Abstract
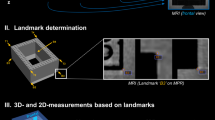
The objective of this study was to examine the repeatability and reproducibility of landmark localization on panoramic images for PA (Posteroanterior) cephalometric analysis. Lateral, PA and panoramic images of 20 patients were acquired for landmark localization by 2 different observers 2 times each of them. 14 bilateral landmarks were plotted on 20 PA and 20 panoramic images which makes a total of 40 × 28x4 = 4480 landmarks which were plotted to compute the measurements. The calibration of all three images was performed and measurements of each landmark were recorded from its position to the mid-sagittal plane. The repeatability and reproducibility of the panoramic images and PA cephalometric images was found good and sufficient to use in further experiments. The study’s findings on repeatability and reproducibility back up the premise of obtaining PA analysis using panoramic radiographs. As a result, it’s safe to presume that the repeatability of landmark placement among appropriately educated observers is sufficient to provide reliable test findings from panoramic radiographs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is received from the clinic with IEC approval and can be made available for the validation purposes only.
References:
Hirschfelder U, Piechot E, Schulte M, Leher A (2004) Abnormalities of the TMJ and the musculature in the oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (OAV). A CT study. J Orofac Orthop 65:204–216
Gupta A (2023) On imaging modalities for cephalometric analysis: a review. Multimed Tools Appl
Schmid W, Mongini F, Felisio A (1991) A computer-based assessment of structural and displacement asymmetries of the mandible. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 100:19–34
Chebib FS, Chamma AM (1981) Indices of craniofacial asymmetry. Angle Orthod 51(214):26
Grummons DC, Kappeyne van de Coppello MA (1987) Frontal asymmetry analysis. J Clin Orthod 21:448–65
Ricketts RM, Grummons D (2003) Frontal cephalometrics: practical applications, part 1. World J Orthod 4:297–316
Grummons D, Ricketts RM (2004) Frontal cephalometrics: practical applications, part 2. World J Orthod 5(2):99–119
Kitai N et al (2004) Craniofacial morphology in an unusual case with nasal aplasia studied by roentgencephalometry and three-dimensional CT scanning. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 41:208–213
Hwang H-S, Hwang CH, Lee K-H, Kang B-C (2006) Maxillofacial 3-dimensional image analysis for the diagnosis of facial asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 130:779–785
McDavid WD, Tronje G, Welander U, Morris CR (1981) Effects of errors in film speed and beam alignment on the image layer in rotational panoramic radiography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 52:561–564
Friedland B (1998) Clinical radiological issues in orthodontic practice. Semin Orthod 4:64–78
Yeo DK, Freer TJ, Brockhurst PJ (2002) Distortions in panoramic radiographs. Aust Orthod J 18:92–98
Titiz I, Laubinger M, Keller T, Hertrich K, Hirschfelder U (2012) Repeatability and reproducibility of landmarks—a three-dimensional computed tomography study. Eur J Orthod 34:276–286
Gupta A (2022) RegCal: registration-based calibration method to perform linear measurements on PA (posteroanterior) cephalogram- a pilot study. Multimed Tools Appl 81:41869–41879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11609-1
De Oliveira AE, Cevidanes LH, Phillips C, Motta A, Burke B, Tyndall D (2009) Observer reliability of three-dimensional cephalometric landmark identification on cone-beam computerized tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:256–265
Houston WJ, Maher RE, McElroy D, Sherriff M (1986) Sources of error in measurements from cephalometric radiographs. Eur J Orthod 8(3):149–151
Vincent AM, West VC (1987) Cephalometric landmark identification error. Aust Orthod J 10(2):98–104
Chadwick JW, Prentice RN, Major PW, Lam EW (2009) Image distortion and magnification of 3 digital CCD cephalometric systems. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:105–112
Schulze RK, Gloede MB, Doll GM (2002) Landmark identification on direct digital versus film-based cephalometric radiographs: a human skull study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 122:635–642
Gupta A, Kharbanda OP, Balachandran R, Sardana V, Kalra S, Chaurasia S et al (2017) Precision of manual landmark identification between as-received and oriented volume-rendered cone-beam computed tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 151:118–131
Gupta A, Kharbanda O, Sardana V, Balachandran R, Sardana H (2015) A knowledge-based algorithm for automatic detection of cephalometric landmarks on CBCT images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10:1737–1752
Gupta A, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, Balachandran R, Sardana HK (2016) Accuracy of 3D cephalometric measurements based on an automatic knowledge-based landmark detection algorithm. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11:1297–1309
Gupta A (2020) Challenges for Computer Aided Diagnostics using X-Ray and Tomographic Reconstruction Images in craniofacial applications. Int J Comput Vis Robot 10:360–371
Gupta A (2019) Current research opportunities of image processing and computer vision. Comput Sci 20(4). https://doi.org/10.7494/csci.2019.20.4.3163
Cohen MM Jr (1995) Perspectives on craniofacial asymmetry. III. Common and/or well-known causes of asymmetry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 24:127–133
Sayinsu K, Isik F, Trakyali G, Arun T (2007) An evaluation of the errors in cephalometric measurements on scanned cephalometric images and conventional tracings. Eur J Orthod 29:105–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards." The ethical approval was received from Institutional Ethics Committee of AIIMS (All India Institutes of Medical Sciences), Bathinda to conduct this study under IEC No. IEC-01/2020–015.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Rana, S.S., Eranhikkal, A. et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of landmark localization on panoramic images for PA (Posteroanterior) cephalometric analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 35979–35993 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16961-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16961-y