Abstract
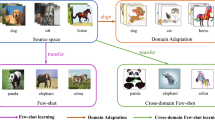
Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) focuses on transferring knowledge learned from the source domain to the target domain. In the classic setting, test data only come from the target domain. Recently, a more reasonable setting Generalized ZSL (G-ZSL) evaluates the model by recognizing instances from both the source and the target domain. However, G-ZSL still have some unrealistic assumptions. One of such hypotheses is the class-fixed setting: during the training time, G-ZSL algorithms only learn to recognize a fixed class set, and we cannot modify the target model unless retraining. The capacity of learning continuously and efficiently is crucial for learning algorithms in a real scenario. In this paper, we extend G-ZSL to a more realistic setting: instead of supposing the class-fixed training strategy, the incoming data come in the way of class-incremental order. In different learning episodes, disjoint groups of categories are utilized to train the G-ZSL models. As the training process goes on, the source domain is expanding. In such a Class-Incremental Generalized Zero-Shot Learning (CIG-ZSL) setting, learning algorithms are expected to not only transfer the learned knowledge to the target domain but also to remember the previously learned knowledge. We propose a Dual Path Learner (DPL) algorithm to validate the possibility of solving the CIG-ZSL task. Experiments on several benchmarks show that DPL has the capacity of remembering the knowledge learned from previous source instances and be able to migrate all the knowledge to the target domain as the expanding of the source domain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akata Z, Perronnin F, Harchaoui Z, Schmid C (2016) Label-embedding for image classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(7):1425–1438
Ben-David S, Kushilevitz E, Mansour Y (1997) Online learning versus offline learning. Mach Learn 29(1):45–63
Bendale A, Boult T (2015) Towards open world recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1893–1902
Candy PC (1991) Self-Direction for Lifelong Learning. A Comprehensive Guide to Theory and Practice, ERIC
Chao WL, Changpinyo S, Gong B, Sha F (2016) An empirical study and analysis of generalized zero-shot learning for object recognition in the wild. In ECCV
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In CVPR
Farhadi A, Endres I, Hoiem D, Forsyth D (2009) Describing objects by their attributes. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on, pages 1778–1785. IEEE
Felix R, Kumar VBG, Reid I, Carneiro G (2018) Multi-modal cycle-consistent generalized zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 21–37
Field J (2000) Lifelong learning and the new educational order. ERIC
Frome A, Corrado GS, Shlens J, Bengio S, Dean J, Ranzato MA, Mikolov T (2013) DeViSE: A deep visual-semantic embedding model. In NIPS
Fu Y, Hospedales TM, Xiang T, Gong S (2015) Transductive multi-view zero-shot learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(11):2332–2345
Fu Y, Sigal L (2016) Semi-supervised vocabulary-informed learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5337–5346
Fu Y, Xiang T, Jiang YG, Xue X, Sigal L, Gong S (2018) Recent advances in zero-shot recognition: Toward data-efficient understanding of visual content
Kankuekul P, Kawewong A, Tangruamsub S, Hasegawa O (2012) Online incremental attribute-based zero-shot learning. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Kingma D, Ba J (2015) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In ICLR
Kirkpatrick J, Pascanu R, Rabinowitz N, Veness J, Desjardins G, Rusu AA, Milan K, Quan J, Ramalho T, Grabska-Barwinska A, et al (2017) Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, page 201611835
Lampert CH, Nickisch H, Harmeling S (2013) Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE TPAMI
Lampert CH, Nickisch H, Harmeling S (2014) Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(3):453–465
Larochelle H, Erhan D, Bengio Y (2008) Zero-data learning of new tasks. In AAAI
Liu S, Long M, Wang J, Jordan M (2018) Generalized zero-shot learning with deep calibration network. In NIPS
McCloskey M, Cohen NJ (1989) Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. In Psychology of learning and motivation, volume 24, pages 109–165. Elsevier
Mensink T, Verbeek J, Perronnin F, Csurka G (2013) Distance-based image classification: Generalizing to new classes at near-zero cost. In IEEE TPAMI
Mensink T, Verbeek J, Perronnin F, Csurka G (2012) Metric learning for large scale image classification: Generalizing to new classes at near-zero cost. In ECCV
McCloskey M, Cohen NJ (1989) Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. Psychology of Learning and Motivation
Norouzi M, Mikolov T, Bengio S, Singer Y, Shlens J, Frome A, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Zero-shot learning by convex combination of semantic embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5650
Parikh D, Grauman K (2011) Relative attributes. In ICCV
Patterson G, Hays J (2012) Sun attribute database: Discovering, annotating, and recognizing scene attributes. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Pentina A, Lampert CH (2014) A PAC-bayesian bound for lifelong learning. In International Conference on Machine Learning
Rebuffi SA, Kolesnikov A, Sperl G, Lampert CH (2017) icarl: Incremental classifier and representation learning. In CVPR
Rohrbach M, Stark M, Schiele B (2011) Evaluating knowledge transfer and zero-shot learning in a large-scale setting. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on, pages 1641–1648. IEEE
Ruvolo P, Eaton E (2013) Ella: An efficient lifelong learning algorithm. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 507–515
Schlimmer JC, Fisher D (1986) A case study of incremental concept induction. In AAAI 86:496–501
Socher R, Ganjoo M, Sridhar H, Bastani O, Manning CD, Ng AY (2013) Zero-shot learning through cross-modal transfer. In NIPS
Thrun S, Mitchell TM (1995) Lifelong robot learning. Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Verma VK, Arora G, Mishra A, Rai P (2018) Generalized zero-shot learning via synthesized examples. In The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, Perona P, Belongie S (2011) The Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011 Dataset. Technical Report CNS-TR-2011-001, California Institute of Technology
Xian Y, Lampert CH, Schiele B, Akata Z (2018) Zero-shot learning-a comprehensive evaluation of the good, the bad and the ugly. IEEE TPAMI
Xian Y, Lorenz T, Schiele B, Akata Z (2018) Feature generating networks for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Yang FSY, Zhang L, Xiang T, Torr PHS, Hospedales TM (2018) Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning
Yu X, Aloimonos Y (2010) Attribute-based transfer learning for object categorization with zero/one training example. In European Conference on Computer Vision
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests and conflicts of interests
All the authours come from Fudan University, China. And the conflicts of interest domain would be fudan.edu.cn. There is no fund supporting this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Feng, R. & Fu, Y. Class-Incremental Generalized Zero-Shot Learning. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 38233–38247 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16316-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16316-7