Abstract
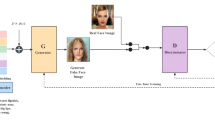
The current text-to-face synthesis models only utilize text descriptions for image synthesis, neglecting the prior information of basic facial features. This leads to insufficient learning of both coarse-grained facial features, such as face shape and positions of the basic organs, and fine-grained facial features, such as facial wrinkles and hair textures, by the generators in each stage. As a result, the quality of the generated faces is low. To address this issue, we propose a generic face template. It includes only common facial information, such as face contour, shapes and relative positions of the basic organs. Moreover, to embed the face template into the first-stage generator of three stages for assisting face generation, we design a Facial Coarse-grained Feature Excitation Module (FCFEM). FCFEM extracts the coarse-grained feature channel weights of the face template. And it performs channel recalibration on the intermediate feature maps of the first-stage generator. This helps to generate more precise and complete initial face images. Therefore, it can enhance the ability of the generators in the latter two stages to learn fine-grained features. Experiments on the Multi-Modal CelebA-HQ dataset demonstrate that the multi-stage models using our method generate face images with higher quality and realism compared to the original models. They also achieve higher semantic consistency between generated images and text descriptions.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the repository [30], https://github.com/IIGROUP/MM-CelebA-HQ-Dataset.
References
Chen X, Qing L, He X, Luo X, Xu Y (2019) Ftgan: A fully-trained generative adversarial networks for text to face generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.05729
Cheng J, Wu F, Tian Y, Wang L, & Tao D (2020) Rifegan: Rich feature generation for text-to-image synthesis from prior knowledge. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 10911–10920
Di X, Patel VM (2019) Facial synthesis from visual attributes via sketch using multiscale generators. IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science 2(1):55–67
Gatt A, Tanti M, Muscat A, Paggio P, Farrugia RA, Borg C, Camilleri KP, Rosner M, Van der Plas L (2018) Face2text: Collecting an annotated image description corpus for the generation of rich face descriptions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.03827
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27
Heusel M, Ramsauer H, Unterthiner T, Nessler B, Hochreiter S (2017) Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 7132–7141
Karras T, Aila T, Laine S, Lehtinen J (2017) Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196
Karras T, Laine S, Aila T (2019) A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 4401–4410
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 740–755. Springer
Li B, Qi X, Lukasiewicz T, Torr P (2019) Controllable text-to-image generation. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32
Liu Z, Luo P, Wang X, Tang X (2015) Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 3730–3738
Luo X, He X, Chen X, Qing L, Zhang J (2022) Dualg-gan, a dual-channel generator based generative adversarial network for text-to-face synthesis. Neural Netw 155:155–167
Lu Y, Tai YW, Tang CK (2018) Attribute-guided face generation using conditional cyclegan. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 282–297
Nasir OR, Jha SK, Grover MS, Yu Y, Kumar A, Shah RR (2019) Text2facegan: Face generation from fine grained textual descriptions. In 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), pages 58–67. IEEE
Odena A, Olah C, Shlens J (2017) Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier gans. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 2642–2651. PMLR
Park H, Yoo Y, Kwak N (2018) Mc-gan: Multi-conditional generative adversarial network for image synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.01123, 2018
Qiao X, Han Y, Wu Y, Zhang Z (2021) Progressive text-to-face synthesis with generative adversarial network. In 2021 16th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2021), pages 1–8. IEEE
Qiao T, Zhang J, Xu D, Tao D (2019) Mirrorgan: Learning text-to-image generation by redescription. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1505–1514
Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S (2015) Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06434
Reed S, Akata Z, Yan X, Logeswaran L, Schiele B, Lee H (2016) Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 1060–1069. PMLR
Ruan S, Zhang Y, Zhang K, Fan Y, Tang F, Liu Q, Chen E (2021) Dae-gan: Dynamic aspect-aware gan for text-to-image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 13960–13969
Stap D, Bleeker M, Ibrahimi S, ter Hoeve M (2020) Conditional image generation and manipulation for user-specified content. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.04909
Sun J, Deng Q, Li Q, Sun M, Ren M, Sun Z (2022) Anyface: Free-style text-to-face synthesis and manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 18687–18696
Sun J, Li Q, Wang W, Zhao J, Sun Z (2021) Multi-caption text-to-face synthesis: Dataset and algorithm. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pages 2290–2298
Tao M, Tang H, Wu F, Jing XY, Bao BK, Xu C (2022) Df-gan: A simple and effective baseline for text-to-image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 16515-16525
Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, Perona P, Belongie S (2011) The caltech-ucsd birds-200-2011 dataset
Wang Y, Dantcheva A, Bremond F (2018) From attribute-labels to faces: face generation using a conditional generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops
Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, Li P, Zuo W, Hu Q (2020) Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 11534–11542
Xia W, Yang Y, Xue JH, Wu B (2021) Tedigan: Text-guided diverse face image generation and manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2256–2265
Xu T, Zhang P, Huang Q, Zhang H, Gan Z, Huang X, He X (2018) Attngan: Fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1316–1324
Yin G, Liu B, Sheng L, Yu N, Wang X, Shao J (2019) Semantics disentangling for text-to-image generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2327–2336
Yuan Z, Zhang J, Shan S, Chen X (2021) Attributes aware face generation with generative adversarial networks. In 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pages 1657–1664. IEEE
Zhang H, Xu T, Li H, Zhang S, Wang X, Huang X, Metaxas DN (2018) Stackgan++: Realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(8):1947–1962
Zhang H, Xu T, Li H, Zhang S, Wang X, Huang X, Metaxas DN (2017) Stackgan: Text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 5907–5915
Zhu M, Pan P, Chen W, Yang Y (2019) Dm-gan: Dynamic memory generative adversarial networks for text-to-image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5802–5810
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, H. A face template: Improving the face generation quality of multi-stage generative adversarial networks using coarse-grained facial priors. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 21677–21693 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16183-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16183-2