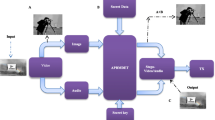
Abstract
In 2006 X. Zhang and S, Wang suggested efficient steganographic embedding by Exploiting Modification Direction (EMD) where each important secrecy bit is converted to (2n + 1) -ary notational system which produces by n pixel values where 1 pixel is increased or decreased. To date, many researchers have implemented EMD algorithms that are less secure and produce less embedding capacity and imperceptibility. So, to reduce these limitations a combination of audio-video crypto-steganography using the Digital Forensic Detection Array EMD (DFDAEMD) algorithm is used. It uses (3m2 + 4 m + 2) ary notation to embed three pixels at a time for enhancing the embedding capacity and security of secret data. The observed and verified software results confirm that the implemented security model provides better Authentication, Imperceptibility, Robustness, Embedding Capacity (EC), Embedding Rate (ER), and very good recovery of both secret and original data as compared to any existing EMD methods.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Arab F, Abdullah SM, Hashim SZ, Manaf AA, Zamani M (2016) A Robust Video Watermarking Technique for the Tamper Detection of Surveillance System. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2800-5
Chang CC, Wu HL (2014) A large payload information hiding scheme using two level exploiting modification direction. Tenth IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, pp 512–515. https://doi.org/10.1109/IIH-MSP.2014.133
Dalal M, Juneja M (2021) Steganography and Steganalysis (in digital forensics): a cybersecurity guide. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl 80(4):5723–5771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09929-9
Hajizadeh H, Ayatollahi A, Mirzakuchaki S (2013) A new high capacity and EMD-based image steganography scheme in spatial domain. In: IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), pp 1–6
Hong W, Chen T-S (2012) A novel data embedding method using adaptive pixel pair matching. IEEE Trans Inform Forensic Sec 7(1):176–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09929-910.1109/TIFS.2011.2155062
Kao WC, Wang CC (2013) Data Hiding Based on Generalized Exploiting Modification Direction Method. Imaging Sci J 61:484–490
Kartik JV, Reddy BV (2013) Authentication of secret information in image steganography. Int J Latest Trends Eng Technol 3(1):97–104
Kasana G, Singh K, Bhatia SS, (2015) “ Data Hiding Algorithm for Images Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Arnold Transform”, J Inform Process Syst (JIPS) 1–14 https://doi.org/10.3745/JIPS.03.0042
Kuo WC, Wuu LC, Kuo SH (2012) The high embedding steganography method based on general multi EMD. In: IEEE International Conference Information Security and Intelligence Control (ISIC), pp 286–289
Kuo WC, Chang SY, Wang CC, Chang CC (2016) Secure Multi-Group Data Hiding Based on Gemd map. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3165-5
Lee CF, Weng CY, Chen KC (2017) An Efficient Reversible Data Hiding with Reduplicated Exploiting Modification Direction using Image Interpolation and Edge Detection. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl 76:9993–10016
Leng H-S, Tseng H-W (2019) Generalize the EMD scheme on an n-dimensional hypercube with maximum payload. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl 78(2):18363–18377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7228-x
Liao X, Yu Y, Li B, Li Z, Qin Z (2019) A New Payload Partition Strategy in Color Image Steganography. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2896270
Liao X, Li K, Zhu X, Liu KR (2020) Robust Detection of Image Operator Chain with Two-stream Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE J Select Topics Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2020.3002391
Liao X, Yin J, Chen M, Qin Z (2020) Adaptive Payload Distribution in Multiple Images Steganography Based on Image Texture Features. IEEE Trans Depend Secure Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/TDSC.2020.3004708
Liu Y, Chang CC, Huang PC (2017) Extended Exploiting-Modification-Direction Data Hiding with High Capacity. IEEE ICVIP. https://doi.org/10.1145/3177404.3177452
Liu Y, Yang C, Sun Q (2018) “Enhance embedding capacity of generalized exploiting modification directions in data hiding” IEEE access, Digital Object Identifier https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2787803
Moon SK, Raut RD (2015) Efficient Performance Analysis of Data Hiding Technique for Enhancement of Information Security, Robustness and Perceptibility. Indersci Int J Electron Sec Digit Forensics 7(4):305–329
Moon SK, Raut RD (2018) Innovative data security model using forensic audio-video steganography for improving hidden data security and robustness. Indersci Int J Inform Comput Sec 10(4):374–395
Mustafa RJ, Elleithy K, Abdelfattah E (2017) Video-steganography techniques: taxonomy, challenges, and future directions. In: IEEE Long Island Systems, Applications, and Technology Conference (LISAT), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/LISAT.2017.8001965
Niu X, Ma M, Tang R, Yin Z (2015) Image steganography via fully exploiting modification direction. Int J Sec Appl 9(5):243–254
Sadek MM, Khalifa AS, Mostafa MG (2014) Video-steganography: a comprehensive review. Springer J Multimed Tools Appl 74(17):7063–7094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1952-z
Saha S, Ghosal SK, Chakraborty A, Dhargupta S, Sarkar R, Mandal JK (2018) Improved exploiting modification direction-based steganography using a weightage. Array Electron Lett. https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2017.3336,2018
Saha S, Chakraborty A, Chatterjee A, Dhargupta S, Ghosal SK, Sarkar R (2020) Extended exploiting modification direction based steganography using hashed-weightage array. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08951-1
Sairam TD, Boopathybagan K (2020) An improved high capacity data hiding scheme using pixel value adjustment and Modulus operation. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl 79:17003–17013
Shen S-y, Huang L-h, Yu S-s (2018) A Novel Adaptive Data Hiding Based on Improved EMD and Interpolation. Springer J Multimedia Tools Appl 77:12563–12579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4905-5
Singh L, Singh AK, Singh PK (2018) Secure Data Hiding Techniques: A Survey. Springer J Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6407-5,2018
Younus ZS, Hussain MK (2019) Image Steganography using Exploiting Modification Direction for Compressed Encrypted Data. J King Saud Univ Comput Inform Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.04.008
Zhang X, Wang S (2006) Efficient steganographic embedding by exploiting modification direction. IEEE Commun Lett 10:781–783
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest and no fund received from any agency.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, S.K. Forensic multi-dimensional Ary exploited modified direction data embedding approach to increase imperceptibility and robustness of secured data. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 35091–35120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14500-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14500-3