Abstract
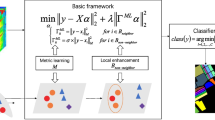
Remote sensing image classification is a very challenging problem and covariance descriptor can be introduced in the feature extraction and representation process for remote sensing image. However, due to the reason that covariance descriptor lies in non-Euclidean manifold, conventional extreme learning machine (ELM) cannot effectively deal with this problem. In this paper, we propose an improved ELM framework which incorporates the collaborative coding to tackle the covariance descriptor classification problem. First, a new ELM-guided dictionary learning and coding model is proposed. Then the iterative optimization algorithm is developed to solve the model. By evaluating the proposed approach on the UCMERCED high-resolution aerial image dataset, we show the effectiveness of the proposed strategy.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Alexandre, E., Cuadra, L., Salcedo-Sanz, S., Pastor-Sanchez, A., & Casanova-Matero, C. (2015). Hybridizing extreme learning machines and genetic algorithms to select acoustic features in vehicle classification applications. Neurocomputing, 152, 58–68.
An, L., Yang, S., & Bhanu, B. (2015). Efficient smile detection by extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 149, 354–363.
Arsigny, V., Fillard, P., Pennec, X., & Ayache, N. (2006a). Geometric means in a novel vector space structure on symmetric positive-definite matrices. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 29(1), 328–347.
Arsigny, V., Fillard, P., Pennec, X., & Ayache, N. (2006b). Log-Euclidean metrics for fast and simple calculus on diffusion tensors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56, 411–421.
Bai, Z., Huang, G. B., Kasun, L. L. C., & Vong, C. M. (2015). Local receptive fields based extreme learning machine. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 10(2), 18–29.
Bencherif, M. A., Bazi, Y., Guessoum, A., Alajlan, N., Melgani, F., & Alhichri, H. (2015). Fusion of extreme learning machine and graph-based optimization methods for active classification of remote sensing images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(3), 527–531.
Bo, L., & Sminchisescu, C. (2009). Efficient match kernels between sets of features for visual recognition. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 22, 35–143.
Cao, J., Chen, T., & Fan, J. (2016). Landmark recognition with compact BoW histogram and ensemble ELM. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 75(5), 2839–2857.
Cao, J., & Lin, Z. (2015). Extreme learning machine on high dimensional and large data applications: A survey. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 103796, 1–13.
Cao, J., Lin, Z., Huang, G. B., & Liu, N. (2012). Voting based extreme learning machine. Information Sciences, 15(1), 66–77.
Cao, J., Zhao, Y., Lai, X., Ong, M. E. H., Yin, C., Koh, Z., et al. (2015). Landmark recognition with sparse representation classification and extreme learning machine. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 352(10), 4528–4545.
Chen, X., & Koskela, M. (2015). Skeleton-based action recognition with extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 149, 387–396.
Decherchi, S., Gastaldo, P., Cambria, E., & Redi, J. (2013). Circular-ELM for the reduced-reference assessment of perceived image quality. Neurocomputing, 102, 78–89.
Erdem, E., & Erdem, A. (2013). Visual saliency estimation by nonlinearly integrating features using region covariances. Journal of Vision, 13(4), 1–20.
Gao, S., Tsang, I. W., & Chia, L. T. (2013). Sparse representation with kernels. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(2), 423–434.
Han, M., & Liu, B. (2015). Ensemble of extreme learning machine for remote sensing image classification. Neurocomputing, 149, 65–70.
Harandi, M., & Salzmann, M. (2015). Riemannian coding and dictionary learning: Kernels to the rescue. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3926–3935.
Huang, G. B., & Chen, L. (2007). Convex incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 70, 3056–3062.
Huang, G. B., & Chen, L. (2008). Enhanced random search based incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 71, 3460–3468.
Huang, G. B., Chen, L., & Siew, C. K. (2006a). Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 17(4), 879–892.
Huang, G., Song, S., Gupta, J. N., & Wu, C. (2014). Semi-supervised and unsupervised extreme learning machines. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 44(12), 2405–2417.
Huang, G. B., Zhou, H., Ding, X., & Zhang, R. (2012). Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 42(2), 513–529.
Huang, G. B., Zhu, Q. Y., Mao, K. Z., Siew, C. K., Saratchandran, P., & Sundararajan, N. (2006b). Can threshold networks be trained directly? IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 53(3), 187–191.
Huang, G. B., Zhu, Q. Y., & Siew, C. K. (2006c). Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 70, 489–501.
Kim, M. (2014). Efficient kernel sparse coding via first-order smooth optimization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 25(8), 1447–1459.
Li, P., Wang, Q., Zuo, W., & Zhang, L. (2013). Log-Euclidean kernels for sparse representation and dictionary learning. In IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 1601–1608.
Minhas, R., Baradarani, A., Seifzadeh, S., & Wu, Q. J. (2010). Human action recognition using extreme learning machine based on visual vocabularies. Neurocomputing, 73, 1906–1917.
Nguyen, H., Patel, V. M., Nasrabadi, N., & Chellappa, R. (2013). Design of non-linear kernel dictionaries for object recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(12), 5123–5135.
Porikli, F., Tuzel, O., & Meer, P. (2006). Covariance tracking using model update based on Lie Algebra. In IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 728–735.
Rong, H. J., Huang, G. B., Sundararajan, N., & Saratchandran, P. (2009). Online sequential fuzzy extreme learning machine for function approximation and classification problems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 39(4), 1067–1072.
Rong, H. J., Jia, Y. X., & Zhao, G. S. (2014). Aircraft recognition using modular extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 128, 166–174.
Tang, J., Deng, C., & Huang, G. B. (2016). Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 27(4), 809–821.
Tang, J., Deng, C., Huang, G. B., & Zhao, B. (2015). Compressed-domain ship detection on spaceborne optical image using deep neural network and extreme learning machine. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 53(3), 1174–1185.
Tuzel, O., Porikli, F., & Meer, P. (2006). Region covariance: A fast descriptor for detection and classification. In European conference on computer visoin, pp. 589–600.
Tuzel, O., Porikli, F., & Meer, P. (2008). Pedestrian detection via classification on Riemannian manifolds. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 30(10), 1713–1727.
Wang, L., Liu, H., & Sun, F. (2016). Dynamic texture video classification using extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 174, 278–285.
Yang, Y., & Newsam, S. (2010). Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL international conference on advances in geographic information systems, pp. 270–279.
Yang, Y., & Newsam, S. (2010). Spatial pyramid co-occurrence for image classification. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 1465–1472.
Yang, Y., & Wu, Q. M. J. (2015). Multilayer extreme learning machine with subnetwork nodes for representation learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, PP(99), 1–14.
Zhu, W., Miao, J., Hu, J., & Qing, L. (2014). Vehicle detection in driving simulation using extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 128, 160–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the National Key Project for Basic Research, China, under Grant 2013CB329403, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61327809, and in part by the National High-Tech Research and Development Plan under Grant 2015AA042306.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Liu, H., Wang, S. et al. Remote sensing image classification using extreme learning machine-guided collaborative coding. Multidim Syst Sign Process 28, 835–850 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-016-0403-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-016-0403-6