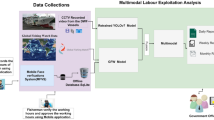
Abstract
Labor exploitation in Taiwan’s Distant Water Fishing (DWF) industry has been a significant issue for many years. Migrant fishermen from Southeast Asian countries, including Indonesia and the Philippines, have reported being subjected to poor working conditions, long work hours, and low pay. Our research aims to identify and address labor exploitation in Taiwan’s DWF vessels through the development of a three-module system. The first module is a mobile application interface used to collect data from fishermen and captains. The second module is responsible for collecting data from an offline SQLite database and Closed-circuit television (CCTV) footage from DWF vessels. The third module employs fisherman detection and tracking models to analyze working hours. We have developed two models to analyze labor exploitation in DWF vessels: a statistical assessment method and a Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) assessment methods. The statistical assessment method provides a quick response, while the MOT assessment method tracks all fishermen in CCTV footage and computes their 24-h work time, which is then compared with the mobile application data to identify instances of labor exploitation. We applied statistical assessment methods to analyze CCTV footage from January 25th, 2022, to January 31st, 2022, and MOT assessment methods were applied to CCTV footage from February 7th, 2022, to February 13th, 2022. Our analysis indicates that there were no instances of labor exploitation during this time frame.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bae K-H, Kim S-H, Go H-Y, Park K-H, Lee S, Lee S (2019) One year test-retest reliability of the korea sasang constitutional diagnostic questionnaire (ks-15) in university students. J Sasang Const Med 31(2):12–21
Bewley A, Ge Z, Ott L, Ramos F, Upcroft B (2016) Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), p 3464–3468
Cao J, Weng X, Khirodkar R, Pang J, Kitani K (2022) Observation-centric sort: Rethinking sort for robust multi-object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.14360. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Ciaparrone G, Sánchez FL, Tabik S, Troiano L, Tagliaferri R, Herrera F (2020) Deep learning in video multi-object tracking: A survey. Neurocomputing 381:61–88
Dendorfer P, Osep A, Milan A, Schindler K, Cremers D, Reid I, Roth S, Leal-Taixé L (2021) Motchallenge: A benchmark for single-camera multiple target tracking. Int J Comput Vision 129(4):845–881
Girshick R (2015) Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, p 1440–1448
Howard AG, Zhu M, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W, Weyand T, Andreetto M, Adam H (2017) Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Jackson B, Bales K, Owen S, Wardlaw J, Boyd DS (2019) Analysing slavery through satellite technology: how remote sensing could revolutionise data collection to help end modern slavery. J Mod Slavery 4(2):61–199
Kalman RE (1960) A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. J Basic Eng 82(1):35–45
Leal-Taixé L, Milan A, Schindler K, Cremers D, Reid I, Roth S (2017) Tracking the trackers: an analysis of the state of the art in multiple object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.02781. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Li W, Xiong Y, Yang S, Xu M, Wang Y, Xia W (2021) Semi-tcl: Semi-supervised track contrastive representation learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.02396. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Luo W, Xing J, Milan A, Zhang X, Liu W, Kim T-K (2021) Multiple object tracking: A literature review. Artif Intell 293:103448
McDonald GG, Costello C, Bone J, Cabral RB, Farabee V, Hochberg T, Kroodsma D, Mangin T, Meng KC, Zahn O (2021) Satellites can reveal global extent of forced labor in the world’s fishing fleet. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(3):e2016238117
Mumic N, Filzmoser P (2021) A multivariate test for detecting fraud based on benford’s law, with application to music streaming data. Stat Methods Appl 30(3):819–840
Pang J, Qiu L, Li X, Chen H, Li Q, Darrell T, Yu F (2021) Quasi-dense similarity learning for multiple object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 164–173
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A (2016) You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 779–788
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Advances in neural information processing systems. In: Twenty-ninth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, December 7-12-2015, Canada
Selig ER, Nakayama S, Wabnitz CCC, Österblom H, Spijkers J, Miller NA, Bebbington J, Decker Sparks JL (2022) Revealing global risks of labor abuse and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing. Nat Commun 13(1):1–11
Stadler D, Beyerer J (2021) On the performance of crowd-specific detectors in multi-pedestrian tracking. In 2021 17th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), p 1–12. IEEE
Swartz W, Cisneros-Montemayor AM, Singh GG, Boutet P, Ota Y (2021) Ais-based profiling of fishing vessels falls short as a “proof of concept” for identifying forced labor at sea. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(19):e2100341118
Tai T-H, Kao S-M, Ho W-C (2020) International soft laws against iuu fishing for sustainable marine resources: adoption of the voluntary guidelines for flag state performance and challenges for taiwan. Sustainability 12(15):6013
Wang C-Y, Bochkovskiy A, Mark Liao H-Y (2022) Yolov7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.02696. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Wang Z, Zheng L, Liu Y, Wang S (2019) Towards real-time multi-object tracking, 2(3):4. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.12605. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Wojke N, Bewley A, Paulus D (2017) Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), p 3645–3649
Wolek A, McMahon J, Dzikowicz BR, Houston BH (2020) Tracking multiple surface vessels with an autonomous underwater vehicle: field results. IEEE J Ocean Eng 47(1):32–45
Yang F, Zhang X, Liu B (2022) Video object tracking based on yolov7 and deepsort. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.12202. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Yen K-W, Liuhuang L-C (2021) A review of migrant labour rights protection in distant water fishing in taiwan: From laissez-faire to regulation and challenges behind. Mar Policy 134:104805
Yu E, Li Z, Han S, Wang H (2022) Relationtrack: Relation-aware multiple object tracking with decoupled representation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3150169
Zhang Y, Sun P, Jiang Y, Yu D, Yuan Z, Luo P, Liu W, Wang X (2021) Bytetrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.06864. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Zhang Y, Wang C, Wang X, Zeng W, Liu W (2021) Fairmot: On the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking. Int J Comput Vision 129(11):3069–3087
Zhou X, Koltun V, Krähenbühl P (2020) Tracking objects as points. In European Conference on Computer Vision, p 474–490. Springer
Zhou X, Wang D, Krähenbühl P (2019) Objects as points. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.07850. Accessed 6 Jul 2023
Funding
This work is supported by the National Science and Technology Council(NSTC) of Taiwan through research project 110–2420-H-194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karthikeyan, P., Chang, C.C. & Hsiung, PA. Labor exploitation investigation using statistical and multiple object tracking assessment methods. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 46085–46108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16094-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16094-2