Abstract
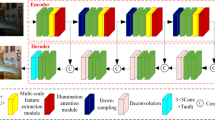
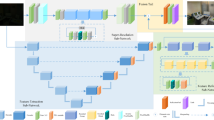
Low-light image enhancement is a long-term low-level vision problem, which aims to improve the visual quality of images captured in low illumination environment. Convolutional neural network (CNN) is the foundation of the majority of low-light image enhancement algorithms now. The limitations of CNN receptive field lead to the inability to establish long-range context interaction. In recent years, Transformer has received increasing attention in computer vision due to its global attention. In this paper, we design the Swin Transformer and ResNet-based Generative Adversarial Network (STRN) for low-light image enhancement by combining the advantages of ResNet and the Swin Transformer. The STRN consists of a U-shaped generator and multiscale discriminators. The generator is composed of a shallow feature extraction, a deep feature extraction, and an image reconstruction module. To calculate the global and local attention, we alternately use Swin Transformer blocks and ResNet in the deep feature processing module. The self perceptual loss and the spatial consistency loss are employed to constrain the random paired training of STRN. The experimental results on benchmark datasets and real-world low-light images demonstrate that the proposed STRN achieves state-of-the-art performance on low-light image enhancement tasks in terms of visual quality and evaluation metrics.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
LOL and MIT-Adobe FiveK data sets come from public data sets.
References
Park M-W, In Kim J, Lee Y-J, Park J, Suh W (2017) Vision-based surveillance system for monitoring traffic conditions. Multimedia Tools Appl 76(23):25343–25367
Wang Q, Lu X, Zhang C, Yuan Y, Li X (2022) Lsv-lp: Large-scale videobased license plate detection and recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(1):752–767
Huang O, Long W, Bottenus N, Lerendegui M, Trahey GE, Farsiu S, Palmeri ML (2020) Mimicknet, mimicking clinical image post-processing under black-box constraints. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 39(6):2277–2286
Liu Y, Li Q, Yuan Y, Du Q, Wang Q (2021) Abnet: Adaptive balanced network for multiscale object detection in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–14
Wang S, Zhou T, Lu Y, Di H (2021) Contextual transformation network for lightweight remote-sensing image super-resolution. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–13
Li C, Guo C, Han L-H, Jiang J, Cheng M-M, Gu J, Loy CC (2021) Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 01:1–1
Liu J, Xu D, Yang W, Fan M, Huang H (2021) Benchmarking lowlight image enhancement and beyond. Int J Comput Vis 129(4):1153–1184
Pizer SM (1990) Contrast–limited adaptive histogram equalization: Speed and effectiveness stephen m. pizer, r. eugene johnston, james p. ericksen, bonnie c. yankaskas, keith e. muller medical image display research group. In: Proceedings of the First Conference on Visualization in Biomedical Computing, Atlanta, Georgia, vol. 337, p. 1
Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Kabir MH, Dewan MAA, Chae O (2007) A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 53(2):593–600
Jobson DJ, Rahman Z-u, Woodell GA (1997) A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans Image process 6(7):965–976
Wang S, Zheng J, Hu H-M, Li B (2013) Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(9):3538–3548
Guo X, Li Y, Ling H (2016) Lime: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(2):982–993
Fu X, Zeng D, Huang Y, Zhang X-P, Ding X (2016) A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2782–2790
Ying Z, Li G, Gao W (2017) A bio–inspired multi–exposure fusion framework for low–light image enhancement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00591
Lore KG, Akintayo A, Sarkar S (2017) Llnet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognition 61:650–662
Wei C, Wang W, Yang W, Liu J (2018) Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.04560
Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K (2007) Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(8):2080–2095
Ma L, Ma T, Liu R, Fan X, Luo Z (2022) Toward fast, flexible, and robust low–light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5637–5646
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Guo X (2019) Kindling the darkness: A practical lowlight image enhancer. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1632–1640
Zhang Y, Guo X, Ma J, Liu W, Zhang J (2021) Beyond brightening lowlight images. International Journal of Computer Vision 129(4):1013–1037
Zhu A, Zhang L, Shen Y, Ma Y, Zhao S, Zhou Y (2020) Zero–shot restoration of underexposed images via robust retinex decomposition. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6. IEEE
Zheng C, Shi D, Shi W (2021) Adaptive unfolding total variation network for low–light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4439–4448
Yang W, Wang S, Fang Y, Wang Y, Liu J (2020) From fidelity to perceptual quality: A semi–supervised approach for low–light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3063–3072
Xu X, Wang R, Fu C-W, Jia J (2022) Snr–aware low–light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 17714–17724
Jiang Y, Gong X, Liu D, Cheng Y, Fang C, Shen X, Yang J, Zhou P, Wang Z (2021) Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:2340–2349
Guo, C., Li, C., Guo, J., Loy, C.C., Hou, J., Kwong, S., Cong, R (2020) Zero–reference deep curve estimation for low–light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1780–1789
Liu R, Ma L, Zhang J, Fan X, Luo Z (2021) Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low–light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10561–10570
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10012–10022
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, et al (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Han K, Xiao A, Wu E, Guo J, Xu C, Wang Y (2021) Transformer in transformer. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34:15908–15919
Wang W, Xie E, Li X, Fan D-P, Song K, Liang D, Lu T, Luo P, Shao L (2021) Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 568–578
Zhang B, Gu S, Zhang B, Bao J, Chen D, Wen F, Wang Y, Guo B (2022) Styleswin: Transformer–based gan for high–resolution image generation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11304–11314
Wang Q, Liu Y, Xiong Z, Yuan Y (2022) Hybrid feature aligned network for salient object detection in optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–15
Wang S, Zhou T, Lu Y, Di H (2022) Detail-preserving transformer for light field image super-resolution. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 36:2522–2530
Zamir SW, Arora A, Khan S, Hayat M, Khan FS, Yang M-H (2022) Restormer: Efficient transformer for high–resolution image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5728–5739
Wang Z, Cun X, Bao J, Zhou W, Liu J, Li H (2022) Uformer: A general u–shaped transformer for image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 17683–17693
Nie L, Chen T, Wang Z, Kang W, Lin L (2022) Multi-label image recognition with attentive transformer-localizer module. Multimedia Tools and Applications 81(6):7917–7940
Agilandeeswari L, Meena SD (2022) Swin transformer based contrastive selfsupervised learning for animal detection and classification. Multimedia Tools Appl, 1–26
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30
Xiao T, Singh M, Mintun E, Darrell T, Dollár P, Girshick R (2021) Early convolutions help transformers see better. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34:30392–30400
Isola P, Zhu J-Y, Zhou T, Efros AA (2017) Image–to—image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1125–1134
Jolicoeur-Martineau A (2018) The relativistic discriminator: a key element missing from standard gan. arXiv arXiv:1807.00734
Mao X, Li Q, Xie H, Lau RY, Wang Z, Paul Smolley S (2017) Least squares generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2794–2802
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for largescale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
Yang W, Wang W, Huang H, Wang S, Liu J (2021) Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 30:2072–2086
Bychkovsky V, Paris S, Chan E, Durand F (2011) Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In: CVPR 2011, pp. 97–104. IEEE
Gharbi M, Chen J, Barron JT, Hasinoff SW, Durand F (2017) Deep bilateral learning for real-time image enhancement. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 36(4):1–12
Hu Y, He H, Xu C, Wang B, Lin S (2018) Exposure: A white-box photo post-processing framework. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37(2):1–17
Park J, Lee J-Y, Yoo D, Kweon IS (2018) Distort–and–recover: Color enhancement using deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5928–5936
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans on Image Processing 13(4):600–612
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2012) Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(3):209–212
Mittal A, Moorthy AK, Bovik AC (2012) No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Transactions on image processing 21(12):4695–4708
Guo X, Hu Q (2023) Low-light image enhancement via breaking down the darkness. International Journal of Computer Vision 131(1):48–66
Yang K-F, Cheng C, Zhao S-X, Yan H-M, Zhang X-S, Li Y-J (2023) Learning to adapt to light. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1–20
Chen X, Li J, Hua Z (2023) Retinex low-light image enhancement network based on attention mechanism. Multimedia Tools Appl 82(3):4235–4255
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62272240 and Grant 61802203, in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications under Grant NY221081, and in part by Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province under Grant SJCX23_0280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Hu, C., Zhang, B. et al. Swin transformer and ResNet based deep networks for low-light image enhancement. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 26621–26642 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16650-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16650-w