Abstract
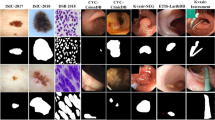
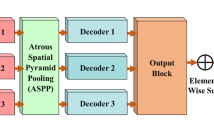
Existing medical image segmentation methods achieve impressive progress but remain challenged by high diversity in region scales or capricious boundaries. Meanwhile, they usually ignore another favorable factor, i.e., correlations between region and boundary, resulting in limitations to performance improvement. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, aiming at accurate segmentation by collaborating region detection and boundary localization subtasks as well as interacting relations between them. In particular, we first put forward a novel multi-level adaptive feature learning module, which can select discriminative information from backbone features by constructing holistic adaptive weights. Then, a collaborative multi-step refinement module is designed to excavate the reciprocal benefits between two subtasks via reasoning their high correlations cues. Moreover, we propose parallel iterative decoders, i.e., region/boundary iterative decoder, each of which consists of attention-based dual iteration paths to effectively aggregate multi-scale features. By cooperating with these three creative parts, our method sets the new state-of-the-art segmentation performance on five polyp benchmarks, where it achieves a mean Dice score of 92.9% on CVC-ClinicDB dataset. Furthermore, we extensively evaluate our method on both skin lesion segmentation from ISIC 2018 and nuclei segmentation from 2018 Data Science Bowl dataset, demonstrating its excellent generalization ability.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were generated or analyzed in this study.
References
An F-P, Liu J- (2021) Medical image segmentation algorithm based on multilayer boundary perception-self attention deep learning model. Multimed Tools Applic 80(10):15017–15039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10515-w
Azad R, Asadi-Aghbolaghi M, Fathy M, Escalera S (2019) Bi-directional convlstm u-net with densley connected convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision workshops, pp 406–415. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00052
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(12):2481–2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Bernal J, Sánchez F J, Fernández-Esparrach G, Gil D, Rodríguez C, Vilariño F (2015) Wm-dova maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput Med Imaging Graph 43:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.02.007
Caicedo J C, Goodman A, Karhohs K W, Cimini B A, Ackerman J, Haghighi M, Heng C, Becker T, Doan M, McQuin C et al (2019) Nucleus segmentation across imaging experiments: the 2018 data science bowl. Nat Methods 16(12):1247–1253
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille A L (2018) Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Chen Z, Zhou H, Lai J, Yang L, Xie X (2021) Contour-aware loss: boundary-aware learning for salient object segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:431–443. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3037536
Cheng M, Kong Z, Song G, Tian Y, Liang Y, Chen J (2021) Learnable oriented-derivative network for polyp segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 720–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_68
Codella N C F, Gutman D, Celebi M E, Helba B, Marchetti M A, Dusza S W, Kalloo A, Liopyris K, Mishra N, Kittler H, Halpern A (2018) Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (isbi), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic). In: 2018 IEEE 15th International symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018), pp 168–172. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2018.8363547
Dai Y, Gieseke F, Oehmcke S, Wu Y, Barnard K (2021) Attentional feature fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 3560–3569. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00360
Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Zhou T, Chen G, Fu H, Shen J, Shao L (2020) Pranet: parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 263–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_26
Fang Y, Chen C, Yuan Y, Tong R K-Y (2019) Selective feature aggregation network with area-boundary constraints for polyp segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 302–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32239-7_34
Feng S, Zhao H, Shi F, Cheng X, Wang M, Ma Y, Xiang D, Zhu W, Chen X (2020) Cpfnet: context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(10):3008–3018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2983721
Fu J, Liu J, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang C, Lu H (2019) Stacked deconvolutional network for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process
Gu R, Wang G, Song T, Huang R, Aertsen M, Deprest J, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T, Zhang S (2020) Ca-net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(2):699–711. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3035253
Guo F, Li W, Kuang Z, Tang J (2021) Mes-net: a new network for retinal image segmentation. Multimed Tools Applic 80(10):14767–14788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10580-1
Jha D, Smedsrud P H, Riegler M A, Halvorsen P, Lange T , Johansen D, Johansen H D (2020) Kvasir-seg: a segmented polyp dataset. In: International conference on multimedia modeling, pp 451–462
Jiang X, Luo Q, Wang Z, Mei T, Wen Y, Li X, Cheng K-T, Yang X (2020) Multi-phase and multi-level selective feature fusion for automated pancreas segmentation from ct images. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 460–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_45
Kervadec H, Bouchtiba J, Desrosiers C, Granger E, Dolz J, Ayed I B (2021) Boundary loss for highly unbalanced segmentation. Medical Image Anal 67:101851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101851
Lee H J, Kim J U, Lee S, Kim H G, Ro Y M (2020) Structure boundary preserving segmentation for medical image with ambiguous boundary. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4817–4826. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00487
Li H, Xiong P, Fan H, Sun J (2019) Dfanet: deep feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9522–9531. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00975
Li Y, Zhang Y, Cui W-G, Lei B, Kuang X, Zhang T (2022) Dual encoder-based dynamic-channel graph convolutional network with edge enhancement for retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 41(8):1975–1989. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2022.3151666
Liu L, Wu F-X, Wang Y-P, Wang J (2020) Multi-receptive-field CNN for semantic segmentation of medical images. IEEE J Biomed Health Informatics 24(11):3215–3225. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2020.3016306
Liu X, Yang L, Chen J, Yu S, Li K (2022) Region-to-boundary deep learning model with multi-scale feature fusion for medical image segmentation. Biomed Signal Process Control 71:103165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103165
Liu Y, Zhou J, Liu L, Zhan Z, Hu Y, Fu Y, Duan H (2022) Fcp-net: a feature-compression-pyramid network guided by game-theoretic interactions for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 41(6):1482–1496. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2021.3140120
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965
Nguyen T-C, Nguyen T-P, Diep G-H, Tran-Dinh A-H, Nguyen T V, Tran M-T (2021) Ccbanet: cascading context and balancing attention for polyp segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 633–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_60
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc L L, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh S, Hammerla N Y, Kainz B et al (2018) Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv:1804.03999
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H (2020) Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9413–9422. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00943
Patel K, Bur A M, Wang G (2021) Enhanced u-net: a feature enhancement network for polyp segmentation. In: 2021 18th Conference on robots and vision (CRV), pp 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1109/CRV52889.2021.00032
Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Dehghan M, Zaiane O R, Jagersand M (2020) U2-net: going deeper with nested u-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recogn 106:107404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 234–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Silva J, Histace A, Romain O, Dray X, Granado B (2014) Toward embedded detection of polyps in WCE images for early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9(2):283–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0926-3
Srivastava A, Jha D, Chanda S, Pal U, Johansen HE D, Johansen D, Riegler M A, Ali S, Halvorsen PE (2022) Msrf-net: a multi-scale residual fusion network for biomedical image segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(5):2252–2263. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2021.3138024
Sun J, Darbehani F, Zaidi M, Wang B (2020) Saunet: shape attentive u-net for interpretable medical image segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 797–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_77
Ta N, Chen H, Lyu Y, Wu T (2022) Ble-net: boundary learning and enhancement network for polyp segmentation. Multimedia Syst, 1–14
Tajbakhsh N, Gurudu S R, Liang J (2016) Automated polyp detection in colonoscopy videos using shape and context information. IEEE Trans Medical Imaging 35(2):630–644. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2487997
Te G, Liu Y, Hu W, Shi H, Mei T (2020) Edge-aware graph representation learning and reasoning for face parsing. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 258–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_16
Tomar N K, Jha D, Riegler M A, Johansen H D, Johansen D, Rittscher J, Halvorsen P, Ali S (2022) Fanet: a feedback attention network for improved biomedical image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
Vázquez D, Bernal J, Sánchez F J, Fernández-Esparrach G, López A M, Romero A, Drozdzal M, Courville A C (2017) A benchmark for endoluminal scene segmentation of colonoscopy images. Journal of Healthcare Engineering
Wang S, Liu M, Lian J, Shen D (2020) Boundary coding representation for organ segmentation in prostate cancer radiotherapy. IEEE Trans Med Imag 40(1):310–320. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3025517
Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, Li P, Zuo W, Hu Q (2020) Eca-net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 11531–11539. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155
Wang J, Wei L, Wang L, Zhou Q, Zhu L, Qin J (2021) Boundary-aware transformers for skin lesion segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 206–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_20
Wang K, Zhang X, Zhang X, Lu Y, Huang S, Yang D (2022) Eanet: iterative edge attention network for medical image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 127:108636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108636
Wang R, Lei T, Cui R, Zhang B, Meng H, Nandi A K (2022) Medical image segmentation using deep learning: a survey. IET Image Process 16 (5):1243–1267. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12419
Wang R, Chen S, Ji C, Fan J, Li Y (2022) Boundary-aware context neural network for medical image segmentation. Med Image Anal 78:102395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102395
Wang X, Li Z, Huang Y, Jiao Y (2022) Multimodal medical image segmentation using multi-scale context-aware network. Neurocomputing 486:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.11.017
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F3net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 34, pp 12321–12328
Wei J, Wang S, Wu Z, Su C, Huang Q, Tian Q (2020) Label decoupling framework for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 13025–13034. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01304
Wei J, Hu Y, Zhang R, Li Z, Zhou S K, Cui S (2021) Shallow attention network for polyp segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 699–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_68
Wu H, Chen S, Chen G, Wang W, Lei B, Wen Z (2022) Fat-net: feature adaptive transformers for automated skin lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 76:102327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102327
Xie S, Girshick R, Dollr P, Tu Z, He K (2017) Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5987–5995. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.634
Yin Z, Liang K, Ma Z, Guo J (2022) Duplex contextual relation network for polyp segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE 19th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI52829.2022.9761402
Yue G, Han W, Jiang B, Zhou T, Cong R, Wang T (2022) Boundary constraint network with cross layer feature integration for polyp segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(8):4090–4099. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2022.3173948
Zhang R, Li G, Li Z, Cui S, Qian D, Yu Y (2020) Adaptive context selection for polyp segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 253–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_25
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (2017) Pyramid scene parsing network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 6230–6239. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.660
Zhao C, Shuai R, Ma L, Liu W, Wu M (2022) Segmentation of skin lesions image based on u-net++. Multimed Tools Applic 81(6):8691–8717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12067-z
Zhong J, Wang W, Wu H, Wen Z, Qin J (2020) Polypseg: an efficient context-aware network for polyp segmentation from colonoscopy videos. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 285–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_28
Zhou Z, Siddiquee M M R, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2019) Unet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(6):1856–1867. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2959609
Zhou S, Wang J, Wang L, Zhang J, Wang F, Huang D, Zheng N (2020) Hierarchical and interactive refinement network for edge-preserving salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3027992
Funding
This research is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB0804202, 2018YFB0804203), the Regional Joint Fund of NSFC (U19A2057), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61876070), the Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project (20190303134SF), and Jilin University Interdisciplinary Integration and Innovation Young Scholars Free Exploration Project (JLUXKJC2021QZ01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ta, N., Chen, H., Du, B. et al. Collaborative region-boundary interaction network for medical image segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 30399–30421 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15505-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15505-8