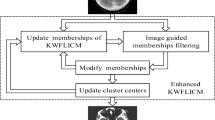
Abstract
For images with high noise, existing robust fuzzy clustering-related methods are difficult to obtain satisfactory segmentation results. Hence, this paper proposes a novel single fuzzifier interval type-2 kernel-based fuzzy local and non-local information c-means clustering driven by a deep neighborhood structure for strong noise image segmentation. Based on the neighborhood window around the current pixel, we firstly construct the novel deep neighborhood window structure, which is composed of neighborhood window around the current pixel and neighborhood window around pixels in the neighborhood window around the current pixel. Secondly maximally and minimally neighborhood weighted distances between current pixels and clustering centers are obtained through deep neighborhood window structure. Thirdly, two local neighborhood distances are used to modify upper and lower fuzzy membership of robust single fuzzifier interval type-2 fuzzy clustering with kernel metric and local versus non-local information, and an enhanced robust interval type-2 kernel-based fuzzy clustering with single fuzzifier is presented for strong noise image segmentation. Experimental results indicate that the proposed algorithm has better segmentation performance and stronger anti-noise robustness, and outperforms existing state-of-the-art robust fuzzy clustering-related algorithms in the presence of high noise. In particular, the segmentation accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 20% higher than that of the important KWFLICM algorithm and has increased by 10% compared with the FALRCM algorithm proposed in recent years.






































Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author S. Peng, upon reasonable request.
References
Abhishek, Jeph A, Rhee FCH (2013) Interval type-2 fuzzy c-means using multiple kernels. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp 1–8
Ahmed MN, Yamany SM, Mohamed N et al (2002) A modified fuzzy c-mean algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21(3):193–199
Ali A, Zhu Y, Zakarya M (2021) A data aggregation based approach to exploit dynamic spatio-temporal correlations for citywide crowd flows prediction in fog computing. Multimed Tools Appl 80:31401–31433
Ali A, Zhu Y, Zakarya M (2021) Exploiting dynamic spatio-temporal correlations for citywide traffic flow prediction using attention based neural networks. Inf Sci 577:852–870
Ali A, Zhu Y, Zakarya M (2022) Exploiting dynamic spatio-temporal graph convolutional neural networks for citywide traffic flows prediction. Neural Netw 145:233–247
Alruwaili M, Siddiqi MH, Javed MA (2020) A robust clustering algorithm using spatial fuzzy c-means for brain MR images. Egyptian Inf J 21:51–66
Ambati LS (2021) EI-Gayar O (2021) Human activity recognition: a comparison of machine learning approaches. J Midwest Assoc Inf Syst 1:49–60
Ambati LS, EI-Gayar O, Nawar N (2020) Influence of the digital divide and socio-economic factors on prevalence of diabetes. Issues Inf Syst 21(4):103–113
Bai X, Zhang Y, Liu H, Wang Y (2018) Intuitionistic center-free FCM clustering for MR brain image segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(5):2039–2051
Bezdek JC, Ehrlich R, Full W et al (1984) FCM: The fuzzy c -means clustering algorithm. Comput Geosci 10(2):191–203
Bezdek JC, Hathaway RJ, Sabin MJ et al (1987) Convergence theory for fuzzy c-means: counterexamples and repairs. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 17(5):873–877
Cai W, Chen S, Zhang D (2007) Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 40(3):825–838
Chen S, Zhang D (2004) Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B (Cybernetics) 34(4):1907–1916
Dante M, Francisco J, Alberto J (2013) A fuzzy clustering algorithm with spatial robust estimation constraint for noisy color image segmentation. Pattern Recogn Lett 34:400–413
EI-Gayar O F, Ambati L S, Nawar N (2020) Wearables, artificial intelligence, and the future of healthcare. In: AI and Big Data’s Potential for Disruptive Innovation 5:104–129
Fan JL, Zhen WZ, Xie WW (2003) Suppressed fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recogn Letters 24:1607–1612
Feng QY, Chen L, Chen CLP, Guo L (2020) Deep fuzzy clustering-A representation learning approach. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(7):1420–1433
Feng Q, Chen L, Chen CLP, Guo L (2020) Deep fuzzy clustering—a representation learning approach. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(7):1420–1433
Gong M, Liang Y, Shi J, Ma W et al (2013) Fuzzy c-means clustering with local information and kernel metric for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(2):573–584
Gong M, Zhou Z, Ma J (2012) Change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on image fusion and fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(4):2141–2151
Guo Y, Sengur A (2013) A novel color image segmentation approach based on neutrosophic set and modified fuzzy c-means, Circuits. Syst Signal Process 32(4):1699–1723
He H, Xing H, Hu D, Yu X (2019) Novel fuzzy uncertainty modeling for land cover classification based on clustering analysis. Sci China Earth Sci 62(2):438–450
Hu J, Pan Y, Li T (2021) TW-Co-MFC: Two-level weighted collaborative multi-view fuzzy clustering based on maximum entropy for multi-view data. Tsinghua Sci Technol 26(2):185–198
Hwang C, Rhee CH (2007) Uncertain fuzzy clustering: Interval type-2 fuzzy approach to c-means. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15:107–120
Jha P, Tiwari A, Bharill N, Ratnaparkhe M, Mounika M, Nagendra N (2021) Apache Spark based kernelized fuzzy clustering framework for single nucleotide polymorphism sequence analysis. Computational Biology and Chemistry Article 92:107454
Kalhori MRN, FazelZarandi MH (2021) A new interval type-2 fuzzy reasoning method for classification systems based on normal forms of a possibility-based fuzzy measure. Inf Sci 581:7–586
Kamili A, Fatima I, Hassan M, Parrah SA, Vijaya KV, Ambati LS (2020) Embedding information reversibly in medical images for e-health. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 39(6):8389–8398
Karnik NN, Mendel JM (2001) Centroid of a type-2 fuzzy set. Inf Sci 132(1):195–220
Kiechle M, Storath M, Weinmann A, Kleinsteuber M (2018) Model-based learning of local image features for unsupervised texture segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(4):1994–2007
Kotaridis I, Lazaridou M (2021) Remote sensing image segmentation advances: A meta-analysis. Social Science Electronic Publishing 172:309–322
Krinidis S, Chatzis V (2010) A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(5):1328–1337
Lam CY, Tai K (2018) Modeling infrastructure interdependencies by integrating network and fuzzy set theory. Int J Crit Infrastruct Prot 22:51–61
Lei T, Jia X, Zhang Y, He L, Meng H et al (2018) Significantly fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm based on morphological reconstruction and membership filtering. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(5):3027–3041
Lei T, Zhang X, Jia X, Liu S, Zhang Y (2019) Research progress on image segmentation based on fuzzy clustering. Acta Electron Sin 47(8):1776–1791
Liu B, He S, He D, Zhang Y, Guizani M (2019) A spark-based parallel fuzzy c-means segmentation algorithm for agricultural image big data. IEEE Access 7:42169–42180
Liu S, Ma J, Yin L, Li H et al (2020) Multi-focus color image fusion algorithm based on super-resolution reconstruction and focused area detection. IEEE Access 8:90760–90778
Long M, Li Z, Xie X, Li G, Wang Z (2018) Adaptive image enhancement based on guide image and fraction-power transformation for wireless capsule endoscopy. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 12(5):993–1003
Mahmoudi MR, Heydari MH, Pho K (2020) Fuzzy clustering to classify several regression models with fractional Brownian motion error. Alex Eng J 59(4):2811–3281
Mai SD, Ngo LT (2015) Interval type-2 fuzzy c-means clustering with spatial information for land-cover classification. Intell Inf Database Syst 9011:387–397
McCulloch J, Wagner C (2019) Measuring the directional or non-directional distance between type-1 and type-2 fuzzy sets with complex membership functions. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(7):1506–1515
Mendel JM (2004) Computing derivatives in interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 12(1):84–98
Mendel JM, John RIB (2002) Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10(2):117–127
Mishro PK, Agrawal S, Panda R, Abraham A (2020) A novel type-2 fuzzy c-means clustering for brain MR image segmentation. IEEE Trans Cybern 51(8):3901–3912
Mittal M, Verma A, Kaur I, Kaur B, Sharma M (2019) An efficient edge detection approach to provide better edge connectivity for image analysis. IEEE Access 7:33240–33255
Na IS, Le H, Kim SH, Lee GS, Yang HJ (2015) Extraction of salient objects based on image clustering and saliency. Pattern Anal Appl 18:667–675
Ngo LT, Mai DS, Pedrycz W (2015) Semi-supervising interval type-2 fuzzy c-means clustering with spatial information for multi-spectral satellite image classification and change detection. Comput Geosci 83:1–16
Nguyen DD, Ngo LT (2013) Multiple kernel interval type-2 fuzzy c-means clustering. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp 1–8
Nie F, Liu C, Wang R, Wang Z, Li X (2021) Fast fuzzy clustering based on anchor graph. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Systms 30(7):375–2387
Opbroek AV, Achterberg HC, Vernooij MW, Bruijne MD (2019) Transfer learning for image segmentation by combining image weighting and kernel learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(1):213–224
Ruiz-Garcia G, Hagras H, Pomares H, Ruiz IR (2019) Toward a fuzzy logic system based on general forms of interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(12):2381–2395
Shirkhorshidi AS, Wah TY, Shirkhorshidi SMR, Aghabozorgi S (2019) Evolving Fuzzy clustering approach: An epoch clustering that enables heuristic post pruning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(3):560–568
Su T, Liu T, Zhang S, Qu Z, Li R (2020) Machine learning-assisted region merging for remote sensing image segmentation. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 168:89–123
Szilagyi L, Benyo Z, Szilagyi SM et al (2003) MR brain image segmentation using an enhanced fuzzy c-means algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp 724–726
Tang Y, Ren F, Pedrycz W (2020) Fuzzy c-means clustering through SSIM and patch for image segmentation. Applied Soft Computing 87:105928
Vu MN, Ngo LT (2016) A multiple kernels interval type-2 possibilistic c-means. Recent Dev Intell Inf Database Syst 642:63–73
Wang Q, Wang X, Fang C, Jiao J (2021) Fuzzy image clustering incorporating local and region-level information with median memberships. Appl Soft Comput 105:107245
Wang Q, Wang X, Fang C, Yang W (2020) Robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with adaptive spatial and intensity constraint and membership linking for noise image segmentation. Appl Soft Comput 92:106318
Wu C (2020) Progress on robust fuzzy clustering for image segmentation. J Xi’an Univ Posts Telecommun 25(6):1–25
Wu C, Guo X (2021) A novel single fuzzifier interval type-2 fuzzy c-means clustering with local information for land-cover segmentation. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 14:5903–5917
Wu C, Liu N (2021) Suppressed robust picture fuzzy clustering for image segmentation. Soft Comput 25:3751–3774
Wu D, Mendel JM (2007) Enhanced Karnik-Mendel algorithms for interval type-2 fuzzy sets and systems. In: NAFIPS 2007–2007 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society, pp 184–189
Wu C, Yang X (2019) Robust credibilistic fuzzy local information clustering with spatial information constraints. Digital Signal Process 97:1–24
Yang J, Jiang Y, Zhang Y (2020) Edge fuzzy clustering by eliminating undesirable features in garment texture image segmentation. IEEE Access 8:45368–45377
Yin P, Yuan R, Cheng Y, Wu Q (2020) Deep guidance network for biomedical image segmentation. IEEE Access 8:116106–116116
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Zhang H, Bruzzone L, Shi W, Hao M, Wang Y (2018) Enhanced spatially constrained remotely sensed imagery classification using a fuzzy local double neighborhood information c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE J Sel Topics Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 11(8):2896–2910
Zhang A, Jiang G, Zhang Y, Tan Z (2018) Remote sensing image change detection based on an adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy clustering. J Geomatics Sci Technol 35(4):376–382
Zhang X, Pan W, Wu Z, Chen J et al (2020) Robust image segmentation using fuzzy c-means clustering with spatial information based on total generalized variation. IEEE Access 8:95681–95697
Zhang X, Sun Y, Liu H, Hou Z et al (2020) Improved clustering algorithms for image segmentation based on non-local information and back projection. Inf Sci 550(6):129–144
Zhao F, Fan JL, Liu HQ (2014) Optimal-selection-based suppressed fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with self-tuning non local spatial information for image segmentation. Expert Syst Appl 41(9):4083–4093
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 61671377), Wu and Peng would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions to improve the overall quality of the paper. Besides, Wu and Peng would like to thank School of Electronic Engineering, Xi’an University of Posts & Telecommunications, Xi’an, China for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Peng, S. Deep neighborhood structure driven interval type-2 kernel fuzzy c-means clustering with local versus non-local information. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 43455–43515 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15230-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15230-2