Abstract
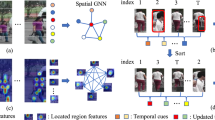
Video-based pedestrian re-identification (ReID) is able to match the same pedestrian from various cameras in a complex real-world scene. The extracted representations can’t contain all the useful information about the persons, due to the occlusion and misalignment of human areas between video sequences, and thus lack integrity and discrimination. To resolve this issue, we propose a new Spatial-Temporal Aware Network, which can mine and complement person features with feature relationships and intra-frame cues. According to the high correlation of the feature nodes of the same person between different video sequences, we employ the learned pedestrian feature nodes to construct the temporal relationship graph. In detail, the Temporal Interaction Module is designed to locate relevant pedestrian regions by modeling the correlation of feature nodes with reference nodes; and the Temporal Attention Module that we have designed is used to select more specific reference nodes. Then, we apply the designed Spatial Reference Module to adaptively mine each frame for fine-grained cues, making the spatial-temporal characteristics of persons more discriminative. We have implemented numerous experiments to demonstrate the excellent performance of STAN, such as achieving 88.0\(\%\) mAP and 89.5\(\%\) Rank-1 accuracy on the MARS dataset.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to [REASON(S) WHY DATA ARE NOT PUBLIC] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Andriluka M, Roth S, Schiele B (2008) People-tracking-by-detection and people-detection-by-tracking. In: 2008 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 1–8
Tang S, Andriluka M, Andres B, Schiele B (2017) Multiple people tracking by lifted multicut and person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 3539–3548
Khan FM, Brémond F (2016) Person re-identification for real-world surveillance systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.05975
Wang X (2013) Intelligent multi-camera video surveillance: A review. Pattern Recognit Lett 34(1):3–19
Chen XS et al (2020) Salience-guided cascaded suppression network for person re-identification. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Electr Network, 2020. pp 3297–3307
Su C et al (2017) Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification. In: 16th IEEE International conference on computer vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017. pp 3980–3989
Wei L, Zhang S, Gao W, Tian Q (2018) Person Transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In 31st IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, 2018. IEEE, pp 79–88
Wang C, Zhang Q, Huang C, Liu W, Wang X (2018) Mancs: A Multi-task Attentional Network with Curriculum Sampling for Person Re-Identification. In: 15th European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018, vol. 11208, pp 384–400
Zhang Z, Lan C, Zeng W, Chen Z (2020) Multi-granularity reference-aided attentive feature aggregation for video-based person re-identification. Ed. IEEE
Eom C, Lee G, Lee J, Ham B (2021) Video-based person re-identification with spatial and temporal memory networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. pp 12036–12045
Wang Y, Zhang P, Gao S, Geng X, Lu H, Wang D (2021) Pyramid spatial-temporal aggregation for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. pp 12026–12035
Bhuiyan A, Huang JX (2022) STCA: Utilizing a spatio-temporal cross-attention network for enhancing video person re-identification. Image Vis Comput 123:104474
McLaughlin N, del Rincon JM, Miller P (2016) Recurrent convolutional network for video-based person re-identification. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, 2016. IEEE, pp 1325–1334
Xu S, Cheng Y, Gu K, Yang Y, Chang S, Zhou P (2017) Jointly attentive spatial-temporal pooling networks for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 4733–4742
Chung D, Tahboub K, Delp EJ (2017) A two stream siamese convolutional neural network for person re-identification. In: 16th IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017. IEEE, pp 1992–2000
Gu XQ, Chang H, Ma BP, Shan SG (2022) Motion feature aggregation for video-based person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:3908–3919
Zhang R et al (2019) SCAN: self-and-collaborative attention network for video person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(10):4870–4882
Liu J, Zha Z-J, Chen X, Wang Z, Zhang Y (2019) Dense 3D-convolutional neural network for person re-identification in videos. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 15(1):8
Fu Y, Wang X, Wei Y, Huang T, Aaai (2019) STA: spatial-temporal attention for large-scale video-based person re-identification. In: 33rd AAAI Conference on artificial intelligence / 31st innovative applications of artificial intelligence conference / 9th AAAI symposium on educational advances in artificial intelligence, Honolulu, HI, 2019. pp 8287–8294
Li J, Wang J, Tian Q, Gao W, Zhang S (2019) Global-local temporal representations for video person re-identification. In: IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019. IEEE, pp 3957–3966
Gu X, Chang H, Ma B, Zhang H, Chen X (2020) Appearance-preserving 3d convolution for video-based person re-identification. European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 228–243
Gao J, Nevatia R (2018) Revisiting temporal modeling for video-based person reid. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.02104
Pei S, Fan X (2021) Multi-level fusion temporal-spatial co-attention for video-based person re-identification. Entropy 23(12):1686
Liu C-T, Wu C-W, Wang Y-CF, Chien S-Y (2019) Spatially and temporally efficient non-local attention network for video-based person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.01683
Song W, Zheng J, Wu Y, Chen C, Liu F (2021) Discriminative feature extraction for video person re-identification via multi-task network. Appl Intell 51:788–803
Liu X, Zhang P, Yu C, Lu H, Qian X, Yang X (2021) A video is worth three views: Trigeminal transformers for video-based person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.01745
Wu D, Ye M, Lin G, Gao X, Shen J (2022) Person re-identification by context-aware part attention and multi-head collaborative learning. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 17:115–126
Yang F, Wang X, Zhu X, Liang B, Li W (2022) Relation-based global-partial feature learning network for video-based person re-identification. Neurocomputing 488:424–435
Bai S, Ma B, Chang H, Huang R, Shan S, Chen X (2021) SANet: Statistic attention network for video-based person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 32(6):3866–3879
Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B (2017) In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA. IEEE, pp 2818–2826
Zheng L et al (2016) Mars: A video benchmark for large-scale person re-identification. European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 868–884
Wang T, Gong S, Zhu X, Wang S (2014) Person re-identification by video ranking. European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 688–703
Wu Y, Lin Y, Dong X, Yan Y, Ouyang W, Yang Y (2018) Exploit the unknown gradually: One-shot video-based person re-identification by stepwise learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 5177–5186
Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, Cucchiara R, Tomasi C (2016) Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 17–35
Luo H, Gu Y, Liao X, Lai S, Jiang W (2019) Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: 32nd IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, 2019. IEEE, pp 1487–1495
Zhang G, Chen Y, Dai Y, Zheng Y, Wu Y (2021) Reference-aided part-aligned feature disentangling for video person re-identification. In: 2021 IEEE International conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). IEEE, pp 1-6
Kiran M, Bhuiyan A, Nguyen-Meidine L, Blais-Morin LA, Ben Ayed I, Granger E (2021) Flow guided mutual attention for person re-identification. Image Vis Comput 113:104246
Wang Z et al (2021) Robust video-based person re-identification by hierarchical mining. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol
Chen Z, Zhou Z, Huang J, Zhang P, Li B, Assoc Advancement Artificial I (2020) Frame-guided region-aligned representation for video person re-identification. In: 34th AAAI Conference on artificial intelligence / 32nd innovative applications of artificial intelligence conference / 10th AAAI symposium on educational advances in artificial intelligence, New York, NY, 2020, vol 34. pp 10591–10598
Jiang M, Leng B, Song G, Meng Z (2020) Weighted triple-sequence loss for video-based person re-identification. Neurocomputing 381:314–321
Subramaniam A, Nambiar A, Mittal A (2019) Co-segmentation inspired attention networks for video-based person re-identification. In: IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019. , IEEE, pp 562–572
Lin G, Zhao S, Shen J (2021) Video person re-identification with global statistic pooling and self-attention distillation. Neurocomputing 453:777–789
Fu H, Zhang K, Li HY, Wang JY, Wang Z (2022) Spatial temporal and channel aware network for video-based person re-identification. Image Vis Comput 118:104356
Liu Y, Yuan Z, Zhou W, Li H, Aaai (2019) Spatial and temporal mutual promotion for video-based person re-identification. In: 33rd AAAI Conference on artificial intelligence / 31st innovative applications of artificial intelligence conference / 9th AAAI symposium on educational advances in artificial intelligence, Honolulu, HI, 2019. pp 8786–8793
Li PK, Pan PB, Liu P, Xu ML, Yang Y (2021) Hierarchical temporal modeling with mutual distance matching for video based person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 31(2):503–511
Hou R et al (2019) VRSTC: Occlusion-free video person re-identification. In: 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, 2019. pp 7176–7185
Yang X, Liu L, Wang N, Gao X (2021) A two-stream dynamic pyramid representation model for video-based person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:6266–6276
Gu XQ, Ma BP, Chang H, Shan SG, Chen XL (2019) Temporal knowledge propagation for image-to-video person re-identification. In IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019. IEEE, pp 9646–9655
Porrello A, Bergamini L, Calderara S (2020) Robust re-identification by multiple views knowledge distillation. European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 93–110
Hirzer M, Beleznai C, Roth PM, Bischof H (2011) Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. pp 91–102
Li J, Zhang S, Huang T (2020) Multi-scale temporal cues learning for video person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:4461–4473
Batool E, Gillani S, Naz S, Bukhari M, Maqsood M, Yeo S-S, Rho S (2023) POSNet: a hybrid deep learning model for efficient person re-identification. J Supercomput 1–29
Song W, Zheng J, Wu Y, Chen C, Liu F (2020) Video-based person re-identification using a novel feature extraction and fusion technique. Multimed Tools Appl 79:12471–12491
Ouyang D, Zhang Y, Shao J (2019) Video-based person re-identification via spatio-temporal attentional and two-stream fusion convolutional networks. Pattern Recognit Lett 117:153–160
Cheng L, Jing X-Y, Zhu X, Ma F, Hu C-H, Cai Z, Qi F (2020) Scale-fusion framework for improving video-based person re-identification performance. Neural Comput Appl 32:12841–12858
Chen L, Yang H, Gao Z (2020) Comprehensive feature fusion mechanism for video-based person re-identification via significance-aware attention. Signal Process Image Commun 84:115835
Tagore NK, Chattopadhyay P, Wang L (2020) T-MAN: a neural ensemble approach for person re-identification using spatio-temporal information. Multimed Tools Appl 79(37–38):28393–28409
Wang X, Zhao X (2019) Temporal regularized spatial attention for video-based person re-identification. pp 2249–2253
Gong W, Yan B, Lin C (2020) Flow-guided feature enhancement network for video-based person re-identification. Neurocomputing 383:295–302
Lu Z, Zhang G, Huang G, Yu Z, Pun C-M, Zhang W, Chen J, Ling W-K (2022) Video person re-identification using key frame screening with index and feature reorganization based on inter-frame relation. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13(9):2745–2761
Li J, Piao Y (2022) Video person re-identification with frame sampling-random erasure and mutual information-temporal weight aggregation. Sensors 22(8):3047
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Jun Wang, Qi Zhao, Di Jia , Yonghua Zhang and Miaohui Zhang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xing Ren and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “Spatial-temporal aware network for video-based person re-identification”.
Ethical and informed consent for data used
The data used did not involve human participants and animal studies.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhao, Q., Jia, D. et al. Spatial-temporal aware network for video-based person re-identification. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 36355–36373 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16911-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16911-8