Abstract
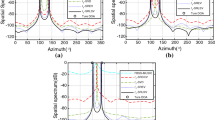
This paper considers a new azimuth-elevation DOA estimation algorithm for multiple signals using electromagnetic vector sensor array. We firstly exploit the planar-plus-an-isolated sensor array geometry (Li et al. in IEE Proc Radar Sonar Navig 143(5):295–299, 1996) to define a full rank cross-covariance matrix. Then we develop an efficient ESPRIT-like algorithm using the so-called propagator to estimate the steering vectors of electromagnetic vector sensor, without performing eigen-decomposition into signal subspaces. Finally, we compute the vector cross product to obtain the closed-form azimuth-elevation angle estimates. The new algorithm does not require 2D iterative searching, and is applicable to coherent (fully correlated) signals and spatially correlated noise. In addition, the proposed algorithm offers enhanced estimation precision by sparse array aperture extension, but suffers no DOA cyclical ambiguity. Monte-Carlo simulations are presented to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal M., Prasad S. (2000) A modified likelihood function approach to DOA estimation in the presence of unknown spatially correlated Gaussian noise using a uniform linear array. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 48(10): 2743–2749
Al-Ardi E. M., Shubair R. M., Al-Mualla M. E. (2004) Computationally efficient high-resolution DOA estimation in multipath environment. Electronics Letters 40(14): 908–910
Belouchrani A., Amin M. G., Meraim K. A. (1997) Direction finding in correlated noise fields based on joint block-diagonalization of spatio-temporal correlation matrices. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 4(9): 266–268
Cron B. F., Sherman C. H. (1962) Spatial correlation functions for various noise models. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 34: 1732–1736
Friedlander B., Weiss A. J. (1995) Direction finding using noise covariance modeling. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 43(7): 1557–1567
Góansson, B., & Ottersten, B. (1999). Direction estimation in partially unknown noise fields. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 47(9), 2375–2385.
He J., Liu Z. (2008) Two-dimensional direction finding of acoustic sources by a vector sensor array using the propagator method. Signal Processing 88(10): 2492–2499
He J., Liu Z. (2009) Computationally efficient 2D direction finding and polarization estimation with arbitrarily spaced electromagnetic vector sensors at unknown locations using the propagator method. Digital Signal Processing 19(3): 491–503
Ho K.-C., Tan K.-C., Nehorai A. (1999) Estimating directions of arrival of completely and incompletely polarized signals with electromagnetic vector sensors. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 47(10): 2845–2852
Ho K.-C., Tan K.-C., Ser W. (1995) Investigation on number of signals whose directions-of-arrival are uniquely determinable with an electromagnetic vector sensor. Signal Processing 47(1): 41–54
LeCadre J. (1989) Parametric methods for spatial signal processing in the presence of unknown colored noise field. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing 37(7): 965–983
Li J. (1993) Direction and polarization estimation using arrays with small loops and short dipoles. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 41: 379–387
Li P., Sun J., Yu B. (1996) Two-dimensional spatial spectrum estimation of coherent signals without spatial smoothing and eigendecomposition. IEE Proceedings—Radar, Sonar and Navigation 143(5): 295–299
Marcos S., Marsal A., Benidir M. (1995) The propagator method for source bearing estimation. Signal Processing 42: 121–138
Munier J., Delisle G. Y. (1991) Spatial analysis using new properties of the cross-spectral matrix. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 39(3): 746–749
Nehorai A., Paldi E. (1994) Vector-sensor array processing for electromagnetic source localization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 42(2): 376–398
Pesavento M., Gershman A. B. (2001) Maximum-likelihood direction of arrival estimation in the presence of unknown nonuniform noise. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 49(7): 1310–1324
Pillai S. U., Kwon B. H. (1989) Forward/backward spatial smoothing techniques for coherent signal identification. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing 37: 8–15
Qi C. Y., Wang Y. L., Zhang Y. S., Han Y. (2005) Spatial difference smoothing for DOA estimation of coherent signals. IEEE signal processing letters 12(11): 800–802
Rahamim D., Tabrikian J., Shavit R. (2004) Source localization using vector sensor array in a multipath environment. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 52(11): 3096–3103
Roy R., Kailath T. (1989) ESPRIT-Estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing 37: 984–995
Schmidt R.O. (1986) Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Transactions on Antennas Propagation 34: 276–280
Shan T. J., Wax M., Kailath T. (1985) On spatial smoothing for direction- of-arrival estimation of coherent signals. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing 33: 806–811
Stoica P., Viberg M., Wong K. M., Wu Q. (1996) Maximum-likelihood bearing estimation with partly calibrated arrays in spatially correlated noise field. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 44(4): 888–899
Tayem N., Kwon H. M. (2005) L-shape 2-dimensional arrival angle estimation with propagator method. IEEE Transactions on Antennas Propagation 53(5): 1622–1630
Thalham R. J. (1981) Noise correlation functions for an isotropic noise field. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 69: 213–215
Thomas P. H., Haykin S. (1986) Stochastic modelling of radar clutter. Proceedings of IEE, Part F 133: 476–481
Viberg M., Stoica P., Ottersten B. (1995) Array processing in correlated noise fields based on instrumental variables and subspace fitting. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 43(5): 1187–1199
Viberg M., Stoica P., Ottersten B. (1997) Maximum likelihood array processing in spatially correlated noise fields using parameterized signals. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 45(4): 996–1004
Vorobyov S. A., Gershman A. B., Wong K.M. (2005) Maximum likelihood direction-of-arrival estimation in unknown noise fields using sparse sensor arrays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 53(1): 34–43
Wong K. T. (2001) Direction finding/polarization estimation-dipole and/or loop triads. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 37(2): 679–684
Wong K. T., Li L., Zoltowski M. D. (2004) Root-MUSIC-based direction-finding and polarization-estimation using diversely-polarized possibly-collocated antennas. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propagation Letters 3(8): 129–132
Wong K. M., Reilly J. P., Wu Q., Qiao S. (1992) Estimation of the directions of arrival of signals in unknown correlated noise. Part I: The MAP approach and its implementation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 40(8): 2007–2017
Wong K. T., Zoltowski M. D. (1997) Uni-vector-sensor ESPRIT for multisource azimuth, elevation, and polarization estimation. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 45(10): 1467–1474
Wong K. T., Zoltowski M. D. (2000a) Closed-form direction finding and polarization estimation with arbitrarily spaced electromagnetic vector-sensors at unknown locations. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 48(5): 671–681
Wong K. T., Zoltowski M. D. (2000b) Self-Initiating MUSIC based direction finding and polarization estimation in spatio-polarizational beamspace. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 48(8): 1235–1245
Wu Y., Liao G., So H. C. (2003) A fast algorithm for 2-D direction-of-arrival estimation. Signal Processing 83: 1827–1831
Wu Q., Wong K. M. (1994) UN-MUSIC and UN-CLE: An application of generalized correlation analysis to the estimation of the directions of arrival of signals in unknown correlated noise. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 42(9): 2331–2343
Ye H., DeGroat R. D. (1995) Maximum likelihood DOA estimation and asymptotic Cramer-Rao bounds for additive unknown colored noise. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 43(4): 938–949
Zoltowski M. D., Wong K. T. (2000) ESPRIT-based 2-D direction finding with a sparse uniform array of electromagnetic vector sensors. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 48(8): 2195–2204
Zoltowski M. D., Wong K. T. (2000) Closed-form eigenstructure-based direction finding using arbitrary but identical subarrays on a sparse uniform Cartesian array grid. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 48(8): 2205–2210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, C., He, J., Zhu, X. et al. Efficient 2D DOA estimation of coherent signals in spatially correlated noise using electromagnetic vector sensors. Multidim Syst Sign Process 21, 239–254 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-010-0100-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-010-0100-9