami M, Berahmand K, Forouzandeh S (2021) A novel community detection based genetic algorithm for feature selection. Journal of Big Data 8(1):1–27
Rostami M, Berahmand K, Nasiri E et al (2021) Review of swarm intelligence-based feature selection methods. Eng Appl Artif Intell 100:104210
Rostami M, Forouzandeh S, Berahmand K et al (2020) Integration of multi-objective PSO based feature selection and node centrality for medical datasets. Genomics 112(6):4370–4384
Schuler CJ, Hirsch M, Harmeling S, Schölkopf B. (2016) Learning to deblur. TPAMI 38(7):1439–1451
Sun J, Cao W, Xu Z, Ponce J (2015) Learning a convolutional neural network for non-uniform motion blur removal. In: CVPR, pp 769–777
Sun L, Cho S, Wang J, Hays J (2013) Edge-based blur kernel estimation using patch priors. In: ICCP, pp 1–8
Tao X, Gao H, Shen X, Wang J, Jia J (2018) Scale-recurrent network for deep image deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 8174C8182
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. TIP 13:600–612
Wang Q, Han T, Qin Z et al (2020) Multi-task attention network for lane detection and fitting. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 33(3):1066–1078. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3039675
Xie S, Girshick R, Dollr P et al (2017) Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: CVPR, pp 1492–1500
Xu L, Jia J (2010) Two-phase kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring. In: ECCV, pp 157–170
Xu L, Zheng S, Jia J (2013) Unnatural l0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring. In: CVPR, pp 1107–1114
Yuan Y, Xiong Z, Wang Q (2019) VSSA-NET: vertical spatial sequence attention network for traffic sign detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 28 (7):3423–3434
Zhang Z, Chen H, Yin X et al (2021) Joint generative image deblurring aided by edge attention prior and dynamic kernel selection. Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing
Zhang H, Yang J, Zhang Y, Huang TS (2011) Sparse representation based blind image deblurring. In: ICME, pp 1–6
Zhu JY, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: ICCV, pp 2223C2232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Q. A multi-path attention network for non-uniform blind image deblurring. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 36909–36928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14470-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14470-6