Abstract
In the field of neuroscience, a significant challenge lies in extracting essential features from biological signals like Electroencephalography (EEG). Utilized as a non-invasive method, EEG records brain activities through metal electrodes on the scalp. The analysis of EEG data finds applications in various domains, including concealed information tests, aimed at detecting deception. This paper introduces the Spatial Spiking Neural Network, a supervised approach for classifying EEG data collected during concealed information tests. Temporal EEG data undergoes filtration using a Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter, while Common Spatial Pattern (CSP) is employed to extract spatial components. Binary classification is achieved through an integrate-and-fire neuron model, where the frequency of spike generation determines the classification. Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offers advantages in terms of temporal precision, event-driven processing, and low power consumption. Their spike-based communication allows for efficient handling of sparse data and recognition of temporal patterns, contributing to robustness and energy efficiency. The proposed model is applied separately to each subject’s EEG data, and the results are compared with traditional classification algorithms. The proposed approach attains a peak accuracy of 90.15%, showcasing superior performance compared to alternative methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
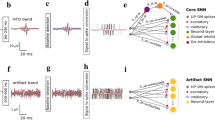
Availability of data and materials
Upon special request
Code availability
Upon special request
References
Huang H, Xie Q, Pan J, He Y, Wen Z, Yu R, Li Y (2019) An eeg-based brain computer interface for emotion recognition and its application in patients with disorder of consciousness. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing
Raza H, Rathee D, Zhou SM, Cecotti H, Prasad G (2019) Covariate shift estimation based adaptive ensemble learning for handling non-stationarity in motor imagery related eeg-based brain-computer interface. Neurocomputing 343:154–166
Lawhern VJ, Solon AJ, Waytowich NR, Gordon SM, Hung CP, Lance BJ (2018) Eegnet: a compact convolutional neural network for eeg-based brain-computer interfaces. J Neural Eng 15(5):056013
Zhang Y, Zhou G, Jin J, Zhao Q, Wang X, Cichocki A (2015) Sparse bayesian classification of eeg for brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(11):2256–2267
Sovilj PM, Milovancev SS, Vujicic V (2011) Digital stochastic measurement of a nonstationary signal with an example of eeg signal measurement. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 60(9):3230–3232
Alchalabi AE, Shirmohammadi S, Eddin AN, Elsharnouby M (2018) Focus: detecting adhd patients by an eeg-based serious game. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 67(7):1512–1520
Mucarquer JA, Prado P, Escobar M, El-Deredy W, Zañartu M (2020) Improving eeg muscle artifact removal with an emg array. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 69(3):815–824
Gao Z, Li S, Cai Q, Dang W, Yang Y, Mu C, Hui P (2019) Relative wavelet entropy complex network for improving eeg-based fatigue driving classification. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 68(7):2491–2497
Li Y, Zhang J, Cui W, Yuan H, Wei H (2020) A multiple beta wavelet-based locally regularized ultraorthogonal forward regression algorithm for time-varying system identification with applications to eeg. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 69(3):916–928
Farwell LA, Donchin E (1991) The truth will out: Interrogative polygraphy (“lie detection”) with event-related brain potentials. Psychophysiology 28(5):531–547
Bablani A, Edla DR, Tripathi D, Cheruku R (2019) Survey on brain-computer interface: an emerging computational intelligence paradigm. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 52(1):1–32
Rosenfeld JP, Soskins M, Bosh G, Ryan A (2004) Simple, effective countermeasures to p300-based tests of detection of concealed information. Psychophysiology 41(2):205–219
Rosenfeld JP, Labkovsky E, Winograd M, Lui MA, Vandenboom C, Chedid E (2008) The complex trial protocol (ctp): a new, countermeasure-resistant, accurate, p300-based method for detection of concealed information. Psychophysiology 45(6):906–919
Kubo K, Nittono H (2009) The role of intention to conceal in the p300-based concealed information test. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 34(3):227–235
Meixner JB, Rosenfeld JP (2011) A mock terrorism application of the p300-based concealed information test. Psychophysiology 48(2):149–154
Wang D, Miao D, Blohm G (2013) A new method for eeg-based concealed information test. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 8(3):520–527
Akhavan A, Moradi MH, Vand SR (2017) Subject-based discriminative sparse representation model for detection of concealed information. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 143:25–33
Abootalebi V, Moradi MH, Khalilzadeh MA (2009) A new approach for eeg feature extraction in p300-based lie detection. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 94(1):48–57
Arasteh A, Moradi MH, Janghorbani A (2016) A novel method based on empirical mode decomposition for p300-based detection of deception. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur 11(11):2584–2593
Gao J, Lu L, Yang Y, Yu G, Na L, Rao N (2012) A novel concealed information test method based on independent component analysis and support vector machine. Clin EEG Neurosci 43(1):54–63
Farahani ED, Moradi MH (2017) Multimodal detection of concealed information using genetic-svm classifier with strict validation structure. Inform Med Unlocked
Koles ZJ, Lazar MS, Zhou SZ (1990) Spatial patterns underlying population differences in the background eeg. Brain Topogr 2(4):275–284
Tomioka R, Dornhege G, Nolte G, Blankertz B, Aihara K, Müller KR (2006) Spectrally weighted common spatial pattern algorithm for single trial eeg classification. Dept. Math. Eng., Univ. Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan, Tech. Rep 40
Samek W, Vidaurre C, Müller KR, Kawanabe M (2012) Stationary common spatial patterns for brain-computer interfacing. J Neural Eng 9(2):026013
Kang H, Nam Y, Choi S (2009) Composite common spatial pattern for subject-to-subject transfer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 16(8):683–686. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2009.2022557
Lu H, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2009) Regularized common spatial patterns with generic learning for eeg signal classification. In: Engineering in medicine and biology society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp 6599–6602. IEEE
Lotte F, Guan C (2011) Regularizing common spatial patterns to improve bci designs: unified theory and new algorithms. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(2):355–362. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2010.2082539
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. Physiol J 117(4):500–544
Abbott LF (1999) Lapicque’s introduction of the integrate-and-fire model neuron (1907). Brain research bulletin 50(5–6):303–304
Koch C, Segev I (1998) Methods in Neuronal Modeling: from Ions to Networks. MIT press
Izhikevich EM, FitzHugh R (2006) Fitzhugh-nagumo model. Scholarpedia 1(9):1349
Kasabov N, Capecci E (2015) Spiking neural network methodology for modelling, classification and understanding of eeg spatio-temporal data measuring cognitive processes. Inf Sci 294:565–575
Kasabov N (2012) Neucube evospike architecture for spatio-temporal modelling and pattern recognition of brain signals. In: Iapr workshop on artificial neural networks in pattern recognition, pp 225–243. Springer
Nuntalid N, Dhoble K, Kasabov N (2011) Eeg classification with bsa spike encoding algorithm and evolving probabilistic spiking neural network. In: International conference on neural information processing, pp 451–460. Springer
Schrauwen B, Van Campenhout J (2003) Bsa, a fast and accurate spike train encoding scheme. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks, 2003, vol 4, pp 2825–2830. IEEE
Ghosh-Dastidar S, Adeli H (2009) A new supervised learning algorithm for multiple spiking neural networks with application in epilepsy and seizure detection. Neural Netw 22(10):1419–1431
Xu F, Pan D, Zheng H, Ouyang Y, Jia Z, Zeng H (2024) Eescn: a novel spiking neural network method for eeg-based emotion recognition. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 243:107927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107927
Li W, Fang C, Zhu Z, Chen C, Song A (2024) Fractal spiking neural network scheme for eeg-based emotion recognition. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 12:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1109/JTEHM.2023.3320132
Gong P, Wang P, Zhou Y, Zhang D (2023) A spiking neural network with adaptive graph convolution and lstm for eeg-based brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 31:1440–1450. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3246989
Sam A, Boostani R, Hashempour S, Taghavi M, Sanei S (2023) Depression identification using eeg signals via a hybrid of lstm and spiking neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 31:4725–4737. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3336467
Svojanovsky A. Brain Products. http://www.brainproducts.com/ Accessed 15 May 2017
Svojanovsky A. Easycap. http://www.brainproducts.com/productdetails.php?id=20 Accessed 15 May 2017
Maass W (1997) Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw 10(9):1659–1671
Gerstner W (1995) Time structure of the activity in neural network models. Phys Rev E 51(1):738
Gerstner W, Sprekeler H, Deco G (2012) Theory and simulation in neuroscience. Science 338(6103):60–65
Purves D, FD Augustine GJ (2001) Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials. Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11117/
Chandra B, Babu KN (2013) A new spiking neuron model. In: The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp 1–5. IEEE
Kumar S (2004) Neural Networks: a Classroom Approach. Tata McGraw-Hill Education
The Mathworks, Inc.: MATLAB Version 9.0.0.321247 (R2016b). Natick, Massachusetts (2016). The Mathworks, Inc
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) Eeglab: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial eeg dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134(1):9–21
Bablani A, Edla DR, Tripathi D, Kuppili V (2019) An efficient concealed information test: eeg feature extraction and ensemble classification for lie identification. Mach Vis Appl 30:813–832
Dodia S, Edla DR, Bablani A, Cheruku R (2020) Lie detection using extreme learning machine: a concealed information test based on short-time fourier transform and binary bat optimization using a novel fitness function. Comput Intell 36(2):637–658
Bablani A, Edla DR, Tripathi D, Venkatanareshbabu K (2018) Subject based deceit identification using empirical mode decomposition. Procedia Comput Sci 132:32–39
Bablani A, Edla DR, Dodia S (2018) Classification of eeg data using k-nearest neighbor approach for concealed information test. Procedia Comput Sci 143:242–249
Bablani A, Edla DR, Kuppili V, Ramesh D (2020) A multi stage eeg data classification using k-means and feed forward neural network. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health 8(3):718–724
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
study conception and design: Damoder Reddy Edla and Dharavath Ramesh Implementation: Anushree Bablani and Ramalingaswamy Cheruku; draft manuscript preparation: Boddu Vijayasree and Saugat Battacharya. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors don’t have any conflict of interest with anyone
Ethics approval
Taken
Consent to participate
Taken
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ramalingaswamy Cheruku and Vijayasree Boddu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Edla, D.R., Bablani, A., Bhattacharyya, S. et al. Spatial spiking neural network for classification of EEG signals for concealed information test. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 79259–79280 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18698-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18698-8



