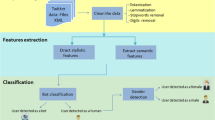
Abstract
Recently, online social networks, such as Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, etc., have grown exponentially with a large amount of information. These social networks have huge volumes of data, especially in textual form, which are unstructured and anonymous. This type of data usually leads to cybercrimes like cyberbullying, cyberterrorism, etc. and their analysis has nowadays become a serious challenge. From this perspective and to remedy this topical issue, various techniques have been proposed in the literature. Among the proposed solutions, author profiling represents the newest and most adopted technique by most researchers to discover hidden textual information. The objective of this technique is to identify the demographic or psychological aspects (age, sex, personality, mother tongue, etc.) of an author by examining the text that he has published. In recent years, this area of research has attracted many researchers who seek solutions for potential applications in various fields like marketing, computer forensics, security, etc. Within the scope of this article, we describe the author profiling task. Then, we present a brief thematic taxonomy and an illustration of some profiling solutions from the literature. In particular, different machine and deep learning techniques are detailed and discussed. This work also provides an overview of the main approaches, which we have studied in the literature, highlights the weak points and the strong points of each of these approaches. At the end of this study, a discussion of some research questions is presented and some future directions to circumvent the weaknesses detected in the approaches studied are presented in order to motivate academics and practitioners, who are interested in this problem that we assume essential, to advance solutions for profiling perpetrators on social networks.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi A, Chen H (2008) Writeprints: a stylometric approach to identity-level identification and similarity detection in cyberspace. ACM Trans Inf Syst (TOIS) 26(2):1–29
Akimushkin C, Amancio DR, Oliveira ON Jr (2018) On the role of words in the network structure of texts: application to authorship attribution. Phys A 495:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.12.054
Álvarez-Carmona M A, López-Monroy A P, Montes-y Gómez M, Villasenor-Pineda L, Meza I (2016) Evaluating topic-based representations for author profiling in social media. In: Ibero-American Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Springer, p 151–162
Alvarez-Carmona M A, Pellegrin L, Montes-y Gómez M, Sánchez-Vega F, Escalante H J, López-Monroy A P, Villaseñor-Pineda L, Villatoro-Tello E (2018) A visual approach for age and gender identification on twitter. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 34(5):3133–3145. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-169497
Anjum MW, Cheema WA (2018) A study of content based methods for author profiling in multiple genres. Int J Sci Eng Res 9:322–327
Ashraf S, Iqbal H R, Nawab R M A (2016) Cross-genre author profile prediction using stylometry-based approach. In: CLEF (Working Notes). Citeseer, p 992–999
Ashraf S, Javed O, Adeel M, Iqbal H, Nawab R M A (2019) Bots and gender prediction using language independent stylometry-based approach. In: CLEF (Working Notes)
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate
Basile A, Dwyer G, Medvedeva M, Rawee J, Haagsma H, Nissim M (2017) N-gram: new groningen author-profiling model. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.03764
Basti R, Jamoussi S, Charfi A, Ben Hamadou A (2019) Arabic twitter user profiling: application to cyber-security, pp 110–117, DOI https://doi.org/10.5220/000816740110011, (to appear in print)
Bayot R, Gonçalves T (2016) Multilingual author profiling using word embedding averages and svms. In: 2016 10th International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management & Applications (SKIMA). IEEE, p 382–386
Bentolila I, Zhou Y, Ismail L K, Humpleman R (2011) System, method, and software application for targeted advertising via behavioral model clustering, and preference programming based on behavioral model clusters. Google Patents. US Patent 8,046,797
Bilal M, Israr H, Shahid M, Khan A (2016) Sentiment classification of roman-urdu opinions using naïve bayesian, decision tree and knn classification techniques. J King Saud Univ-Comput Inf Sci 28(3):330–344
Bougiatiotis K, Krithara A (2016) Author profiling using complementary second order attributes and stylometric features. In: CLEF (Working Notes). p 836–845
Boukhari K, Omri M N et al Approximate matching-based unsupervised document indexing approach: application to biomedical domain
Bsir B, Zrigui M (2018) Enhancing deep learning gender identification with gated recurrent units architecture in social text. Computación Sistemas 22(3):757–766
Cui L, Zhang X, Qin A K, Sellis T, Wu L (2017) Cds: collaborative distant supervision for twitter account classification. Expert Syst Appl 83:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.03.075
Daneshvar S, Inkpen D (2018) Gender identification in twitter using n-grams and lsa. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference of the CLEF Association (CLEF 2018)
Dias R F S, Paraboni I (2019) Combined cnn+ rnn bot and gender profiling. In: Conference and labs of the evaluation forum (Working Notes)
Escalante H J, Montes-y Gómez M, Villaseñor-Pineda L, Errecalde M L (2015) Early text classification: a naïve solution
Fatima M, Hasan K, Anwar S, Nawab R M A (2017) Multilingual author profiling on facebook. Inf Process Manag 53(4):886–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2017.03.005
Fernquist J (2019) A four feature types approach for detecting bot and gender of twitter users. In: Working notes of CLEF 2019 - conference and labs of the evaluation forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 9-12, 2019, volume 2380 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CEUR-WS.org
Flekova L, Preoţiuc-Pietro D, Ungar L (2016) Exploring stylistic variation with age and income on twitter. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pp 313–319
Fourkioti O, Symeonidis S, Arampatzis A (2019) Language models and fusion for authorship attribution. Inf Process Manag 56(6):102061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2019.102061
Gamallo P, Almatarneh S (2019) Naive-bayesian classification for bot detection in twitter. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2019 - Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 9–12, 2019, volume 2380 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CEUR-WS.org
Giachanou A, Ríssola E A, Ghanem B, Crestani F, Rosso P (2020) The role of personality and linguistic patterns in discriminating between fake news spreaders and fact checkers. In: International Conference on Applications of Natural Language to Information Systems. Springer, p 181–192
Johansson F (2019) Supervised classification of twitter accounts based on textual content of tweets. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2019 - Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 9–12, 2019, volume 2380 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CEUR-WS.org
Joo Y, Hwang I (2019) Author profiling on social media: an ensemble learning model using various features, 2380
Juola P (2015) Industrial uses for authorship analysis. Math Comput Sci Ind 1:21–25
Kaati L, Lundeqvist E, Shrestha A, Svensson M (2017) Author profiling in the wild. In: 2017 European Intelligence and Security Informatics Conference (EISIC). IEEE, p 155–158
Kapociute-Dzikicne J, Damaševicius R (2018) Lithuanian author profiling with the deep learning. In: 2018 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS 2018), pp 169–172
Kodiyan D, Hardegger F, Neuhaus S, Cieliebak M (2017) Author profiling with bidirectional rnns using attention with grus: Notebook for pan at clef 2017. In: CLEF 2017 Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Dublin, Ireland, 11-14 September 2017, vol 1866. RWTH Aachen
Kovács G, Balogh V, Mehta P, Shridhar K, Alonso P, Liwicki M (2019) Author profiling using semantic and syntactic features: Notebook for pan at clef 2019, 2380
Kudugunta S, Ferrara E (2018) Deep neural networks for bot detection. Inf Sci 467:312–322
Lakkaraju S K, Tech D, Deng S (2018) A framework for profiling prospective students in higher education. In: Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, Fourth Edition. IGI Global, p 3861–3869
Mabrouk O, Hlaoua L, Omri M N (2018) Fuzzy twin svm based-profile categorization approach. In: 2018 14th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD). IEEE, p 547–553
Mabrouk O, Hlaoua L, Omri M N (2018) Profile categorization system based on features reduction. In: International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Mathematics, ISAIM 2018, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA, January 3–5, 2018
Mechti S, Jaoua M, Faiz R, Bouhamed H, Belguith L H (2016) Author profiling: age prediction based on advanced bayesian networks. Res Comput Sci 110:129–137
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J (2013) Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space
Moreno-Sandoval LG, Puertas E, Plaza-Del-Arco FM, Pomares-Quimbaya A, Alvarado-Valencia JA, Ureña-López A (2019) Celebrity profiling on twitter using sociolinguistic features notebook for pan at clef 2019
Najib F, Cheema W A, Nawab R M A (2015) Author’s traits prediction on twitter data using content based approach. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2015 - Conference and Labs of the Evaluation forum, Toulouse, France, September 8–11, 2015, volume 1391 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CEUR-WS.org
Ortega-Mendoza R M, Franco-Arcega A, López-Monroy A P, Montes-y Gómez M (2016) I, me, mine: the role of personal phrases in author profiling. In: International Conference of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum for European Languages. Springer, p 110–122
Ortega-Mendoza R M, López-Monroy A P, Franco-Arcega A, Montes-y Gómez M (2018) Emphasizing personal information for author profiling: new approaches for term selection and weighting. Knowl-Based Syst 145:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.01.014
Ouni S, Fkih F, Omri M N (2021) Toward a new approach to author profiling based on the extraction of statistical features. Soc Netw Anal Min 11 (1):1–16
Palomino-Garibay A, Camacho-González A T, Fierro-Villaneda R A, Hernández-Farias I, Buscaldi D, Meza-Ruiz I V (2015) A random forest approach for authorship profiling?notebook for pan at clef 2015. Work Notes Pap CLEF, 1391
Para U, Patel MS (2021) A new feature selection technique for author profiling. Des Eng 6:2868–2885
Park G, Schwartz H A, Eichstaedt J C, Kern M L, Kosinski M, Stillwell D J, Ungar L H, Seligman MEP (2015) Automatic personality assessment through social media language. J Pers Soc Psychol 108(6):934
Pennacchiotti M, Popescu A-M (2011) Democrats, republicans and starbucks afficionados: user classification in twitter. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, San Diego, pp 430–438
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning C D (2014) Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), p 1532–1543
Posadas-Durán J-P, Markov I, Gómez-Adorno H, Sidorov G, Batyrshin I, Gelbukh A, Pichardo-Lagunas O (2015) Syntactic n-grams as features for the author profiling task. Work Notes Pap CLEF, 1391
Poulston A, Waseem Z, Stevenson M (2017) Using tf-idf n-gram and word embedding cluster ensembles for author profiling. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2017 - Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Dublin, Ireland, September 11–14, 2017, volume 1866 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings
Prasad S N, Narsimha VB, Reddy P V, Babu A V (2015) Influence of lexical, syntactic and structural features and their combination on authorship attribution for telugu text. Procedia Comput Sci 48:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.04.110
Puertas E, Moreno-Sandoval L G, Plaza-Del-Arco FM, Alvarado-Valencia J A, Pomares-Quimbaya A, Ureña-López A (2019) Bots and gender profiling on twitter using sociolinguistic features notebook for pan at clef 2019, 2380
Rangel F, Rosso P (2016) On the impact of emotions on author profiling. Inf Process Manag 52(1):73–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2015.06.003. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306457315000783
Rangel F, Rosso P (2019) Overview of the 7th author profiling task at pan 2019: bots and gender profiling in twitter. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2019 - Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 9–12, 2019, volume 2380 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings, pp 1–36. CEUR-WS.org
Rangel F, Rosso P, Charfi A, Zaghouani W, Ghanem B, Snchez-Junquera J (2019) Overview of the track on author profiling and deception detection in arabic. In: Working Notes of the Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation (FIRE 2019). CEUR Workshop Proceedings. CEUR-WS.org, Kolkata, India
Rangel F, Rosso P, Chugur I, Potthast M, Trenkmann M, Stein B, Verhoeven B, Daelemans W (2014) Overview of the 2nd author profiling task at pan 2014. In: CLEF 2014 Evaluation labs and workshop working notes papers. Sheffield, pp 1–30
Rangel F, Rosso P, Koppel M, Stamatatos E, Inches G (2013) Overview of the author profiling task at pan 2013. In: CLEF Conference on Multilingual and Multimodal Information Access Evaluation. CELCT, p 352–365
Rangel F, Rosso P, Potthast M, Stein B (2017) Overview of the 5th author profiling task at pan 2017: Gender and language variety identification in twitter. Work Notes Pap CLEF 48:1613–0073
Rangel Pardo F, Rosso P (2013) On the identification of emotions and authors’ gender in facebook comments on the basis of their writing style. CEUR Work Proc CEUR-WS 1096:34–46
Rangel Pardo F M, Celli F, Rosso P, Potthast M, Stein B, Daelemans W (2015) Overview of the 3rd author profiling task at pan 2015. In: Working Notes of CLEF 2015 - Conference and Labs of the Evaluation forum, Toulouse, France, September 8-11, 2015, volume 1391 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings, pp 1–8. CEUR-WS.org
Rico-Sulayes A (2011) Statistical authorship attribution of mexican drug traficking online forum posts. Int J Speech Lang Law 18(1):53–74
Rosso P, Rangel F (2020) Author profiling tracks at fire. SN Comput Scie 1(2):1–11. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42979-020-0073-1
Safara F, Mohammed A S, Potrus M Y, Ali S, Tho Q T, Souri A, Janenia F, Hosseinzadeh M (2020) An author gender detection method using whale optimization algorithm and artificial neural network. IEEE Access 8:48428–48437. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2973509
Sboev A, Litvinova T, Gudovskikh D, Rybka R, Moloshnikov I (2016) Machine learning models of text categorization by author gender using topic-independent features. Procedia Comput Sci 101:135–142
Schwartz H A, Eichstaedt J C, Kern M L, Dziurzynski L, Ramones S M, Agrawal M, Shah A, Kosinski M, Stillwell D, Seligman MEP et al (2013) Personality, gender, and age in the language of social media: The open-vocabulary approach. PloS ONE 8(9):e73791
Sendi M, Omri M N, Abed M (2019) Discovery and tracking of temporal topics of interest based on belief-function and aging theories. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 10(9):3409–3425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1050-6
Sharjeel M, Fatima M, Anwar S, Nawab R M A (2018) Multilingual author profiling on sms track at fire’18. In: Proceedings of the 10th annual meeting of the Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, FIRE 2018, Gandhinagar, India, December 06-09, 2018, pp 16–17
Sierra S, Montes-y Gómez M, Solorio T, González F A (2017) Convolutional neural networks for author profiling. Work Notes CLEF
Soler J, Wanner L (2016) A semi-supervised approach for gender identification. In: Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation LREC 2016, Portorož, Slovenia, May 23–28, 2016, pp 1282–1287. European Language Resources Association (ELRA)
Takahashi T, Tahara T, Nagatani K, Miura Y, Taniguchi T, Ohkuma T (2018) Text and image synergy with feature cross technique for gender identification
Villena-Román J, Cristóbal J C G (2014) Daedalus at pan 2014: guessing tweet author’s gender and age. In: Working Notes for CLEF 2014 Conference, Sheffield, UK, September 15–18, 2014, volume 1180 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings, pp 1157–1163. CEUR-WS.org
Yang M, Chen X, Tu W, Lu Z, Zhu J, Qu Q (2018) A topic drift model for authorship attribution. Neurocomputing 273:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.022
Zhang W, Caines A, Alikaniotis D, Buttery P (2016) Predicting author age from weibo microblog posts. In: Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16). p 2990–2997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouni, S., Fkih, F. & Omri, M.N. A survey of machine learning-based author profiling from texts analysis in social networks. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 36653–36686 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14711-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14711-8