Abstract
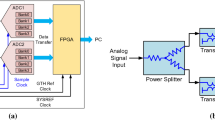
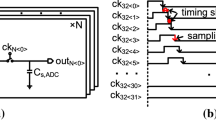
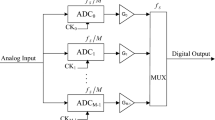
Based on synchronized time interleaved (STI)analog to digital conversion system, an alternative method for ultra-wideband signals sampling has been developed and named as the generalized asynchronous time interleaved (G-ATI) sampling structure. When the input signal bandwidth is large enough, such as 50GHz and above, the STI is generally constructed by three parts: (i) the analog preprocessing circuit that is used to divide the input signal into N sub-channels (N > 2); (ii) the analog sampling circuit that is driven by extremely narrow sampling clock pulses and convert wideband analog signals to discrete pulse signals in each sub-channel; (iii) ADC and digital post processing circuit that is driven by time-based clock and capture the peak value of the pulses and converting them to digital signals. Compared with STI, our G-ATI sampling structure introduces a low-pass filter into the middle of the second and third part in each sub-channel, which can turn the discrete analog signals generated in the second part into continuous signals again. This method has two benefits: one is reducing the bandwidth of each sub-channel before ADC; the other is that the time-based clock does not need to be synchronized with the sampling clock. A simulation of the G-ATI based on an optoelectronic joint sampling system with a total sampling rate of 128 GSPS and 16 time-interleaved sub-channels is executed and the simulation results show the feasibility of the structure of G-ATI.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Agoston, A., Pepper, S., Norton, R., Ebner, J., & Schoen, K. (2003). 100 GHz through-line sampler system with sampling rates in excess of 10 Gsamples/second. In 2003 IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest (Vol. 3, pp. 1519–1521).
Akers, N. P., et al. (1986). RF sampling gates: A brief review. IEE Proceedings A-Physical Science, Measurement and Instrumentation, Management and Education, Reviews, 135(1), 44–49.
Amin, M., & Leung, B. (2016). Design techniques for linearity in time-based sigma delta analog-to-digital converter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 63(5), 433–437.
Brown, J. (1981). Multi-channel sampling of low-pass signals. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 28(2), 101–106. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCS.1981.1084954.
Chen, C.-H., et al. (2016). An incremental analog-to-digital converter with multi-step extended counting for sensor interfaces. In 2016 IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS) (pp. 77–80).
Conway, I. J. (2012). Frequency compression of wideband signals using a distributed sampling technique. Defence Research Establishment Ottawa (Ontario), Vol. 8216.
DPO70000SX-Digital-Oscilloscope-Datasheet-ZH-CN-55C3066210. https://www.cn.tektronix.com. 11 Nov 2015.
Fudge, G. L., et al. (2006). Nyquist folded bandpass sampling receivers and related methods. US Patent applications 2007/0086544, Appl. No.:11/545,642.
Fujioka, H., & Nakai, T. (2010). Stabilising systems with aperiodic sample-and-hold devices: State feedback case. IET Control Theory & Applications, 4(2), 265–272.
Gaillardon, P.-E., et al. (2016). Digital, analog and RF design opportunities of three-independent-gate transistors. In 2016 IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS) (pp. 405–408).
Greshishchev, Y. M., et al. (2010). A 40GS/s 6b ADC in 65nm CMOS. In ISSCC Dig. Tech. Papers (pp. 390–391).
Kahrs, M. (2004). 50 years of RF and microwave sampling. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 52(1), 159–165.
Kang, H.-W., et al. (2016). A sign-equality-based background timing-mismatch calibration algorithm for time-interleaved ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 63(6), 518–522.
Kleinfelder, S. (2003). A multi-GHz, multi-channel transient waveform digitization integrated circuit. In 2002 IEEE nuclear science symposium conference record (Vol. 1, pp. 544–548).
Kleinfelder, S. (2003). Gigahertz waveform sampling and digitization circuit design and implementation. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 50(4), 955–962.
Kull, L., et al. (2014). A 90GS/s 8b 667mW 64x Interleaved SAR ADC in 32nm Digital SOI CMOS. In 2014 IEEE international solid-state circuits conference. 978-1-4799-0920-9.
Liu, S., Ma, H., Lyu, N., & Wang, H. (2018). Adaptive blind timing mismatch calibration with low power consumption in M-channel time-interleaved ADC. Circuits ,Systems, and Signal Processing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0788-6.
Madsen, K. N., et al. (2015). A high-linearity, 30 GS/s track-and-hold amplifier and time interleaved sample-and-hold in an InP-on-CMOS process. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 50(11), 2692–2702.
Matsuzawa, A. (2007). Trends in high speed ADC design. In 2007 7th international conference on ASIC (pp. 245–248).
Monk, T. A., et al. (2016). Iterative gain enhancement in an algorithmic ADC. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 63(4), 459–469.
Murmann, B. ADC Performance Survey 1997–2011. http://www.stanford.edu/~murmann/adcsurvey.html.
Pepper, S. H., & Schoen, K. (2005). NLTLs push sampler products past 100 GHz. Microwaves & RF, 44(10), 88–108.
Qiu, L., Zheng, Y., & Siek, L. (2016). Multichannel time skew calibration for time-interleaved ADCs using clock signal. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 35(8), 2669–2682.
Qiu, L., Zheng, Y., & Siek, L. (2016). A filter bank mismatch calibration technique for frequency-interleaved ADCs. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 35(11), 3847–3862.
Schvan, P., et al. (2008). A 24GS/s 6b ADC in 90nm CMOS. In ISSCC Dig. Tech. Papers (pp. 544–545).
Singh, S., et al. (2015). Frequency response mismatches in 4-channel time-interleaved ADCs: Analysis, blind identification, and correction. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 62(9), 2268–2279.
Sit, J.-J., et al. (2007). A low-power asynchronous interleaved sampling algorithm for cochlear implants that encodes envelope and phase information. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 54(1), 138–149.
Song, J., et al. (2018). Digital iterative harmonic rejection and image cancellation for LPF-less frequency-interleaved analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 13(9), 1–5.
Song, J., et al. (2019). Analysis and correction of combined channel mismatch effects in frequency-interleaved ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 66(2), 655–668.
Szlachetko, B. (2016). Toward wide-band high-resolution analog-to-digital converters using hybrid filter bank architecture. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 35(4), 1257–1282.
Tabasy, E. Z., et al. (2013). A 6b 10GS/s TI-SAR ADC with Embedded 2-Tap FFE/1-Tap DFE in 65nm CMOS. In IEEE symposium on VLSI circuits (pp. 274–275).
The quest for higher real-time oscilloscope bandwidth. Tektronix White Paper, June 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Zhou, J., Liu, Y. et al. Generalized asynchronous time interleaved (G-ATI) sampling structure for ultra-wideband signal. Multidim Syst Sign Process 31, 635–661 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00679-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00679-y