Abstract
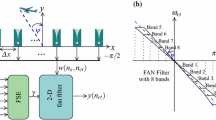
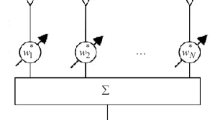
A beamforming system based on two-dimensional (2-D) spatially bandpass infinite impulse response (IIR) plane wave filtering is presented in a multi-dimensional signal processing perspective and the implementation details are discussed. Real-time implementation of such beamforming systems requires modeling of computational electromagnetics for the antennas, radio frequency (RF) analog design aspects for low-noise amplifiers (LNAs), mixed-signal aspects for signal quantization and sampling and finally, digital architectures for the spatially bandpass plane wave filters proposed in Joshi et al. (IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr Syst 20(12):2241–2254, 2012). Multi-dimensional spatio-temporal spectral properties of down-converted RF plane wave signals are reviewed and derivation of the spatially bandpass filter transfer function is presented. An example of a wideband antipodal Vivaldi antenna is simulated at 1 GHz. Potential RF receiver chains are identified including a design of a tunable combline microstrip bandpass filter with tuning range 0.8–1.1 GHz. The 1st-order sensitivity analysis of the beam filter 2-D \(\mathbf z \)-domain transfer function shows that for a 12-bits of fixed-point precision, the maximum percentage error in the 2-D magnitude frequency response due to quantization is as low as \(0.3\,\%\). Monte-Carlo simulations are used to study the effect of quantization on the bit error rate (BER) performance of the beamforming system. 5-bit analog to digital converter (ADC) precision with 8-bit internal arithmetic precision provides a gain of approximately 16 dB for a BER of \(10^{-3}\) with respect to the no beamforming case. ASIC Synthesis results of the beam filter in 45 nm CMOS verifies a real time operating frequency of 429 MHz.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
The input IP3 for a GSM receiver is typically \(-\)21 dBm.
References
Agathoklis, P., & Bruton, L. T. (1983). Practical-BIBO stability of N-dimensional discrete systems. IEE Proceedings, 130(6), 236–242.
Andrews, C., & Molnar, A. C. (2010a). Implications of passive mixer transparency for impedance matching and noise figure in passive mixer-first receivers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 57(12), 3092–3103.
Andrews, C., & Molnar, A. C. (2010b). A passive-mixer-first receiver with baseband-controlled RF impedance matching, \(<\) 6dB NF, and \(>\)27 dBm wideband IIP3. In: IEEE international solid-state circuits conference, pp. 46–47.
Andrews, C., & Molnar, A. C. (2010c). A passive mixer-first receiver with digitally controlled and widely tunable RF interface. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45, 2696–2708.
Behzad, A. (2008). Wireless LAN radios: System definition to transistor design. Wiley-IEEE Press, ISBN:9780470209301.
Bruton, L. T. (2003). Three-dimensional cone filter banks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 50(2), 208–216.
Bruton, L. T., & Bartley, N. R. (1985). Three-dimensional image processing using the concept of network resonance. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 32, 664–672.
Bruton, L. T., & Strecker, T. E. (1983). Two-dimensional discrete filters using spatial integrators. IEE Proceedings of Electronic Circuits and Systems, 130, 271–275.
Chen, P. Y., Van, L. D., Khoo, I. H., Reddy, H. C., & Lin, C. T. (2011). Power-efficient and cost-effective 2-D symmetry filter architectures. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58, 112–125.
Dudgeon, D. E., & Mersereau, R. M. (1984). Multidimensional digital signal processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA: Prentice-Hall. 07632.
Fettweis, A., & Basu, S. (2011). Multidimensional causality and passivity of linear and nonlinear systems arising from physics. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 22, 5–25.
Giannini, V., Nuzzo, P., Soens, C., Vengattaramane, K., Ryckaert, J., Goffioul, M., et al. (2009). A 2-mm\(^2\) 0.1–5 GHz software-defined radio receiver in 45-nm digital CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(12), 3486–3498.
Gunaratne, T., & Bruton, L. (2011a). Adaptive complex-coefficient 2D FIR trapezoidal filters for broadband beamforming in cognitive radio systems. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 30, 587–608.
Gunaratne, T., & Bruton, L. (2011b). Broadband beamforming of dense aperture array (DAA) and focal plane array (FPA) signals using 3D spatio-temporal filters for applications in aperture synthesis radio astronomy. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 22, 213–236.
Hunter, I. C., & Rhodes, J. D. (1982). Electronically tunable microwave bandpass filters. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 30(9), 1354–1360.
Jasik, H. (1993) Antenna engineering handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill, ISBN:9780070323810
Joshi, R. M., Madayanake, A., Bruton, L. T., & Adikari, J. (2012). Synthesis and array processor realization of a 2D IIR beam filter for wireless applications. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 20(12), 2241–2254.
Khoo, I. H., Reddy, H. C., & Rajan, P. K. (2003). Delta operator based 2-D filters: symmetry, stability, and design. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS).
Khoo, I.-H., Reddy, H., Van, L.-D., & Lin, C.-T. (2013). General formulation of shift and delta operator based 2-D VLSI filter structures without global broadcast and incorporation of the symmetry. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 1–34. doi:10.1007/s11045-013-0232-9.
Kraus, J. D., & Marhefka, R. J. (2003). Antennas for all applications. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN: 0072321032.
Lee, C. S., Jung, I. S., & Tchah, K. H. (1999). RF receiver sensitivity of mobile station in CDMA. In Fifth Asia-Pacific conference on communications and fourth optoelectronics and communications conference, pp. 637–640.
Levy, R., Snyder, R. V., & Matthaei, G. (2002). Design of microwave filters. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 50(3), 783–793.
Lin, Y. Z., Liu, C. C., Huang, G. Y., Shyu, Y. T., & Chang, S. J. (2010). A 9-bit 150-MS/s 1.53-mW subranged SAR ADC in 90-nm CMOS. In IEEE symposium VLSI circuits, pp. 243–244.
Lin, Z., & Bruton, L. T. (1989). BIBO stability of inverse 2-D digital filters in the presence of nonessential singularities of the second kind. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 36, 244–254.
Lin, Z., Bruton, L. T., & Bartley, N. R. (1988). Design of highly selective two-dimensional recursive fan filters by relaxing symmetry constraints. Electronics Letters, 24, 1361–1362.
Liu, Z., Ruan, X., & He, J. (2013). Efficient 2-D DOA estimation for coherent sources with a sparse acoustic vector-sensor array. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 24(1), 105–120.
Locher, M., Kuenen, J., Daanen, A., Visser, H., Essink, B. H., Vervoort, P. P., et al. (2008). A versatile, low power, high performance BiCMOS MIMO/diversity direct conversion transceiver IC for WiBro/WiMAX (802.16e). IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(8), 1731–1740.
Madanayake, A. (2008). Real-time FPGA architectures for frequency-planar MDSP. PhD Thesis, University of Calgary, Supervisor: L T Bruton.
Madanayake, A., & Bruton, L. T. (2008a). A speed-optimized systolic array processor architecture for spatio-temporal 2-D IIR broadband beam filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 55(7), 1953–1966.
Madanayake, A., & Bruton, L. T. (2008b). A systolic-array architecture for first-order 3D IIR frequency-planar filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 55(6), 1546–1559.
Madanayake, A., Hum, S. V., & Bruton, L. T. (2008). A systolic array 2D IIR broadband RF beamformer. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Express Briefs, 55(12), 1244–1248.
Madanayake, A., Hum, S. V., & Bruton, L. T. (2012). Effects of quantization in systolic 2D IIR beam filters on UWB wireless communications. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 31(2), 595–610.
Pekau, H., & Haslett, J. W. (2005). A comparison of analog front end architectures for digital receivers. In Proceedings of the Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering, pp. 1073–1077.
Pekau, H., & Haslett, J. W. (2006). Cascaded noise figure calculations for radio receiver circuits with noise-aliasing properties. IEE Proceedings-Circuits, Devices and Systems, 153(6), 517–524.
Rajapaksha, N., Madanayake, A., & Bruton, L. T. (2012). 2D space-time wave-digital multi-fan filter banks for signals consisting of multiple plane waves. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 1–23. doi:10.1007/s11045-012-0183-6.
Reddy, H. C., Khoo, I. H., Moschytz, G. S., & Stubberud, A. R. (1997). Theory and test procedure for symmetries in the frequency response of complex two-dimensional delta operator formulated discrete-time systems. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS).
Rizvi, U. H., Janssen, G. J. M., Weber, J. H. (2008). BER analysis of single-carrier MPAM in the presence of ADC quantization noise. In 19th IEEE international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications.
Sussman-Fort, S. E. (1994). An NIC-based negative resistance circuit for microwave active filters. International Journal of Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Computer-Aided Engineering, 4(2), 130–139.
Sussman-Fort, S. E., & Rudish, R. M. (2009). Non-foster impedance matching of electrically-small antennas. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57, 2230–2241.
Verma, A., & Razavi, B. (2009). A 10b 500MHz 55mW CMOS ADC. InIEEE international solid-state circuits conference, pp. 84–85.
Warnick, K. F., Woestenburg, E. E. M., Belostotski, L., & Russer, P. (2009). Minimizing the noise penalty due to mutual coupling for a receiving array. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57, 1634–1644.
Wei, Y., Zhang, X., Bai, Y., & Tang, L. (2013). A novel range alignment method for ISAR based on linear T/R array model. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 1–15. doi:10.1007/s11045-013-0229-4.
Wen, F., Ng, B., & Reddy, V. (2013). Extending the concept of IIR filtering to array processing using approximate spatial IIR structure. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 24(1), 157–179.
Wijenayake, C., Madanayake, A., & Bruton, L. T. (2012). Broadband multiple cone-beam 3D IIR digital filters applied to planar dense aperture arrays. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 60(11), 5136–5146.
Yngvesson, K., Korzeniowski, T., Kim, Y. S., Kollberg, E., & Johansson, J. (1989). The tapered slot antenna a new integrated element for millimeter-wave applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 37, 365–374.
Zhang, X., Chen, C., Li, J., & Xu, D. (2012). Blind DOA and polarization estimation for polarization-sensitive array using dimension reduction MUSIC. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 1–16. doi:10.1007/s11045-012-0186-3.
Zhu, W., & Chen, B. X. (2013). Novel methods of DOA estimation based on compressed sensing. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 1–11. doi:10.1007/s11045-013-0239-2.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Arjuna Madanayake gratefully acknowledges the financial support from the US National Science Foundation (NSF) Grant #1247940 for EARS and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) Grant #N000141310079.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madanayake, A., Wijenayake, C., Joshi, R. et al. Electronically scanned RF-to-bits beam aperture arrays using 2-D IIR spatially bandpass digital filters. Multidim Syst Sign Process 25, 313–335 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-013-0250-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-013-0250-7