Abstract
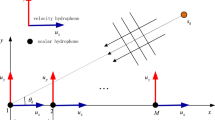
This paper presents a propagator-based algorithm for underwater acoustic 2-D direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation with arbitrarily spaced vector hydrophones at unknown locations. The proposed algorithm requires only linear operations but no eigen-decomposition or singular value decomposition into the signal and noise subspaces. Comparing with its ESPRIT counterpart (Wong and Zoltowski, IEEE J Oceanic Eng 22:566–575, 1997a), the proposed propagator algorithm has its computational complexity reduced by this ratio: the number of sources to quadruple the number of vector hydrophones. Simulation results show that at high and medium signal-to-noise ratio, the proposed propagator algorithm’s estimation accuracy is similar to its ESPRIT counterpart.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berliner M.J., Lindberg J.F. (1996) Acoustic Particle Velocity Sensors: Design, Performance and Applications. AIP, Woodbury, NY
Champagne B. (1994) Adaptive eigendecomposition of data covariance matrices based on first-order perturbations. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 42: 2758–2770
D’Spain G.L., Hodgkiss W.S., Edmonds G.L. (1991) The simultaneous measurement of infrasonic acoustic particle velocity and acoustic pressure in the ocean by freely drifting swallow floats. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 16: 195–207
D’Spain, G. L., Hodgkiss, W. S., Edmonds, G. L., Nickles, J. C., Fisher, F. H., & Harriss, R. A. (1992). Initial analysis of the data from the vertical difar array. In IEEE Oceans 92 (pp. 346–351).
Hawkes M., Nehorai A. (1998) Acoustic vector sensor beamforming and Capon direction estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 46: 2291–2304
Hawkes M., Nehorai A. (1999) Effects of sensor placement on acoustic vector sensor array performance. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 24: 33–40
Hawkes M., Nehorai A. (2000) Performance measures for estimating vector systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 48: 1737–1749
Hawkes M., Nehorai A. (2000) Acoustic vector sensor processing in the presence of a reflecting boundary. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 48: 2981–2993
Hawkes M., Nehorai A. (2001) Acoustic vector-sensor correlations in ambient noise. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 26: 337–347
He, J., & Liu, Z. (2007). Underwater acoustic azimuth and elevation angle estimation using spatial invariance of two identically oriented vector hydrophones at unknown locations in impulsive noise. Digital Signal Processing. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2007.10.012.
Hochwald B., Nehorai A. (1996) Identifiability in array processing models with vector-sensor applications. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 44: 83–95
Lesie C.B., Kendall J.M., Jones J.L. (1956) Hydrophone for measuring particle velocity. Journal of the Acoustical Soceity of America 28(4): 711–715
Li P., Sun J., Yu B. (1996) Two-dimensional spatial spectrum estimation of coherent signals without spatial smoothing and eigendecomposition. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar Navix. 143(5): 295–299
Marcos S., Marsal A., Benidir M. (1995) The propagator method for source bearing estimation. Signal Processing 42: 121–138
Munier J., Delisle G.Y. (1991) Spatial analysis using new properties of the cross-spectral matrix. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 39(3): 746–749
Nehorai A., Paldi E. (1994) Acoustic vector sensor array processing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 42: 2481–2491
Nickles, J. C., Edmonds, G., Harriss, R., Fisher, F., Hodgkiss, W. S., Giles, J., & D’Spain, G. L. (1992). A vertical array of directional acoustic sensors. In IEEE Oceans 92 (pp. 340–345).
Roy R., Kailath T. (1989) Esprit-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing 37: 984–995
Schmidt R.O. (1986) Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 34: 276–280
Shchurov, V. A., Ilyichev, V. I., & Kuleshov, V. P. (1994). Ambient noise energy motion in the near-surface layer in ocean wave-guide. Journal of Physics, 4(5, part 2), 1273–1276.
Tayem N., Kwon H.M. (2005) L-shape two-dimensional arrival angle estimation with propagator method. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagations 53(5): 1622–1630
Tichavsky P., Wong K.T., Zoltowski M.D. (2001) Near-field/far-field azimuth and elevation angle estimation using a single vector hydrophone. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 49: 2498–2510
Wong K.T., Zoltowski M.D. (1997) Closed-form underwater acoustic direction-finding with arbitrarily spaced vector hydrophones at unknown locations. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 22: 566–575
Wong K.T., Zoltowski M.D. (1997) Extended-aperture underwater acoustic multi-source azimuth/ elevation direction-finding using uniformly but sparsely spaced vector hydrophones. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 22: 659–672
Wong K.T., Zoltowski M.D. (1999) Root-music-based azimuth-elevation angle-of-arrival estimation with uniformly spaced but arbitrarily oriented velocity hydrophones. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 47: 3250–3260
Wong K.T., Zoltowski M.D. (2000) Self-initiating velocity-field beamspace music for underwater acoustic direction-finding with irregularly spaced vector hydrophones. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 25: 262–273
Wong K.T., Chi H. (2002) Beam patterns of an underwater acoustic vector hydrophone located away from any reflecting boundary. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 27: 628–637
Wu Y., Liao G., So H.C. (2003) A fast algorithm for 2D direction-ofarrival estimation. Signal Processing 83: 1827–1831
Zha D.F., Qiu T.S. (2006) Underwater sources location in non-gaussian impulsive noise environments. Digtal Signal Processing 16: 149–163
Zoltowski M.D., Wong K.T. (2000) Closed-form eigenstructure- based direction finding using arbitrary but identical subarrays on a sparse uniform rectangular array grid. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 48(8): 2205–2210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Liu, Z. Computationally efficient underwater acoustic 2-D source localization with arbitrarily spaced vector hydrophones at unknown locations using the propagator method. Multidim Syst Sign Process 20, 285–296 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-008-0069-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-008-0069-9